Understanding Survey Drop-Offs (Drop Outs)
Surveys are essential for gathering valuable information and insights from respondents. However, one common problem researchers face is survey drop-offs, also known as dropouts. In this article, we will explore the concept of survey drop-offs, their impact on data quality, strategies to reduce them, and ways to improve survey completion rates.
🔩 The Nuts and Bolts:
- Surveys are useful for gathering valuable insights, but survey drop-offs can occur and significantly affect data quality.
- Several psychological factors contribute to survey drop-offs and should be considered when designing surveys.
- The reasons for abandonment include survey length, language complexity, and timing.
- Strategies to reduce drop-offs include designing engaging surveys, considering timing and frequency, offering incentives, and leveraging technology.
- Researchers can improve completion rates and obtain reliable data by analyzing respondent characteristics and interpreting drop-off data.
Defining Survey Drop-Offs
Survey drop-offs refer to instances where respondents start a survey but fail to complete it. This could be due to various reasons, such as lack of time, disinterest, or technical difficulties. Understanding why respondents drop off can help design more engaging surveys and improve completion rates.
Regarding survey drop-offs, it’s important to delve deeper into the factors contributing to this phenomenon. By understanding the psychology behind survey drop-offs, researchers and survey designers can gain valuable insights into how to prevent them and increase response rates.
The Psychology Behind Survey Drop-Offs
Several psychological factors contribute to survey drop-offs. For instance, respondents may lose interest if the survey is too long or if they find the questions repetitive or irrelevant. The survey length can be overwhelming for participants, especially with limited time. Additionally, if respondents feel that their answers are not valued or that the survey is irrelevant to them, they may be more likely to abandon it.
One way to address this issue is by making surveys more interactive and personalized. By incorporating elements such as progress bars, interactive features, and tailored questions, researchers can create a more engaging survey experience. This can help maintain respondents’ interest and motivation throughout the survey, leading to higher completion rates.
Drive your marketing research forward with Helio
Get insights from your target audience in minutes
Common Reasons for Survey Drop-Offs
There are several common reasons why respondents tend to drop out from surveys. One of the main reasons is the length of the questionnaire. Long surveys can be time-consuming and may require a significant commitment from participants. As a result, respondents may feel overwhelmed and abandon the survey.
In addition to survey length, the language used in the survey can also play a role in drop-offs. Respondents may become frustrated and lose interest if the questions are complex or difficult to understand. It is important to use clear and concise language to ensure participants can easily comprehend and respond to the survey questions.
Another factor that can contribute to survey drop-offs is the timing of the survey. If surveys are conducted at inconvenient times for respondents, such as during busy work hours or late at night, they may be less likely to complete them. Researchers should consider the target audience’s schedule and preferences when determining the optimal timing for survey administration.
Identifying and addressing these barriers can go a long way in reducing drop-offs and increasing completion rates. By taking into account the psychology behind survey drop-offs and considering common reasons for abandonment, researchers can design more effective surveys that capture the attention and engagement of respondents.
🚀 If you’re using Helio
Use Preview Mode to experience your survey from the participant’s perspective across different devices.
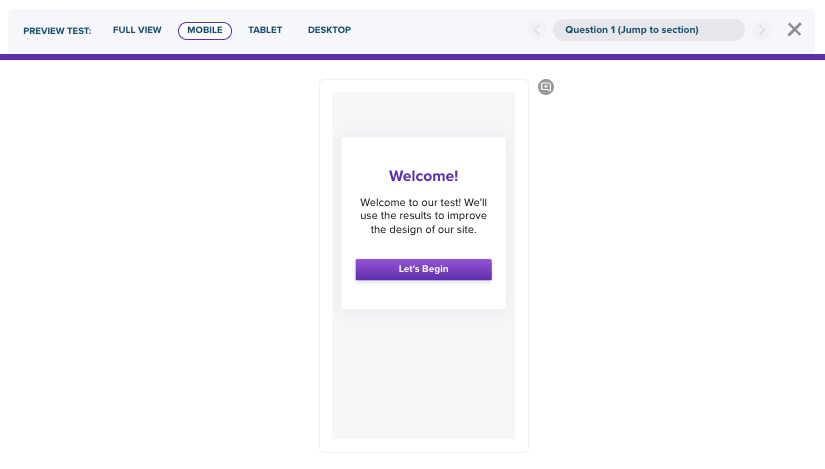
Previewing surveys can help identify pain-points, such as awkward language or high-effort question types.
