Exploring Alternatives to the Minimum Viable Product
In today’s competitive business landscape, innovation is the key to success. One approach that has gained popularity in recent years is the Minimum Viable Product (MVP). This concept involves creating a basic product version and gathering user feedback to iterate and improve it. While the Minimum Viable Product approach has its merits, exploring alternative strategies to ensure optimal product development is important. This article will dive into different methodologies and models that can complement or surpass the MVP approach. Let’s begin by understanding the concept of Minimum Viable Product.
🔩 The Nuts and Bolts:
- The Minimum Viable Product (MVP) approach is a widely recognized product development and innovation strategy.
- To ensure optimal product development, exploring alternative strategies such as the Lean Startup Methodology, the Prototype Model, and the Minimum Marketable Product (MMP) approach is important.
- The Lean Startup considers business models, hypothesis-driven experimentation, and Build-Measure-Learn feedback loops to optimize product development.
- The Prototype Model involves creating a detailed representation of the product before proceeding with full-scale development.
- The MMP approach focuses on creating a marketable product that offers unique value for potential customers.
- Agile Development incorporates principles from both MVP and Lean Startups to build a customer-centric product tailored to changing market needs.
Understanding the Concept of Minimum Viable Product
At its core, the Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is the most basic product form that fulfills the initial vision and provides value to early adopters. It aims to test assumptions, validate hypotheses, and gather user feedback to drive iterative development. The MVP allows a fast and cost-effective way to launch a product and learn from user experiences.
When implementing an MVP strategy, focusing on the core features that address users’ pain points is crucial. By avoiding unnecessary complexity, developers can quickly create a functional prototype that mirrors the intended product. However, while the MVP approach has gained broad recognition, it does have its limitations.
The Role of MVP in Product Development
An MVP acts as a learning experiment, enabling entrepreneurs and product teams to validate their assumptions and gather valuable data. By launching a scaled-down version of their product, they can test various aspects such as market demand, user engagement, and pricing strategies. This iterative feedback loop improves the chances of building a successful product and avoiding costly mistakes.
One of the significant benefits of implementing an Minimum Viable Product is the ability to save time and resources. Instead of investing considerable effort in building a fully-featured product, teams can focus on the most critical aspects and iterate based on user feedback. This approach allows businesses to pivot and adapt quickly to market demands, staying ahead of the competition.
Limitations of the Minimum Viable Product Approach
While the MVP approach has proven successful for many startups, it has limitations. One major concern is the potential for overlooking long-term product sustainability. By rushing to release an Minimum Viable Product and gather feedback, teams risk neglecting essential features or the product’s long-term vision. This short-term focus can lead to customer dissatisfaction and hamper the product’s potential for growth.
Another downside of the MVP approach is the reliance on early adopters for feedback. These early users may have different expectations and tolerance for bugs and incomplete features compared to the wider target audience. Relying solely on their feedback may result in a skewed perspective and hinder the product’s ability to cater to a broader market.
Build something your buyers *truly* want
Subscribe to Closing the Gap—a newsletter to help makers and doers get closer to customers. Learn more.
We believe in protecting your data. Here’s our Privacy Policy.
The Lean Startup Methodology: Beyond Minimum Viable Product
Building upon the foundation laid by the Minimum Viable Product approach, the Lean Startup methodology takes a more comprehensive approach to product development. It emphasizes the importance of validated learning, continuous experimentation, and iterative design. Let’s explore the principles and advantages of this robust framework.
Principles of the Lean Startup Methodology
The Lean Startup methodology introduces several key principles that differ from traditional product development approaches. These include the concept of an actionable business model canvas, hypothesis-driven experimentation, and the Build-Measure-Learn feedback loop.
By building a solid business model canvas, entrepreneurs can identify their customers, value propositions, key activities, and resources. This exercise helps ensure that all product aspects align with the core business objectives. Additionally, hypothesis-driven experimentation involves formulating clear assumptions and testing them through real-world experiments and customer interactions.
The Build-Measure-Learn feedback loop is the backbone of the Lean Startup methodology. It encourages rapid iteration by building minimum viable features, measuring user feedback and data, and learning from the results. This iterative process allows entrepreneurs to pivot if necessary and continuously improve the product based on real customer insights.
How Lean Startup Enhances Product Development
The Lean Startup methodology offers several advantages over the Minimum Viable Product approach. By adopting a more comprehensive approach that focuses on the business model, entrepreneurs can align their products with strategic goals and avoid potential issues that may arise in the long run.
The emphasis on validated learning and hypothesis-driven experiments ensures that real data and customer feedback support decisions. This data-driven approach minimizes the risk of building a product based on assumptions that may not align with market demand.
