How to Create an MVP for Your Business
Building a successful business starts with a great idea, but turning that idea into reality requires careful planning and execution. One approach that has gained popularity in recent years is creating a Minimum Viable Product. In this article, we will explore the concept of an MVP, its importance in business, and the steps to create and launch your own MVP. We will also discuss common mistakes to avoid along the way.
🔩 The Nuts and Bolts:
- Creating an MVP is an effective way to validate a business idea, collect user feedback, and reduce risks.
- tyle=”font-weight: 400;”> It is essential to understand the concept of a Minimum Viable Product, its importance in business, and the necessary steps to develop and launch one.</span>
- Define a value proposition that combines emotional and functional benefits to resonate with users.
- Sketching the MVP helps visualize and test the idea with potential users.
- When building the MVP, prioritize core features that solve the identified problem.
- Regularly seek user feedback, iterate on your MVP based on insights gained, and measure success through metrics to ensure continuous improvement.
- Common mistakes include overcomplicating the product, ignoring user feedback, and failing to test and validate before launch.
Understanding the Concept of a Minimum Viable Product
Before diving into the specifics, let’s first understand what a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is. An MVP is a version of your product with the bare minimum features required to solve a specific problem for your target audience. An MVP aims to validate your business idea and gather feedback from early adopters before investing significant time and resources into building a fully-featured product.
Developing an MVP is a strategic approach that allows entrepreneurs to test the waters before diving headfirst into the market. It’s like dipping your toes in the pool to check the temperature before taking a full plunge. By starting with an MVP, you can gauge the market demand for your product and make informed decisions based on real user feedback.
Imagine you have an idea for a mobile app that helps people track their daily water intake. Instead of spending months and thousands of dollars building a fully-featured app, you can start with an MVP that simply tracks the water consumed and sends reminders to drink more. This basic version allows you to validate the concept and gather feedback on its usefulness and potential improvements.
The Importance of an MVP in Business
Launching an MVP offers several benefits for your business. Firstly, it allows you to test your assumptions and validate your market demand early on. By getting your product in the hands of real users, you can gain valuable insights and refine your offering based on their feedback. This iterative process ensures that you are building a product that truly meets the needs of your target audience.
Furthermore, an MVP helps you minimize risks and maximize efficiency by focusing only on the essential features. It’s like building a sturdy foundation for a house before adding the walls, roof, and fancy decorations. By prioritizing the core functionalities, you can save time, money, and effort while delivering value to your customers.
Another advantage of starting with an MVP is that it allows you to gain a competitive advantage. By getting your product to market faster, you can establish your brand presence and build a user base before competitors catch up. This early mover advantage can be crucial in crowded markets where differentiation is key.
Key Features of a Successful MVP
When creating an MVP, it is crucial to identify the key features that will deliver value to your users. These features should directly address the core problem your product solves. Keep in mind that simplicity is the key. You can build a more focused and user-friendly MVP by removing unnecessary bells and whistles. Prioritize features based on their impact on the user experience and the value they provide to your target audience.
For example, in the case of the water tracking app, the key features of the MVP include a simple interface for inputting water intake, a visual representation of daily progress, and push notifications for reminders. These features directly address the problem of tracking and improving water consumption without adding unnecessary complexities that might overwhelm users or distract from the main goal.
Additionally, it’s important to remember that an MVP is not a one-time release. It’s an ongoing process of learning and iterating. As you gather feedback and insights from your users, you can continuously refine and enhance your product. This iterative approach ensures that your MVP evolves into a fully-featured product that meets your target audience’s needs and expectations.
Build something your buyers *truly* want
Subscribe to Closing the Gap—a newsletter to help makers and doers get closer to customers. Learn more.
We believe in protecting your data. Here’s our Privacy Policy.
Steps to Create Your MVP
Identifying the Core Problem Your Product Solves
Every successful product solves a problem. Start by clearly identifying the pain point that your product aims to address. Conduct thorough market research, surveys, and interviews to understand your target audience’s needs and challenges. This step is crucial as it will lay the foundation for the rest of your MVP development process.
During your market research, dive deep into the demographics and psychographics of your target audience. Understand their preferences, behaviors, and pain points. This will help you gain insights into their motivations and desires, allowing you to create a product that truly resonates with them.
Additionally, analyze your competitors’ products and solutions. Identify their strengths and weaknesses, and find the gaps in the market that your MVP can fill. By understanding the existing landscape, you can position your product effectively and differentiate it from the competition.
Defining Your Value Proposition
Once you have identified the core problem your product solves, you need to define your unique value proposition. Clearly articulate how your product differs and why users should choose it over existing alternatives. This will help you position your MVP effectively and communicate its benefits to your target audience.
Consider conducting a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) to identify your product’s advantages and disadvantages. Highlight your strengths and find ways to mitigate your weaknesses. This analysis will give you a comprehensive understanding of your product’s value and how it can address the pain points of your target audience.
