Understanding Survey Branching: How to Use It Effectively
Surveys are essential for gathering valuable insights from respondents. One feature that can greatly enhance the effectiveness of surveys is branching. Researchers can create more targeted and engaging surveys by effectively understanding and utilizing survey branching. This article will explore the basics of survey branching, the importance of effective branching, steps to implement it, best practices to follow, and how to evaluate its success.
🔩 The Nuts and Bolts:
- Survey branching is a feature that allows researchers to customize the path of respondents through a survey based on their answers.
- Key terms used in survey branching are conditional statements, branching rules, and skip logic.
- Effective survey branching provides numerous benefits – enhancing accuracy and improving respondent experience – for researchers and respondents.
- Implementing survey branching includes planning the survey structure and creating the branching logic, while best practices include avoiding common pitfalls and optimizing for mobile devices.
- Evaluating successful survey branching requires analyzing data collected via branching logic and making adjustments based on feedback from respondents.
Defining Survey Branching
At its core, survey branching allows researchers to customize the path that respondents take through a survey based on their previous answers. Instead of presenting every question to every respondent, branching enables the survey to adapt in real time, directing respondents to relevant questions based on their previous responses. This dynamic approach creates a more personalized experience for respondents and ensures that they only answer questions that apply to them.
Imagine you are conducting a survey on customer satisfaction for a mobile phone company. With survey branching, you can tailor the survey experience for each respondent. For example, if a respondent indicates they are not a current customer, you can skip questions about their experience with the company’s products and services. This saves time for both the respondent and the researcher, as irrelevant questions are automatically skipped.
Subscribe to Closing the Gap
A newsletter to help makers and doers get closer to customers. Learn more.
We believe in protecting your data. Here’s our Privacy Policy.
The Basics of Survey Branching
Survey branching begins with the creation of different paths within a survey. These paths are established based on predetermined conditions or criteria. When a respondent answers a question, the survey software evaluates their response and directs them to the next relevant question. This branching logic allows researchers to collect specific data points based on each respondent’s unique characteristics and preferences.
Let’s say you are surveying travel preferences. You can create different paths based on the respondent’s preferred mode of transportation. If a respondent selects “car,” they can be directed to questions about road trip preferences, while those who select “airplane” can be directed to questions about flight preferences. This targeted approach ensures that respondents are only asked about topics relevant to their chosen mode of transportation.
🚀 If you’re using Helio
Branching Logic lets you build custom pathways for participants in surveys.
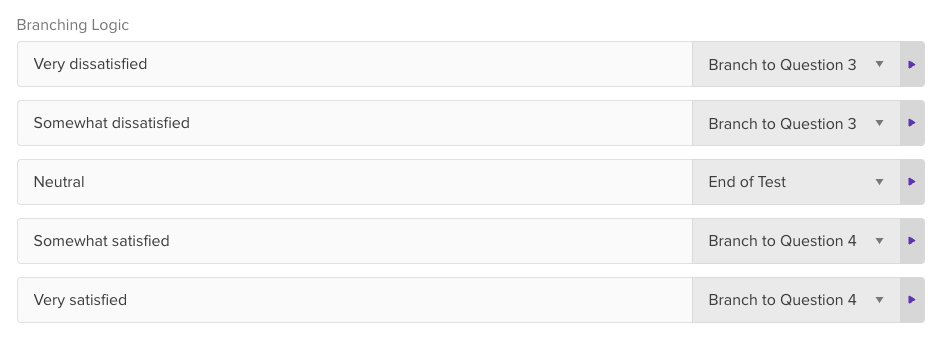
Use branching on multiple choice questions, or branch participants based on where they click on a page.
Key Terms in Survey Branching
To fully understand survey branching, it’s important to be familiar with key terms commonly used in this context. These terms include:
- Conditional Statements: These statements define the conditions determining a respondent’s path. They typically consist of if-then statements that link certain responses to specific survey branches.
- Branching Rules: Branching rules specify which path a respondent should follow based on their answers to specific questions. These rules determine the next set of questions that will be presented to each respondent.
- Skip Logic: Skip logic is a type of branching that skips certain questions or sections of a survey based on a respondent’s previous answers. This ensures that respondents only answer questions that are relevant to them.
Conditional Statements
Conditional statements play a crucial role in survey branching. They allow researchers to define the conditions that trigger a specific branch. For example, if a respondent indicates they are under 18 years old, a conditional statement can be used to direct them to a set of questions tailored to their age group.