Furthermore, the iterative nature of Lean Startup puts entrepreneurs in a constant feedback loop with users. This engagement not only fosters strong relationships but also helps create a product that genuinely meets the needs of its target audience. The Lean Startup methodology goes beyond just developing a minimum viable product; it focuses on creating a sustainable and customer-centric business.
The Prototype Model: A Minimum Viable Product Alternative
Another alternative to the Minimum Viable Product approach is the Prototype Model. This model involves creating a fully functional representation of the product before proceeding with development. Let’s look at what the Prototype Model entails and its advantages.
Defining the Prototype Model
In the Prototype Model, developers create a detailed representation of the product that closely resembles the final version. This prototype is a tangible visual aid for stakeholders and potential users to understand the product’s functionality and design. It allows for comprehensive testing and validation before investing resources in the full-scale development phase.
The Prototype Model can take various forms, including mockups, wireframes, or interactive prototypes. The fidelity level depends on the project’s scope and the prototype’s desired outcome. By involving stakeholders and users early in the process, teams can gather invaluable insights and identify potential issues that may arise later.
Advantages of Using Prototypes in Product Development
The Prototype Model offers numerous advantages that complement the MVP approach. By creating a tangible representation of the product, teams can better communicate their vision and gain stakeholder buy-in. This ensures that everyone involved clearly understands the product’s features and design from the outset.
Additionally, prototypes are valuable for conducting usability testing and gathering user feedback. By involving potential users in the early stages of product development, teams can identify pain points and make necessary improvements before committing to full-scale development. This reduces the risk of building a product that fails to address users’ needs, ultimately saving time and resources.
The Concept of Minimum Marketable Product (MMP)
Building on the foundation of MVP and prototypes, the Minimum Marketable Product (MMP) concept takes a product-centric approach to product development. Let’s explore how MMP differs from the MVP approach and the benefits it offers.
Understanding the MMP Approach
The Minimum Marketable Product approach focuses on developing a viable and marketable product. Instead of solely focusing on the bare minimum features, the MMP approach aims to create a product that provides sufficient value to attract a broader target audience.
The MMP strategy involves identifying the core features that differentiate the product and resonate with potential customers. By considering marketability from the outset, teams can ensure that their product has a competitive edge and is positioned for long-term success.
Benefits of Minimum Marketable Product
By incorporating the Minimum Marketable Product approach, teams can build a stronger foundation for their product to thrive in the market. The product will gain traction with a wider audience by prioritizing marketability alongside viability.
Focusing on the core features that offer a unique value proposition ensures that the product stands out from competitors. Additionally, positioning the product for market success reduces the need for extensive marketing efforts.
By adopting the MMP approach, companies can confidently launch their product, knowing that it meets the needs and desires of their target market. This customer-centric approach increases the chances of success and creates a solid foundation for further growth and expansion.
🚀 If you’re using Helio
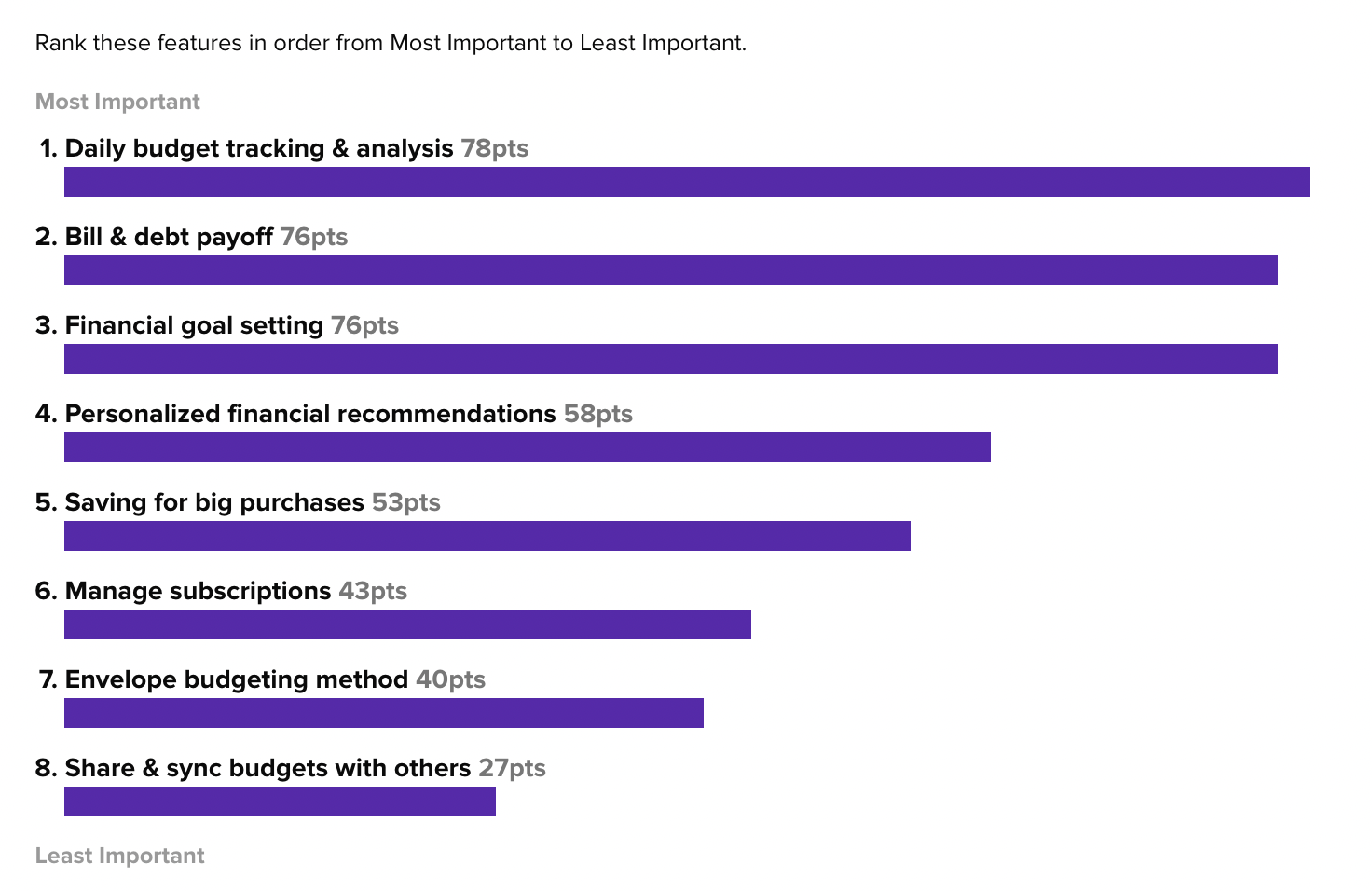
Use rank to confidently identify target market wants and needs.
