Understanding Survey Quotas and How to Use Them Effectively
Do you want to ensure that your surveys capture a representative sample of your target population? Do you want to avoid sampling bias and make your research findings more reliable? If so, then understanding survey quotas and using them effectively is crucial. This article will explore the definition, importance, types, implementation, challenges, and best practices of survey quotas. By the end, you’ll have the knowledge and tools to make the most of this powerful research technique.
🔩 The Nuts and Bolts:
- Survey quotas are a powerful research technique used to ensure that a survey sample accurately represents a target population’s characteristics.
- The importance of survey quotas lies in ensuring representative sampling, avoiding sampling bias, and obtaining actionable insights.
- Different types of quota exist such as demographic, geographic, and behavioral quotas which should be tailored to the specific objectives and characteristics of the target population.
- Implementing survey quotas involves setting up appropriate selection criteria, monitoring progress against them, and making adjustments where necessary.
- Challenges associated with using quotas include ensuring adequate sample sizes within each quota and addressing ethical considerations related to discrimination or stereotypes.
- Best practices for utilizing quotas include thorough planning, setting clear targets, using stratified sampling techniques, promoting quota use to participants, and evaluating success after data collection.
Defining Survey Quotas
Let’s start by defining what survey quotas are. A survey quota refers to a predetermined target for the number of respondents from different demographic or stratified groups. Instead of randomly selecting participants, quotas ensure that your survey sample accurately represents your target population’s characteristics, such as age, gender, ethnicity, or geographical location.
Survey quotas are an essential tool in market research and social science studies. They help researchers obtain a more accurate understanding of the population they are studying by ensuring that the sample is representative of the target audience. This approach allows for more reliable and valid research findings.
When implementing survey quotas, it is crucial to consider the specific demographics or characteristics most relevant to your research objectives. By doing so, you can ensure that your sample accurately reflects the diversity of your study population.
The Importance of Survey Quotas
Survey quotas are vital in ensuring your research findings are reliable and valid. By using quotas, you can obtain a diverse and representative sample that mirrors your study’s real-world population. This allows you to make generalizations and draw more accurate conclusions applicable to your target audience or market.
One of the key advantages of using survey quotas is that they help minimize selection bias. Selection bias occurs when the characteristics of the sample differ significantly from those of the target population, leading to skewed research results. Quotas help mitigate this bias by ensuring that the sample closely resembles the population regarding key demographics.
Moreover, survey quotas enable researchers to analyze subgroups within the population more effectively. By setting quotas for specific demographic groups, such as age or income brackets, researchers can examine these groups’ attitudes, behaviors, and preferences individually. This level of granularity provides valuable insights that can inform targeted marketing strategies or policy decisions.
Different Types of Survey Quotas
There are various types of survey quotas that you can utilize, depending on your research objectives and the characteristics of your target population. Some common types include demographic quotas (e.g., age, gender, income), geographic quotas (e.g., region, urban/rural), and behavioral quotas (e.g., usage frequency, purchase history).
Demographic quotas are among the most commonly used quotas in surveys. They ensure that the sample accurately represents the age, gender, ethnicity, and other demographic characteristics of the target population. By setting demographic quotas, researchers can understand how different demographic groups perceive and respond to certain products, services, or social issues.
Firmographic quotas are used primarily in B2B market research. Companies that sell to other businesses may consider survey quotas for specific audience segments or verticals. Other firmographics may include employee size groups, revenue groups, among others.
Geographic quotas are particularly relevant when studying regional differences or targeting specific markets. By setting quotas based on geographical location, researchers can ensure that the sample includes participants from various regions, such as urban and rural areas or different states or countries. This allows for a more comprehensive understanding of location influences opinions, behaviors, and preferences.
Behavioral quotas are useful when studying consumer behavior or specific user groups. These quotas can be based on usage frequency, purchase history, or engagement with a particular product or service. By setting behavioral quotas, researchers can gain insights into different consumer segments’ motivations, preferences, and needs, enabling businesses to tailor their offerings more effectively.
It is important to note that the selection of survey quotas should be guided by the research objectives and the characteristics of the target population. By carefully selecting the appropriate quotas, you can achieve a balanced and comprehensive representation of your intended population, leading to more accurate and actionable research findings.
Drive your marketing research forward with Helio
Get insights from your target audience in minutes
The Role of Survey Quotas in Research
Now that we understand the definition and importance of survey quotas, let’s delve deeper into their role in research. Survey quotas primarily serve two key purposes: ensuring representative sampling and avoiding sampling bias.
