The Advantages of Qualitative Research: A Comprehensive Overview
In the world of research, there are two primary methods for gathering data: qualitative and quantitative research. While quantitative research relies on numbers and statistics, qualitative research takes a different approach. It delves into a deeper understanding of human behavior, motivations, and experiences. This comprehensive overview will explore the advantages of qualitative research and its critical applications in various fields.
🔩 The Nuts and Bolts:
- Flexibility Enhances Exploration: Qualitative research designs are inherently flexible. They allow researchers to adapt their methods as new insights emerge, ensuring richer and more responsive data collection.
- Deep Contextual Understanding: These designs capture the context within which behaviors and opinions are formed, providing a deeper understanding of the underlying factors influencing subjects.
- Rich Data from Diverse Sources: Qualitative designs often involve multiple data sources, from in-depth interviews to observations, enriching the breadth and depth of information gathered.
- Empathy and Ethical Conduct: By focusing on human subjects, qualitative research designs foster a high degree of empathy and ethical consideration, ensuring participants are treated with respect and sensitivity.
- Iterative Data Analysis: Qualitative research involves iterative analysis processes, where data is continuously analyzed, and theories are refined throughout the study, enhancing the accuracy and relevance of the findings.
- Uncover Subtle Nuances: The strength of qualitative research designs lies in their ability to detect subtle nuances in data, which more structured quantitative approaches might overlook.
- Enhanced Validity through Triangulation: Employing various methods and perspectives within a single study, known as triangulation, enhances the validity of the research findings by cross-verifying data.
Understanding Qualitative Research
Before diving into the advantages, let’s first grasp the essence of qualitative research. It is a method that explores the quality and intricacies of human phenomena. In other words, it seeks to understand the why and how rather than the what and how many. Qualitative research focuses on gaining rich insights and generating theories through thoroughly analyzing non-numerical data.
Qualitative research delves into the depths of human experiences, shedding light on the complexities that quantitative research may overlook. By immersing ourselves in the subjective world of individuals, we can gain a deeper understanding of their motivations, emotions, and perspectives. This approach allows us to capture the nuances and intricacies that make up the fabric of human existence.
Through qualitative research, we can explore the multifaceted nature of human behavior, uncovering the underlying reasons behind specific actions and decisions. It enables us to go beyond numbers and statistics, providing a more comprehensive understanding of the human experience.
Definition and Basic Principles of Qualitative Research
At its core, qualitative research aims to uncover the meaning and significance embedded within human experiences. It involves collecting and analyzing data such as interviews, observations, and textual materials. By immersing ourselves in the rich tapestry of human interactions, we can unravel the intricate threads that shape our understanding of the world.
One of the fundamental principles of qualitative research is reflexivity. This principle acknowledges the subjective influence of the researcher in the research process. It recognizes that the researcher’s background, beliefs, and experiences can shape the interpretation of data. By embracing reflexivity, researchers can navigate their biases and assumptions, allowing for a more nuanced and comprehensive analysis.
Another fundamental principle of qualitative research is the concept of saturation. Saturation refers to the point at which new data no longer provides additional insights or perspectives. It signifies that the researcher has comprehensively understood the phenomenon under investigation. By striving for saturation, researchers ensure that their findings are robust and representative of the complexities inherent in human experiences.
Differentiating Qualitative from Quantitative Research
While qualitative and quantitative research contribute valuable insights, they have distinct differences. Quantitative research uses numerical data and statistical analysis to establish patterns and correlations. It aims to quantify phenomena and generalize findings to a larger population.
On the other hand, qualitative research seeks to understand the intricacies of human experiences and behavior through in-depth analysis of non-numerical data. It emphasizes the subjective nature of human existence and aims to capture the richness and diversity of individual perspectives.
Quantitative research can tell us how many people prefer a particular product, but qualitative research can tell us why they like it and how it impacts their lives. By diving into the complexities of human experiences, qualitative research provides a holistic understanding that quantitative research alone cannot achieve.
Qualitative research allows us to explore the context, motivations, and emotions that underlie human behavior. It enables us to uncover the underlying meanings and interpretations that shape individuals’ actions and decisions. By embracing the qualitative approach, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of the human experience and contribute to developing theories and frameworks that capture the intricacies of our complex world.
Make your design decisions count.
Subscribe to Design Under Pressure. Get insights, UX metrics, and tools for bold, informed design.
We respect your inbox. Just insights. No fluff. Privacy Policy.
The Unique Advantages of Qualitative Research
Now that we have a solid foundation of qualitative research, let’s explore its unique advantages.
In-depth and Detailed Data Collection
One of the main advantages of qualitative research is its ability to capture rich and detailed data. Through interviews, focus groups, and other methods, researchers have the opportunity to delve deep into participants’ thoughts, feelings, and perceptions. This in-depth exploration allows for discovering nuances and complexities that might be missed in quantitative studies.