Furthermore, think about the emotional and functional benefits that your MVP provides. Emotional benefits tap into the users’ feelings and aspirations, while functional benefits focus on the practical advantages. Combining both allows you to create a compelling value proposition that resonates with your target audience on multiple levels.
Sketching Your MVP
Sketching your MVP is an essential step in visualizing your product idea. Use wireframing tools or pen and paper to sketch your product’s user interface. Focus on the core functionality and user flow rather than intricate design details. Share these sketches with your team and potential users to gather early feedback and iterate on your concept.
When sketching your MVP, consider the user experience and user interface principles. Consider how users will interact with your product and ensure the design is intuitive and user-friendly. Incorporate user feedback into your sketches to refine and improve the overall user experience.
Consider creating multiple versions of your sketches to explore different design possibilities. This will allow you to compare and evaluate different approaches, helping you choose the most effective design for your MVP.
Building Your MVP
Building Your MVP
Once you have validated your concept through sketches and feedback, it’s time to build your MVP. Leverage rapid development techniques and tools to bring your MVP to life quickly. Remember, the emphasis here is on speed and functionality, not perfection. Aim to launch your MVP with basic, working features that address the core problem identified earlier.
Consider using agile development methodologies like Scrum or Kanban to manage your MVP development process. These methodologies allow for flexibility and iterative improvements, ensuring you can quickly adapt to user feedback and market demands.
During the development phase, prioritize the core features directly addressing the identified problem. Avoid feature creep and focus on delivering a minimum viable product that provides value to your users. By keeping your MVP lean and focused, you can launch it sooner and gather real-world feedback to guide future iterations.
Testing and Validating Your MVP
Gathering User Feedback
After launching your MVP, actively seek user feedback. Encourage users to provide suggestions, identify pain points, and share their overall experience. This feedback will help you understand how well your MVP solves the problem and identify areas for improvement. Actively engage with your users through surveys, interviews, and user testing sessions to gather qualitative and quantitative feedback.
Iterating and Improving Your MVP
Based on the feedback received, iterate and improve your MVP. Prioritize the most impactful enhancements based on user needs and business objectives. Continuously refine your product, incorporating user feedback and addressing pain points to create a better user experience. Keep the development cycle short and release frequent updates to keep your users engaged and invested in the product’s evolution.
Launching Your MVP
Strategies for a Successful MVP Launch
When launching your MVP, focus on creating a buzz around your product. Leverage social media, online communities, and targeted marketing strategies to generate interest and attract early adopters. Clearly communicate the unique value your MVP offers and how it solves your target audience’s pain points. Consider offering early access or exclusive benefits to incentivize users to try your product and provide feedback.
🚀 If you’re using Helio
Determine your product MVP with ranking.
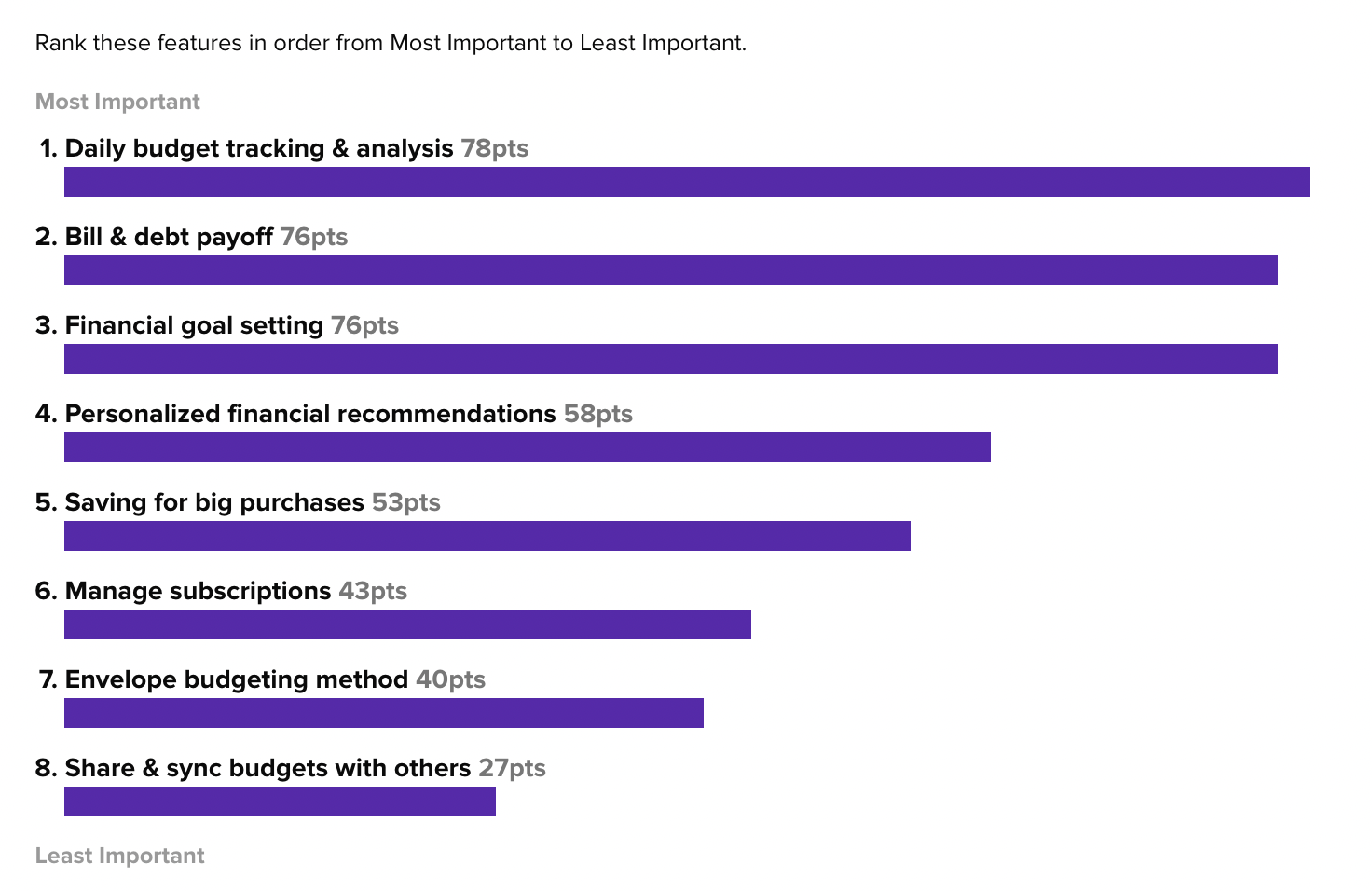
Incentivize users to try your product and provide feedback.
Measuring the Success of Your MVP