Ensuring Representative Sampling
Representative sampling is essential in research to ensure that the data collected accurately reflects the target population’s characteristics. By setting quotas that align with the population’s demographics or stratifications, you can minimize the risk of under or over-representing certain groups. This helps to create a sample that closely mirrors the population and increases the generalizability of your research findings.
For example, imagine you are studying consumer preferences for a new product. If you want your findings to apply to the entire population, including participants from various age groups, genders, income levels, and geographic locations is crucial. By setting quotas for each of these demographic categories, you can ensure that your sample represents the diversity of the population, making your research more robust and reliable.
🚀 If you’re using Helio
Select from over 1,000 ready-made audiences segmented by user behaviors.
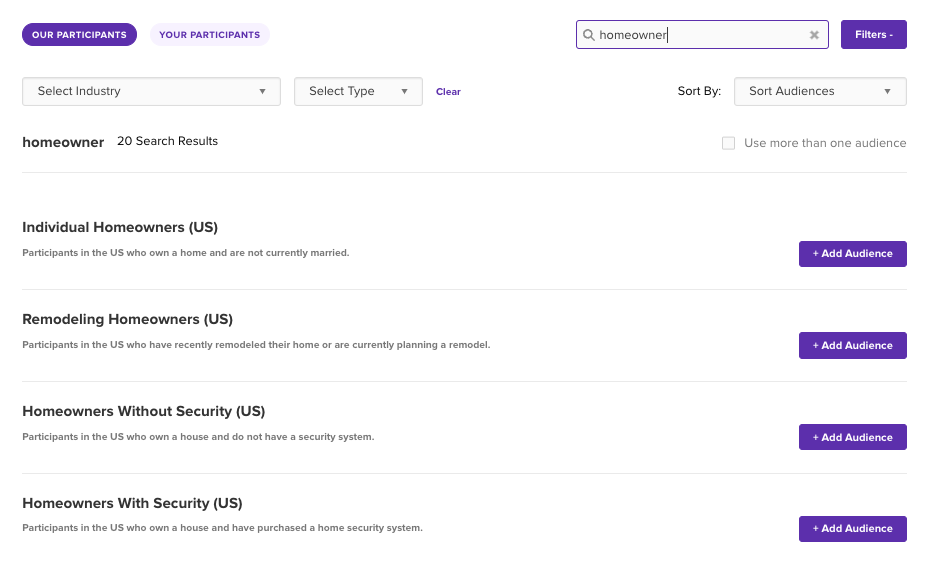
Search through Helio’s ready-made audiences on the Audiences page of your account.
Moreover, representative sampling allows researchers to make accurate inferences about the larger population based on the characteristics of the sample. For instance, if your research aims to understand the political preferences of voters in a particular region, setting quotas based on the proportion of registered voters from each political party can help you obtain a sample that accurately reflects the political landscape of that region.
Avoiding Sampling Bias
Sampling bias occurs when the sample you select systematically differs from the target population, leading to distorted results. Quotas can help mitigate sampling bias by controlling the composition of the sample. By setting quotas based on known population statistics, you can reduce the risk of biased outcomes that may occur when relying solely on random sampling.
One common example of sampling bias is the “volunteer bias.” This bias occurs when individuals who volunteer to participate in a study differ systematically from those who do not. By implementing quotas, researchers can ensure that the sample includes individuals from different backgrounds and characteristics, minimizing the impact of volunteer bias on the research findings.
Another sampling bias is non-response bias, which arises when selected participants do not respond to the survey. Quotas can help address this bias by ensuring that the sample includes sufficient participants from each demographic group. This way, even if some individuals choose not to respond, the overall sample still represents the population accurately.
Furthermore, quotas can correct historical underrepresentation or marginalization of certain groups. For instance, if a particular demographic group has been historically excluded from research studies, setting quotas can help ensure their inclusion and give them a voice in the research process. This helps address social inequalities and provides a more comprehensive understanding of the topic being studied.
In conclusion, survey quotas play a vital role in research by ensuring representative sampling and avoiding sampling bias. By setting quotas that align with the population’s demographics or stratifications, researchers can create a sample that accurately reflects the target population’s characteristics. This, in turn, increases the generalizability of research findings and reduces the risk of biased outcomes. Quotas also help address historical underrepresentation and marginalization, promoting inclusivity and providing a more comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Implementing Survey Quotas in Your Research
Implementing survey quotas in your research may seem challenging, but with proper planning and execution, it can yield valuable insights. Let’s explore the steps involved in setting up and monitoring survey quotas.