For example, a qualitative study on customer satisfaction in a restaurant might uncover what aspects customers appreciate and the underlying emotions and motivations that drive their satisfaction. These deep insights help businesses develop targeted strategies to enhance the overall dining experience.
Moreover, qualitative research allows researchers to observe participants in their natural environment, providing valuable context to their responses. By immersing themselves in the setting, researchers can better understand the factors influencing participants’ behaviors and attitudes.
Flexibility in Research Design
Unlike quantitative research, qualitative research offers flexibility in its design and execution. Researchers have the freedom to adapt their methods and approaches based on the evolving needs of the study. This flexibility enables them to explore unexpected avenues and uncover novel insights.
For instance, if an initial analysis reveals an exciting theme emerging from the data, researchers can explore it further by conducting additional interviews or focusing on related aspects. This adaptive approach allows for a more comprehensive understanding of the research topic and the ability to capture unforeseen perspectives.
Furthermore, qualitative research allows for iterative data collection and analysis. Researchers can continuously refine their research questions and data collection methods as they gain deeper insights. This iterative process enhances the rigor and validity of the findings, ensuring a more robust understanding of the phenomenon under investigation.
Contextual Understanding of Data
Qualitative research is known for its emphasis on context. It seeks to understand the data within its social, cultural, and historical framework. By considering the broader context, researchers can better comprehend the phenomena they are studying.
For example, a qualitative study on immigrants’ experiences in a new country would explore not only their individual perspectives but also the socio-cultural factors that influence their integration. This holistic understanding contributes to developing more inclusive policies and support systems for immigrant communities.
Moreover, qualitative research allows for the exploration of multiple perspectives and the recognition of diverse voices. By engaging with participants from different backgrounds and experiences, researchers can uncover the complexities and variations within a given phenomenon. This recognition of diversity promotes inclusivity and ensures that the findings are representative of the population under study.
In conclusion, qualitative research offers unique advantages regarding in-depth and detailed data collection, flexibility in research design, and contextual understanding of data. These advantages enable researchers to capture rich insights, adapt their methods to unexpected findings, and gain a holistic understanding of the phenomena they study. By expanding our knowledge and experience, qualitative research contributes to developing more informed decisions, policies, and strategies.
Critical Methods in Qualitative Research
Now that we have explored the advantages, let’s delve into the critical methods used in qualitative research.
Interviews and Focus Groups
Interviews and focus groups are widely used methods in qualitative research. These techniques involve engaging participants in conversational settings to gather insights into their experiences, perspectives, and beliefs. Researchers can elicit rich and meaningful responses by creating a comfortable and open environment.
For instance, a researcher conducting a study on workplace satisfaction might conduct in-depth interviews with employees to understand their perceptions of the company culture, leadership style, and growth opportunities. These insights can guide organizations in implementing strategies to improve employee satisfaction and retention.
Observations and Ethnography
Another valuable method in qualitative research is observation. By immersing themselves in the natural setting of the phenomena being studied, researchers can gain firsthand insights into behavior, interactions, and social dynamics. Ethnography, a form of observation, involves long-term immersion in a particular group or community to understand their culture and practices.
For example, an ethnographic study on a music festival would involve the researcher attending the festival, observing attendees’ behavior, and documenting their experiences. This immersion allows for a nuanced understanding of the festival’s impact on the community and the shared rituals that create a sense of belonging.
Content Analysis and Document Review
Qualitative research also includes analyzing documents and other textual materials. This method systematically examines written, visual, or audio information to extract relevant insights. Researchers can analyze historical documents, literature, social media posts, or public records to understand a particular subject better.
For instance, a researcher conducting a content analysis on news articles about climate change can identify prevailing narratives, key stakeholders, and public perceptions. This knowledge can inform communication strategies and policies to raise awareness and address climate-related issues.
🚀 If you’re using Helio
Capture rich insights, adapt methods to unexpected findings, and gain a holistic understanding.