Businesses can create products that meet the needs of their target audience and pave the way for success.
The Role of Agile Development in Product Creation
Finally, let’s explore the role of Agile Development in product creation and how it aligns with the concepts discussed thus far.
Agile Development Explained
Agile Development is an iterative and collaborative approach to software development that focuses on adaptability and flexibility. It emphasizes close collaboration between developers, stakeholders, and users throughout development.
One of the key principles of Agile Development is the ability to respond to changing requirements and priorities. This iterative approach enables teams to continuously refine and improve their product based on user feedback and evolving market needs.
Agile vs. MVP: A Comparative Analysis
While Agile Development shares similarities with the Minimum Viable Product approach, there are distinct differences in their focus and scope. While Minimum Viable Product primarily focuses on validating assumptions and learning from users, Agile Development encompasses a broader range of activities.
Agile Development embraces the principles of the Lean Startup methodology, incorporating iterative development, customer-centricity, and collaboration. It leverages regular feedback loops, continuous integration, and adaptable planning to ensure that the product aligns with user needs and responds to market changes effectively.
By adopting an Agile Development framework, teams can combine the best aspects of the MVP approach with the iterative nature of Lean Startup. This aligns development efforts with user needs and market demands, leading to a more robust and successful product.
Conclusion
While the Minimum Viable Product approach has revolutionized the product development landscape, exploring alternative strategies to maximize success is essential. The Lean Startup methodology, the Prototype Model, the Minimum Marketable Product approach, and Agile Development offer valuable alternatives to supplement or surpass the core principles of MVP.
By understanding the strengths and limitations of each approach, entrepreneurs and product teams can make informed decisions about their development strategies. Through iterative experimentation, market validation, and customer-centricity, businesses can create products that meet the needs of their target audience and pave the way for long-term success in a competitive market.
Minimum Viable Product FAQs
The MVP approach involves creating a basic product version and gathering user feedback to iterate and improve it. Developers can quickly create a functional prototype that mirrors the intended product by focusing on the core features that address users’ pain points.
The Lean Startup methodology offers several advantages over the MVP approach. By building a solid business model canvas, entrepreneurs can identify their customers, value propositions, key activities, and resources. Additionally, hypothesis-driven experimentation involves formulating clear assumptions and testing them through real-world experiments and customer interactions.
The Prototype Model involves creating a fully functional representation of the product before proceeding with development. This prototype is a tangible visual aid for stakeholders and potential users to understand the product’s functionality and design. It allows for comprehensive testing and validation before investing resources in the full-scale development phase.
The Minimum Marketable Product approach focuses on developing a viable and marketable product. By considering marketability from the outset, teams can ensure that their product has a competitive edge and is positioned for long-term success.
Agile Development is an iterative and collaborative approach to software development that focuses on adaptability and flexibility. It emphasizes close collaboration between developers, stakeholders, and users throughout development.