Branching Rules
Branching rules determine the survey flow based on the respondent’s answers. These rules are set up in advance, specifying which questions should be presented next based on the respondent’s previous responses. For instance, if a respondent rates a product as highly satisfactory, the branching rule can direct them to a follow-up question asking for specific feedback on what they liked about the product.
Skip Logic
Skip logic is a powerful feature in survey branching that allows researchers to skip certain questions or sections based on a respondent’s previous answers. This ensures that respondents only answer questions that are relevant to them, saving time and improving the overall survey experience. For example, if a respondent indicates that they have never used a particular product, skip logic can automatically skip questions related to that product, preventing respondents from seeing unnecessary questions.
Researchers can create dynamic and personalized surveys that adapt to each respondent’s unique characteristics and preferences by utilizing these key terms and concepts. Survey branching enhances the accuracy and relevance of the data collected, leading to more meaningful insights and actionable results.
Survey Creation 101
The Importance of Effective Survey Branching
Effective survey branching offers numerous benefits, both for researchers and respondents. Let’s explore some key advantages:
Enhancing Survey Accuracy with Branching
By tailoring the survey experience based on respondents’ previous answers, branching improves the accuracy of data collection. It allows researchers to ask relevant follow-up questions, ensuring a more comprehensive and accurate understanding of respondents’ opinions, preferences, and behaviors.
For example, imagine a survey about customer satisfaction with a particular product. With effective survey branching, if a respondent indicates they are dissatisfied with the product, the survey can automatically branch to a series of follow-up questions designed to gather more detailed feedback about their dissatisfaction. This targeted approach provides researchers with valuable insights and helps them identify specific areas for improvement.
Furthermore, survey branching can also help identify inconsistencies or contradictions in respondents’ answers. For instance, if a respondent indicates a preference for a certain feature in one question but then expresses dissatisfaction with that feature in a later question, the branching logic can alert researchers to potential errors or misunderstandings in the survey responses.
Drive your marketing research forward with Helio
Get insights from your target audience in minutes
Improving Respondent Experience
Survey branching plays a crucial role in providing a positive user experience. Instead of bombarding respondents with irrelevant questions, branching ensures that each question is meaningful and applicable to their unique circumstances. This personalized approach leads to higher respondent satisfaction and increased survey completion rates.
Consider a survey about travel preferences. Without branching, respondents would see generic questions about their travel habits, regardless of whether they are frequent or occasional vacationers. However, with effective survey branching, respondents who indicate they rarely travel can see a different set of questions that focus on their preferences for local attractions or staycation options. This not only saves respondents’ time but also makes them feel valued and understood.
🚀 If you’re using Helio
Branching logic can be used on click tests to direct participants through a survey based on their interaction with a page.
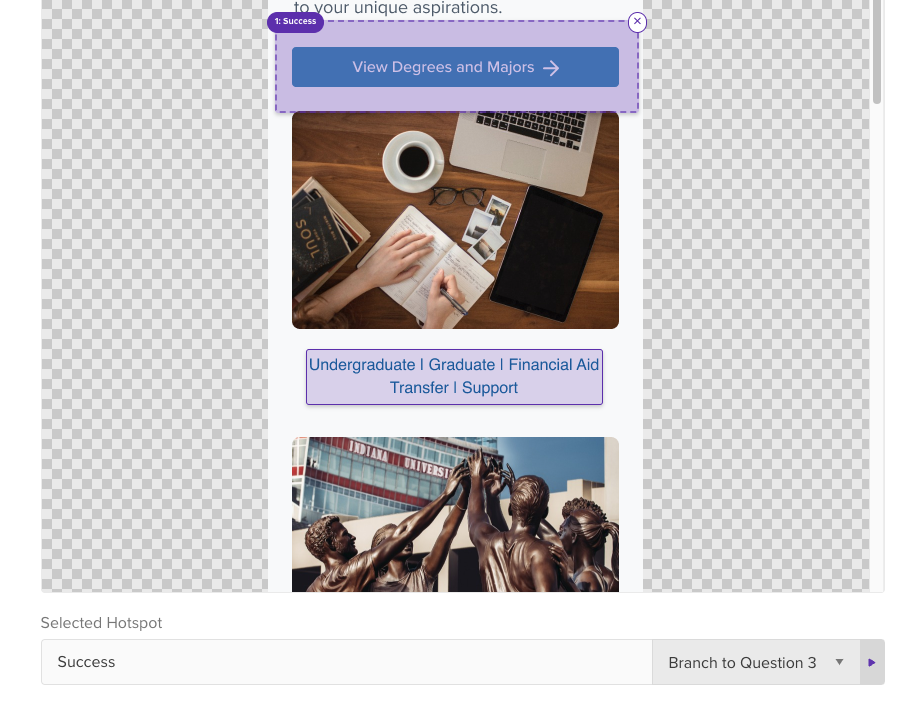
Outline hotspots on a page and decide where hotspot clickers get sent.