As you launch your MVP, it’s essential to establish measurable goals and key performance indicators (KPIs) to track its success. Monitor user engagement, conversion rates, and customer feedback to evaluate the effectiveness of your MVP. Analyze data and iterate on your product strategy based on the insights gained. Remember that an MVP is an ongoing process, and continuous improvement is vital to its long-term success.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Creating an MVP
Overcomplicating Your MVP
One of the biggest mistakes entrepreneurs make is overcomplicating their MVPs. Adding extra features or complex functionalities is tempting, thinking it will impress users. However, this approach often leads to bloated products that fail to address the users’ core needs. Keep your MVP simple and focused, delivering value with the minimum features required.
Ignoring User Feedback
User feedback is the lifeblood of MVP development. Ignoring or dismissing user suggestions can lead to missed opportunities and unhappy customers. Listen to your users, consider their feedback, and incorporate valuable insights into your product roadmap. Remember, your users are the true experts, and their feedback will shape the success of your MVP.
Failing to Test and Validate Your MVP Properly
The success of your MVP depends on how well you test and validate it. Rushing to launch without proper testing can lead to a subpar user experience and missed opportunities for improvement. Conduct thorough user testing, iterate on your MVP based on feedback, and ensure that your product is stable, reliable, and solves the problem effectively.
In conclusion, creating an MVP effectively validates your business idea, gathers early user feedback, and minimizes risks. Following the steps outlined in this article, you can create a successful MVP that resonates with your target audience. Remember to iterate, listen to your users, and continuously improve your product based on their feedback. Stay focused, keep it simple, and watch your MVP pave the way for a thriving business.
MVP FAQs
A Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is a version of your product that has the bare minimum features required to solve a specific problem for your target audience. An MVP aims to validate your business idea and gather feedback from early adopters before investing significant time and resources into building a fully-featured product.
Launching an MVP offers several benefits for your business. Firstly, it allows you to test your assumptions and validate your market demand early on. Secondly, it helps you minimize risks and maximize efficiency by focusing only on the essential features. Additionally, it allows you to gain a competitive advantage by getting your product to market faster.
When creating an MVP, it is crucial to identify the key features that will deliver value to your users. These features should directly address the core problem your product solves. Keep in mind that simplicity is the key. You can build a more focused and user-friendly MVP by removing unnecessary bells and whistles.
s=”yoast-text-mark”>s=”yoast-text-mark”>s=”yoast-text-mark”>s=”yoast-text-mark”>s=”yoast-text-mark”>s=”yoast-text-mark”>s=”yoast-text-mark”>s=”yoast-text-mark”>s=”yoast-text-mark”>s=”yoast-text-mark”>s=”yoast-text-mark”>s=”yoast-text-mark”>s=”yoast-text-mark”>s=”yoast-text-mark”>s=”yoast-text-mark”>yle=”font-weight: 400;”>What steps should I take to create my MVP?
<span class=”yoast-text-mark”>yle=”font-weight: 400;”>The steps to create an MVP include identifying the core problem your product solves, defining your value proposition, sketching your MVP, building your MVP, testing and validating your MVP, and launching your MVP. Additionally, consider using agile methodologies like Scrum or Kanban to manage your MVP development process.