Setting Up Survey Quotas
When setting up survey quotas, you must identify the relevant demographic or stratified variables essential for your research objectives. Determine each group’s desired percentages or targets based on the population makeup. For example, if your target population is evenly split between males and females, your quotas should reflect this distribution. This step requires thoughtful consideration and knowledge of the population being surveyed.
Monitoring and Adjusting Quotas
Once your survey is live, it’s crucial to continuously monitor the response rates for each quota to ensure a balanced representation. If certain quotas are not being met, you may need to modify your recruitment strategies or reevaluate the composition of your sample. Regularly checking the progress against your quotas allows you to make informed adjustments and maintain the integrity of your research.
Subscribe to Closing the Gap
A newsletter to help makers and doers get closer to customers. Learn more.
We believe in protecting your data. Here’s our Privacy Policy.
Challenges in Using Survey Quotas
While survey quotas offer numerous benefits, they can also present challenges. It’s important to be aware of these obstacles and develop strategies to overcome them effectively. Let’s explore some of the common challenges in using survey quotas.
Overcoming Common Obstacles
One common challenge is ensuring an adequate sample size within each quota. Sometimes, specific subgroups within your target population may be harder to reach or less likely to participate. To address this, you can consider implementing targeted recruitment strategies or offering attractive incentives to these groups. You can pave the way for a more balanced and representative sample by actively addressing the obstacles.
Addressing Ethical Considerations
Another challenge revolves around the ethical considerations of using quotas. It’s crucial to ensure that your quotas do not perpetuate stereotypes, discriminate, or violate ethical guidelines. Maintaining transparency and fairness throughout the research process can minimize the potential ethical concerns associated with survey quotas.
Maximizing the Effectiveness of Survey Quotas
Now that we have examined the challenges, let’s focus on maximizing the effectiveness of your survey quotas. By following some best practices, you can ensure that your quotas yield meaningful and reliable research outcomes.
Best Practices for Using Survey Quotas
- Thoroughly plan and define your research objectives before setting up survey quotas.
- Select quotas that align with the characteristics of your target population.
- Regularly monitor the progress of each quota and make necessary adjustments if needed.
- Consider using stratified sampling techniques to enhance the representativeness of your sample.
- Ensure transparency and clear communication about the purpose and use of quotas to participants.
Evaluating the Success of Your Survey Quotas
Lastly, evaluating the effectiveness of your survey quotas after data collection is essential. Analyze the data to ensure that your quotas have achieved the desired balance and representative nature. Compare the survey results to the known population statistics and assess the validity and generalizability of your findings. This evaluation enables you to refine and improve your quotas for future research endeavors.
By understanding survey quotas and using them effectively, you can enhance the accuracy and validity of your research findings. By implementing appropriate quotas, diligently monitoring their progress, and adhering to best practices, you can ensure that your surveys capture a representative and diverse sample. So, the next time you embark on a research project, leverage the power of survey quotas to unlock valuable insights and make more informed decisions.
Survey Creation 101
FAQs
Survey quotas are predetermined targets for respondents from different demographic or stratified groups. They are used to ensure that a survey sample accurately represents a target population’s characteristics.
The importance of survey quotas lies in ensuring representative sampling, avoiding sampling bias, and obtaining actionable insights.
Different types of quotas exist such as demographic, geographic, and behavioral quotas which should be tailored to the specific objectives and characteristics of the target population.
Survey quotas primarily serve two key purposes: ensuring representative sampling and avoiding sampling bias.
Implementing survey quotas involves setting up appropriate selection criteria, monitoring progress against them, and making adjustments where necessary.
Challenges associated with using quotas include ensuring adequate sample sizes within each quota and addressing ethical considerations related to discrimination or stereotypes.
Best practices for utilizing quotas include thorough planning, setting clear targets, using stratified sampling techniques, promoting quota use to participants, and evaluating success after data collection.
Survey quotas are predetermined targets for respondents from different demographic or stratified groups. They are used to ensure that a survey sample accurately represents a target population’s characteristics.
The importance of survey quotas lies in ensuring representative sampling, avoiding sampling bias, and obtaining actionable insights.
Different types of quotas exist such as demographic, geographic, and behavioral quotas which should be tailored to the specific objectives and characteristics of the target population.
Survey quotas primarily serve two key purposes: ensuring representative sampling and avoiding sampling bias.
Implementing survey quotas involves setting up appropriate selection criteria, monitoring progress against them, and making adjustments where necessary.
Challenges associated with using quotas include ensuring adequate sample sizes within each quota and addressing ethical considerations related to discrimination or stereotypes.
Best practices for utilizing quotas include thorough planning, setting clear targets, using stratified sampling techniques, promoting quota use to participants, and evaluating success after data collection.