Navigating the complexities of product development can feel like trying to solve a puzzle with missing pieces. That’s where a well-structured product management workflow comes into play. By streamlining your process from vision to launch, you can ensure that every step aligns with your goals and user needs.
Janna Bastow’s continuous product management workflow offers a structured approach to managing your product’s lifecycle. It helps you plan and execute each stage efficiently, from the initial vision and strategy to the final hunch, and beyond. But what makes this workflow truly effective is the integration of user research at every step. Understanding your users’ needs, gathering feedback, and making data-driven decisions can transform your product from a mere idea into something that resonates with your audience.
This blog post will dive deep into the product management workflow, exploring each stage in detail. We’ll highlight the importance of conducting user research and provide practical tips on gathering and analyzing user feedback effectively. Whether you’re a seasoned product manager or just starting, this guide will help you understand how to incorporate user research into your workflow to create products that meet user needs and drive business success.
So, how do you conduct user research for your product? Let’s break it down step by step.
Understanding the Product Management Workflow
The product management workflow is like a roadmap guiding your product from the initial idea to the final launch and beyond. It’s essential to have a structured approach to ensure every step aligns with your goals and user needs.
The product management process starts with the “why.” In other words, product managers start by understanding why the customer has a need and how their product can be a solution.

What is a Product Management Workflow?
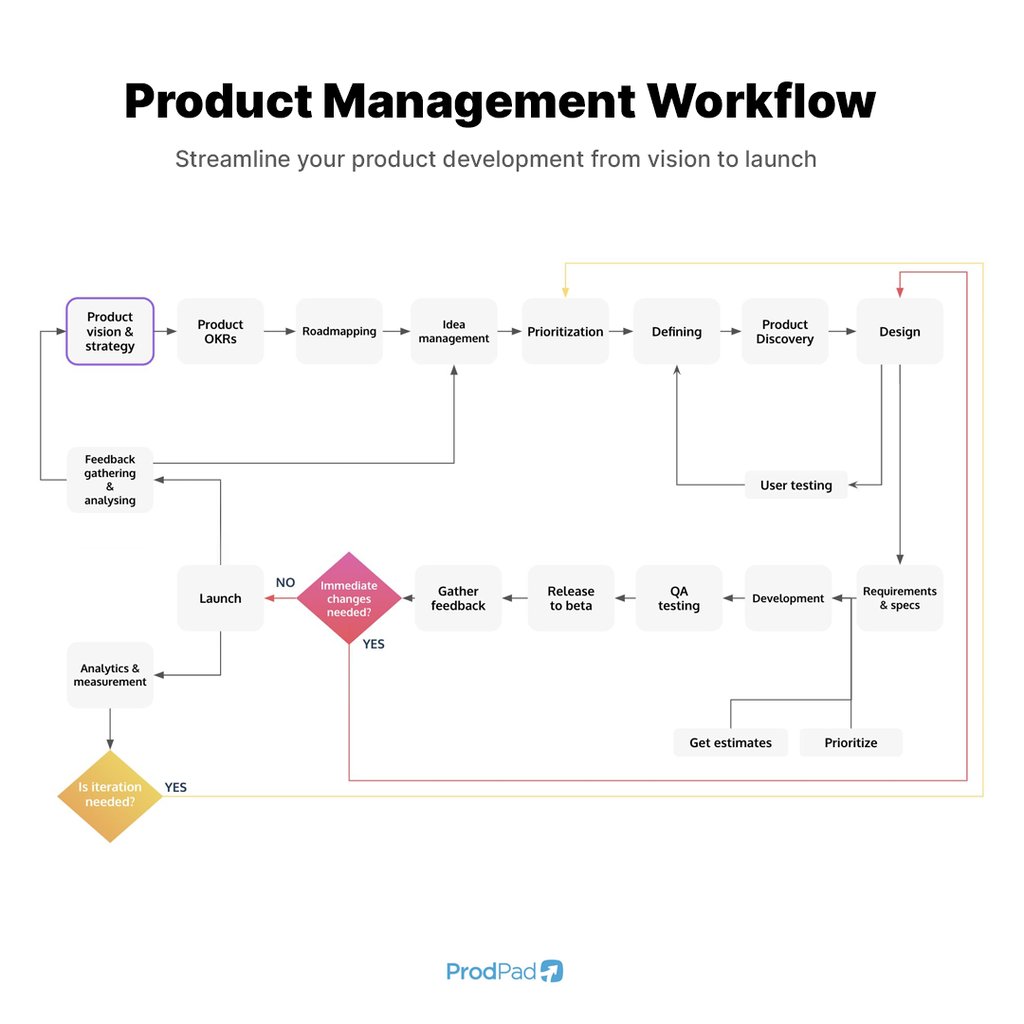
A product management workflow encompasses all the stages of bringing a product to market. It includes steps like vision and strategy, road mapping, idea management, prioritization, product discovery, design, development, testing, launch, feedback gathering, and iteration. This workflow helps teams stay organized, prioritize tasks, and ensure that every aspect of the product development process is covered.