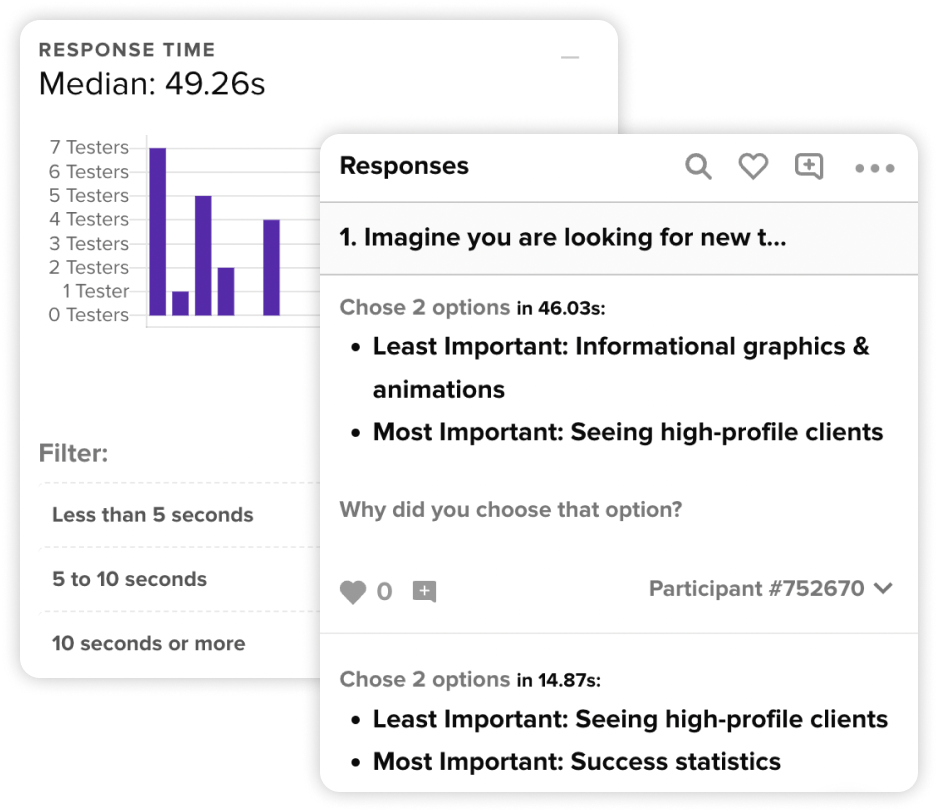
Qualitative research also includes analyzing documents and other textual materials.
Applications of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research finds extensive applications in various fields, including the social sciences, humanities, market research, business strategy, and healthcare.
Social Sciences and Humanities
Qualitative research provides valuable insights into human behavior, cultural practices, and social dynamics in the social sciences and humanities. It allows researchers to understand the complexities of societies, address social inequalities, and explore individuals’ subjective experiences.
For example, a qualitative study on the experiences of LGBTQ+ individuals in educational institutions can illuminate their challenges and offer recommendations for creating inclusive environments.
Market Research and Business Strategy
Qualitative research plays a crucial role in market research and business strategy. By capturing consumer insights, preferences, and motivations, businesses can develop targeted marketing campaigns, improve product design, and enhance customer satisfaction.
For instance, a qualitative study on Generation Z’s shopping habits can help retailers understand their unique preferences and develop strategies to attract and retain this demographic.
Healthcare and Patient Experience
Qualitative research provides valuable insights into patient experiences, treatment effectiveness, and healthcare delivery. It helps healthcare providers understand the impact of medical interventions on individuals and communities, leading to improved patient-centered care.
For example, a qualitative study on the experiences of patients living with chronic illnesses can identify the challenges they face in managing their conditions. This knowledge can shape the development of support programs and interventions tailored to these patients’ specific needs.
Qualitative research offers a comprehensive understanding of human experiences, behavior, and motivations. Its in-depth data collection, flexible research design, and contextual analysis complement quantitative research by providing nuanced insights to develop informed policies, targeted strategies, and improved outcomes. Whether exploring social phenomena, understanding consumer preferences, or enhancing patient-centered care, qualitative research is invaluable in our quest for knowledge and understanding.
Advantages of Qualitative Research FAQs
Qualitative research designs focus on understanding the quality and essence of human experiences. They are essential because they provide depth and detail that help uncover the reasons behind behaviors and beliefs. This is crucial for fields requiring a nuanced understanding of human interactions.
Unlike quantitative designs, which focus on numerical data and statistical analysis, qualitative research designs are structured to explore complex human behaviors and social phenomena in depth, often using unstructured or semi-structured data collection methods.
Common methods include in-depth interviews, participant observation, focus groups, and ethnographic studies. Each method is chosen based on its ability to uncover the specific types of data that the study aims to gather.
Challenges include managing subjectivity, ensuring data credibility, and the intensive time required for data collection and analysis. Addressing these challenges involves precise methodological planning, ongoing reflexivity, and rigorous data triangulation.
By providing detailed insights into consumer and citizen behaviors, qualitative research designs help businesses and policymakers make informed decisions that are more closely aligned with the needs and preferences of their stakeholders.
Ethical considerations include ensuring informed consent, protecting participants’ anonymity and confidentiality, and being sensitive to the research’s impacts on their well-being.
Findings are often presented as comprehensive narratives that include direct quotes from participants, thematic analyses, and contextual interpretations. This narrative approach helps convey the depth of the data and provides a compelling argument for the study’s conclusions.