The Impact of Survey Drop-Offs on Data Quality
Survey drop-offs not only affect completion rates but also have a significant impact on the overall data quality. Understanding how drop-offs affect survey results can help researchers interpret the data accurately and make informed decisions based on the collected information.
Drop-Offs May Introduce Sample Bias
When respondents drop off from a survey, it creates a potential bias in the data collected. The opinions and perspectives of those who dropped off may differ from those who completed the survey, leading to skewed results. This bias can be attributed to factors such as respondent fatigue, lack of interest, or technical difficulties.
Researchers must be aware of this bias and take appropriate measures to mitigate its impact. One way to address this issue is by analyzing the characteristics of the respondents who dropped off. By comparing their demographics, attitudes, and behaviors with those who completed the survey, researchers can identify potential differences contributing to the bias.
Technical Issues May Influence Drop-off
In addition to analyzing respondent characteristics, researchers can also examine the survey’s timing and sequence of questions. It is possible that certain questions or sections of the survey may be more likely to cause drop-offs. Researchers can revise and optimize the survey design by identifying these problematic areas to reduce drop-offs and improve data quality.
Survey Creation 101
Strategies to Reduce Survey Drop-Offs
Reducing survey drop-offs is crucial for obtaining reliable and comprehensive data. By implementing the following strategies, researchers can improve survey completion rates and increase the overall quality of the collected data.
Designing Engaging Surveys
A well-designed survey should be visually appealing, easy to navigate, and have clear instructions. Using simple language, avoiding jargon, and incorporating interactive elements can make the survey more engaging, encouraging respondents to complete it.
For example, researchers can break down questions into smaller, more digestible chunks instead of using long paragraphs of text. This makes the survey visually appealing and makes it easier for respondents to understand and answer each question accurately. Additionally, incorporating visual aids such as images, videos, or infographics can help convey complex ideas or concepts more effectively.
Furthermore, researchers can consider using progress bars or indicators to show respondents how far they are in the survey. This provides a sense of accomplishment and helps manage expectations, letting respondents know how much more time they need to invest in completing the survey.
Timing and Frequency of Surveys
Consider the timing and frequency of your surveys to enhance completion rates. Bombarding respondents with frequent surveys may lead to fatigue and drop-offs. Timing surveys when respondents have available time and spacing them out can increase participation and reduce drop-offs.
It is important to consider the target audience’s schedule and availability. For example, if the survey targets working professionals, sending it during their lunch break or after work hours may increase the chances of completion. Similarly, avoiding weekends or holidays when people are more likely to be busy or away can also help improve response rates.
Additionally, researchers can consider implementing reminder emails or notifications to nudge respondents who have not completed the survey gently. However, it is crucial to balance reminding and being intrusive, as excessive reminders may lead to annoyance and further drop-offs.
🚀 If you’re using Helio
Schedule your surveys to connect with your audience when they would be most engaged.
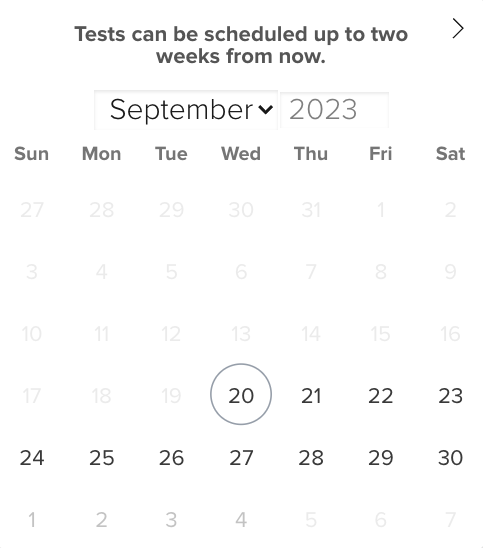
Surveys are scheduled to be delivered on the participant’s local time, up to 2 weeks in advance.
Incentives and Motivations for Completion
Offering incentives, such as gift cards, discounts, or entries into prize drawings, can motivate respondents to complete the survey. People are more likely to invest their time and energy in a survey with the promise of a reward.