Key Stages of the Product Management Workflow
- Product Vision & Strategy: Where you define what you want to achieve with your product. They involve understanding your target market, identifying user needs, and setting clear objectives.
- Roadmapping: Creating a product roadmap involves setting strategic goals and timelines. This helps align the team and stakeholders with the product’s long-term vision.
- Idea Management: Collect and manage ideas for potential features or improvements. This stage involves gathering input from various stakeholders and users to ensure the best ideas arise.
- Prioritization: Not all ideas can be implemented at once. Prioritization helps evaluate and rank ideas based on strategic fit, feasibility, and impact.
- Product Discovery: This stage involves researching to validate assumptions and understand user needs better. It’s about gathering insights from your target audience to inform your product decisions.
- Design: Develop design solutions that address the defined requirements and user needs. This is followed by user testing to validate these designs before moving to development.
- Development: Translate user-tested designs into a working product. This stage involves close collaboration with cross-functional teams to ensure the product is built to specifications.
- User Testing: Conduct thorough user testing to identify any issues or areas for improvement. The insights gathered here help make necessary adjustments before launching the product.
- Launch: Prepare for a user-centered launch by ensuring all aspects of the product are ready for the market. Collect and analyze user feedback post-launch to measure product performance and user satisfaction.
- Feedback Gathering & Analysis: Set up channels for continuous user feedback. Analyze this feedback to identify trends and areas for improvement.
- Iteration: Make data-driven decisions for product iterations. Prioritize changes based on user feedback and performance data to ensure the product continues to meet user needs and business goals.
Why User Research is Essential
User research is the backbone of a successful product management workflow. It provides insights for making informed decisions and ensuring the product aligns with user needs and expectations.
Understanding User Needs and Pain Points
User research helps you understand your users’ needs and problems. You gather valuable insights into their behaviors, preferences, and pain points by conducting surveys, interviews, and usability tests. This information is crucial for developing a product that truly resonates with your target audience.
Reducing Risks and Making Informed Decisions
Relying on assumptions can be risky. User research reduces these risks by providing concrete data to support your decisions. It helps you validate your ideas, prioritize features, and identify potential issues early in development. This way, you can make informed decisions that increase the likelihood of your product’s success.
Enhancing User Satisfaction and Product Success
A product that meets user needs and provides a great user experience is more likely to succeed. User research ensures you are on the right track by continually gathering feedback and making necessary adjustments. This ongoing process of iteration and improvement keeps your product aligned with user expectations, leading to higher user satisfaction and loyalty.
By integrating user research into every stage of the product management workflow, you create a product that meets business goals and delights users. This win-win situation sets your product up for long-term success.
Resources
Step-by-Step User Research in the Workflow
Ensuring a successful product management workflow involves clear vision and strategy, continuous user engagement, and data-driven decisions, all of which align your product with user needs and business goals for sustained success.
- Product Vision & Strategy
- Roadmapping
- Idea Management
- Prioritization
- Product Discovery
- Design
- Development
- User Testing
- Launch
- Feedback Gathering & Analysis
- Iteration
1. Product Vision & Strategy
It is crucial to set a strong foundation with a clear product vision and strategy. Here’s how to integrate user research into this initial stage of the product management workflow.
Define Your Product Vision
First things first, you need a clear product vision. This vision should articulate what you want your product to achieve and the problem it aims to solve. But don’t just dream it up in isolation—bring your users into the picture.
- Start with User Personas: Create detailed user personas representing your target audience. These personas should include demographic information, behaviors, needs, and pain points.
- User Interviews and Surveys: Conduct interviews and surveys to gather insights directly from potential users. Ask about their current challenges, what solutions they’re using, and what features they wish they had.
- Competitive Analysis: Look at your competitors and see what’s working for them. Identify gaps in their offerings that your product can fill.
Aligning Vision with User Needs
Aligning your product vision with user needs is essential for creating something people will use and love. Here’s how to ensure your vision hits the mark:
- Identify Key Problems: Use the insights from your user research to pinpoint the main problems your target audience faces. Your product vision should aim to solve these problems.
- Value Proposition: Define your product’s value proposition. What unique benefits does your product offer? How does it make your users’ lives easier or better?
- Stakeholder Feedback: Engage with stakeholders early on. Get their input and buy-in to ensure that your product vision aligns with business goals and user needs.