Moreover, survey branching can help prevent survey fatigue. Long, monotonous surveys can quickly become tedious and discourage respondents from completing them. Using branching logic to present only relevant questions, researchers can keep respondents engaged and motivated throughout the survey process. This targeted approach also reduces the risk of respondents providing careless or random answers due to survey fatigue.
In conclusion, effective survey branching is valuable for researchers and respondents. It enhances survey accuracy by allowing targeted follow-up questions and helps improve the respondent experience by personalizing the survey journey. By implementing survey branching, researchers can gather more accurate and insightful data while ensuring respondents feel valued and engaged throughout the survey process.
Steps to Implement Survey Branching
Now that we understand the importance of effective survey branching, let’s delve into the practical steps involved in its implementation:
Planning Your Survey Structure
The first step is to plan and outline the structure of your survey. Identify the key questions and determine how they relate to each other. Consider the different paths respondents might take based on their answers and define the branching logic you will use.
Creating Branching Logic
Once you have planned your survey structure, it’s time to create the branching logic. This involves defining the conditions and rules that determine which questions respondents will see based on their answers. Make sure to test the logic to ensure it functions as intended thoroughly.
Best Practices for Survey Branching
While implementing survey branching, it’s important to keep some best practices in mind:
Avoiding Common Pitfalls
Avoid pitfalls such as overcomplicating the logic or creating survey paths that lead to dead ends when using branching. Keep the logic simple and ensure that all paths have a clear progression to prevent confusion for respondents.
Optimizing for Mobile Surveys
Optimizing your surveys for mobile devices is crucial in today’s mobile-centric world. Ensure your branching logic works seamlessly across various screen sizes and devices, providing mobile respondents a smooth and user-friendly experience.
Evaluating the Success of Your Survey Branching
After implementing survey branching, evaluating its effectiveness and making any necessary adjustments is important. Two key aspects of evaluating survey branching are:
Analyzing Survey Data
Examine the data collected through the branching logic to gain valuable insights. Look for patterns and trends among respondents who took different survey paths. This analysis will help you better understand your audience and refine your future survey designs.
Making Adjustments Based on Feedback
Solicit feedback from respondents about their survey experience. Use their input to identify improvement areas and adjust your branching logic accordingly. Regularly iterate and refine the survey to ensure a seamless and engaging experience for future respondents.
Researchers can create more targeted and engaging surveys by understanding survey branching and employing it effectively. This, in turn, leads to higher data accuracy, improved respondent experience, and, ultimately better insights. So, embrace the power of survey branching and unlock its full potential in your research endeavors!
FAQs
At its core, survey branching allows researchers to customize the path that respondents take through a survey based on their previous answers. Instead of presenting every question to every respondent, branching enables the survey to adapt in real time, directing respondents to relevant questions based on their previous responses.
A: Key terms used in survey branching are conditional statements, branching rules, and skip logic. Conditional statements define the conditions determining a respondent’s path and typically consist of if-then statements. Branching rules specify which path a respondent should follow based on their answers to specific questions, while skip logic skips certain questions or sections of a survey based on a respondent’s previous answers.
Effective survey branching offers numerous benefits for researchers and respondents. It enhances survey accuracy by allowing targeted follow-up questions and helps improve the respondent experience by personalizing the survey journey. It also saves the respondent and researcher time, as irrelevant questions are automatically skipped.
At its core, survey branching allows researchers to customize the path that respondents take through a survey based on their previous answers. Instead of presenting every question to every respondent, branching enables the survey to adapt in real time, directing respondents to relevant questions based on their previous responses.
Key terms used in survey branching are conditional statements, branching rules, and skip logic. Conditional statements define the conditions determining a respondent’s path and typically consist of if-then statements. Branching rules specify which path a respondent should follow based on their answers to specific questions, while skip logic skips certain questions or sections of a survey based on a respondent’s previous answers.
Effective survey branching offers numerous benefits for researchers and respondents. It enhances survey accuracy by allowing targeted follow-up questions and helps improve the respondent experience by personalizing the survey journey. It also saves the respondent and researcher time, as irrelevant questions are automatically skipped.