Researchers can explore various incentive options based on their target audience and the nature of the survey. For instance, if the survey is related to a specific product or service, offering a discount or a free trial can incentivize respondents to complete the survey and potentially become customers. Alternatively, if the survey is for academic research, offering participants the opportunity to contribute to scientific knowledge or receive a personalized report based on their responses can serve as a strong motivator.
It is important to communicate the incentives upfront and ensure they are relevant and appealing to the target audience. Additionally, researchers should consider the budgetary implications of offering incentives and ensure that they are feasible within the scope of the study.
Make your design decisions count.
Subscribe to Design Under Pressure. Get insights, UX metrics, and tools for bold, informed design.
We respect your inbox. Just insights. No fluff. Privacy Policy.
Measuring and Analyzing Survey Drop-Offs
To improve survey completion rates, measuring and analyzing drop-off data is essential. By tracking and interpreting the reasons behind drop-offs, researchers can gain insights into areas that need improvement.
Tools for Tracking Drop-Offs
There are various tools available that can help researchers monitor and track survey drop-offs. These tools provide valuable data on where respondents abandon the survey, allowing researchers to identify specific pain points and make necessary adjustments.
Interpreting Drop-Off Data
Analyzing drop-off data involves looking for patterns and trends indicating underlying issues. By understanding the reasons behind drop-offs, researchers can make informed decisions on optimizing survey design and improving completion rates.
Improving Survey Completion Rates
While reducing survey drop-offs is essential, researchers should also focus on improving completion rates to gather comprehensive data. By following best practices and leveraging technology, researchers can increase the likelihood of respondents completing surveys.
Best Practices for Survey Design
Ensure your survey is concise, easy to understand, and relevant to the target audience. By carefully crafting questions and providing clear instructions, researchers can enhance comprehension and reduce the likelihood of drop-offs.
Follow-Up Strategies for Incomplete Surveys
When respondents drop off from a survey, following up with them can help gather partial data and gain insights into their reasons for not completing the survey. Contacting respondents via email, phone, or personalized messages within the survey platform can encourage them to resume and complete the survey.
Leveraging Technology to Improve Completion Rates
Utilize technology to optimize your surveys and improve completion rates. For example, progress bars, auto-save features, and responsive survey designs can enhance the user experience and reduce the likelihood of drop-offs.
In conclusion, understanding survey drop-offs is vital for researchers to improve data quality and increase completion rates. By analyzing the psychology behind drop-offs, addressing common reasons for drop-offs, and implementing effective strategies, researchers can design more engaging surveys, interpret drop-off data, and ultimately improve the overall survey experience for respondents.
Survey Creation 101
FAQs
Survey drop-offs refer to instances where respondents start a survey but fail to complete it. This could be due to various reasons, such as lack of time, disinterest, or technical difficulties.
The common reasons for survey drop-offs are length, language complexity, and timing.
Strategies to reduce drop-offs include designing engaging surveys, considering timing and frequency, offering incentives, and leveraging technology.
Survey drop-offs can significantly impact the overall data quality, leading to potential bias in the data collected. The opinions and perspectives of those who dropped off may differ from those who completed the survey, leading to skewed results.
Some best practices for survey design include using simple language, avoiding jargon, incorporating interactive elements, breaking down questions into smaller chunks, and incorporating visual aids.
Offering incentives, such as gift cards, discounts, or entries into prize drawings, can motivate respondents to complete the survey. People are more likely to invest their time and energy in a survey with the promise of a reward.
Survey drop-offs refer to instances where respondents start a survey but fail to complete it. This could be due to various reasons, such as lack of time, disinterest, or technical difficulties.
The common reasons for survey drop-offs are length, language complexity, and timing.
Strategies to reduce drop-offs include designing engaging surveys, considering timing and frequency, offering incentives, and leveraging technology.
Survey drop-offs can significantly impact the overall data quality, leading to potential bias in the data collected. The opinions and perspectives of those who dropped off may differ from those who completed the survey, leading to skewed results.
Some best practices for survey design include using simple language, avoiding jargon, incorporating interactive elements, breaking down questions into smaller chunks, and incorporating visual aids.
Offering incentives, such as gift cards, discounts, or entries into prize drawings, can motivate respondents to complete the survey. People are more likely to invest their time and energy in a survey with the promise of a reward.