Tools and Methods for Gathering Initial User Insights
You’ll need the tools and methods to gather the initial user insights to shape your product vision. Here are some effective ones:
- Helio Surveys: Use Helio’s survey tools to collect user feedback. Ask questions that reveal users’ needs, preferences, and pain points. Helio allows you to gather detailed responses quickly and efficiently.
- Analytics Tools: Use tools like Google Analytics to analyze user behavior on your current products or similar products. Look for patterns and trends that indicate user preferences and pain points.
- Social Media Listening: Monitor social media channels and forums to see what users say about similar products. This can provide unfiltered insights into their frustrations and desires.
Helio Example
To understand the consumer banking market more clearly, we used Helio testing to develop distinct personas that represent ideal customer profiles (ICP) for a theoretical financial company called Banko.
We connected with an audience of banking consumers in the United States to solicit feedback on surveys about their behaviors and experiences. Evaluative questions were used to gauge what types of actions Banko’s audience currently take when it comes to their finances:
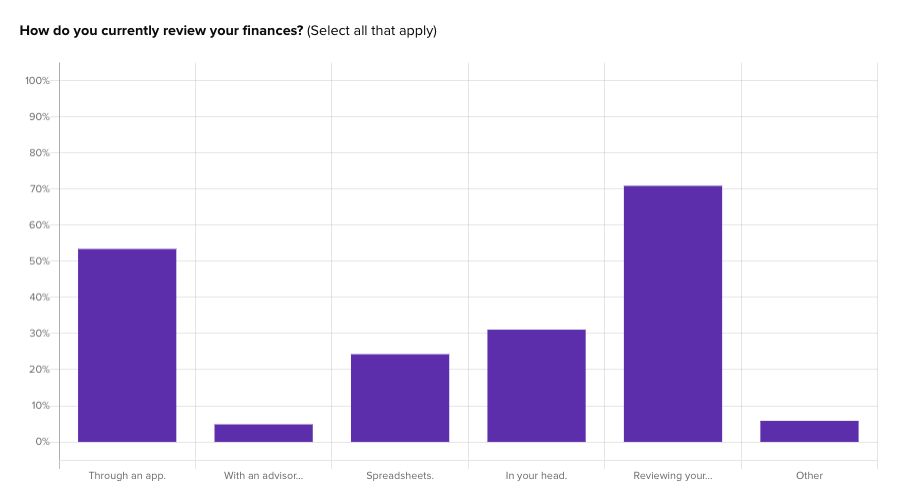
With responses about their experiences gathered, the Banko team then used Helio’s data filters to isolate specific demographic segments that they believed might yield different results:
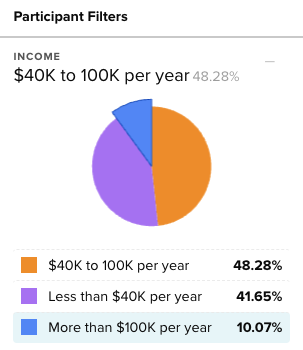
Once the responses are filtered, Helio’s data reports reveal the difference in answers between the new filtered group and the overall audience:
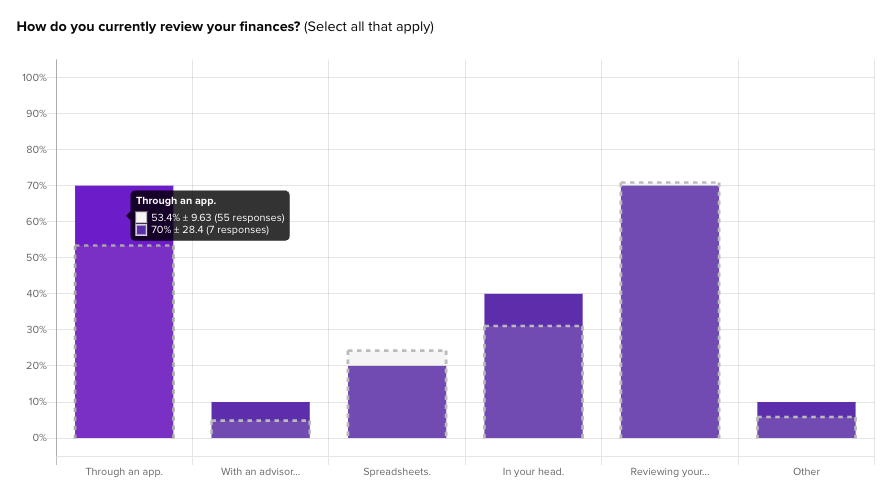
For instance, Banko found that participants with higher incomes over $100k/year are actually much more likely to use an app to track their finances right now.
As the differences in these segments are revealed, the Helio team helped Banko load their results into a Persona framework:
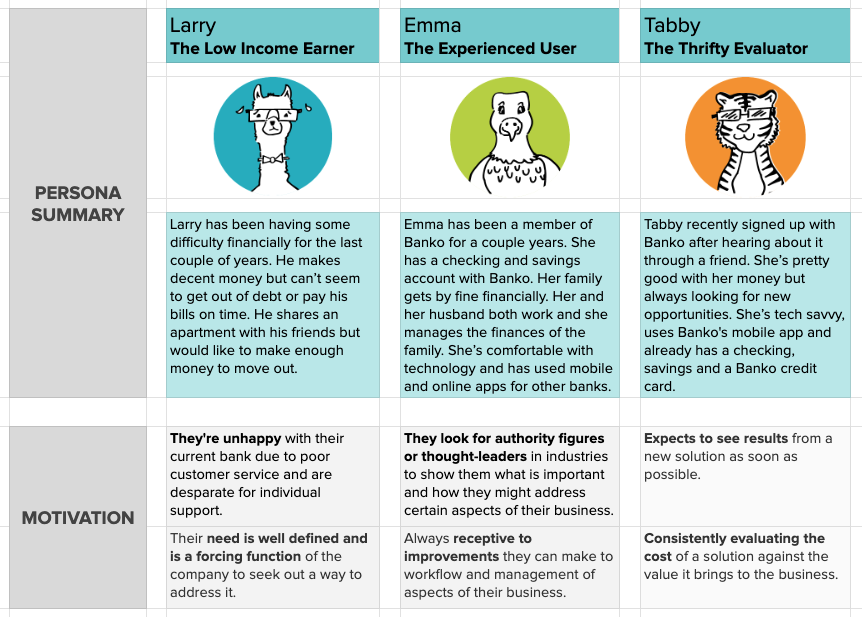
As Banko continues to refine these personas, they will be most key to their marketing efforts and understanding how they can speak to different consumer segments most effectively.
View the Banko Persona Framework
Integrating these steps into your product vision and strategy ensures that your product management workflow starts correctly. You’re not just guessing what users might want—you’re building a product based on real, actionable insights. This approach increases the chances of your product’s success and sets the stage for a user-centered development process that continues throughout the product lifecycle.
2. Roadmapping
Creating a product roadmap is a crucial step in the product management workflow. It sets the direction for your product’s development and ensures that your team stays aligned with your strategic goals. Integrating user research into this process not only makes your roadmap more effective but also ensures that your product meets actual user needs.
Setting Strategic Goals Based on User Feedback
Your roadmap should be driven by user feedback to ensure that it addresses real needs and problems.
- Gather Feedback Regularly: Use surveys, interviews, and feedback tools like Helio to collect user insights regularly. Understand what users value the most and where they encounter problems.
- Analyze Feedback Trends: Look for common themes and trends in the feedback you receive. This helps you identify the most pressing user needs and opportunities for improvement.
- Set Clear, User-Centric Goals: Translate these insights into clear, strategic goals. For example, if users frequently mention difficulties with a specific feature, a goal could be to redesign that feature to enhance usability.
Involving Users in the Roadmap Creation Process
Involving users in the roadmap creation process makes them feel valued and ensures your product development is aligned with their needs.
- User Advisory Panels: Create user advisory panels to get continuous input from a group of dedicated users. These panels can provide ongoing feedback and validate your roadmap decisions.
- Crowdsourcing Ideas: Use platforms like Helio to crowdsource ideas from your user base. This generates a wealth of new ideas and shows users that you value their input.
- Beta Programs: Run beta programs to involve users in testing new features early. This helps you gather feedback before fully committing resources to development and ensures that your roadmap reflects user preferences.
Prioritizing Features That Meet User Needs
Not all features are created equal. Prioritizing features based on user needs ensures that you focus on what matters most to your users.
- Ranking and Likert Scales: Use ranking and Likert scale surveys to ask users to prioritize features. This provides quantitative data on what users consider most important.
- Feasibility and Impact Analysis: Evaluate features based on their feasibility and potential impact. Features highly desired by users but low in development complexity should be prioritized.
- User Stories and Scenarios: Develop user stories and scenarios to understand how different features benefit users in real-world contexts. This helps in visualizing the practical impact of features and prioritizing accordingly.
Helio Example
In our work with beauty brand & skincare provider SkinSavvy, we needed to understand where to focus our design and development efforts across their website, mobile app, and social media platforms. With a large proportion of visitors coming th/rough each of those channels, the team needed validation as to which platform would be their testing grounds for developing patterns that would trickle down into the others.
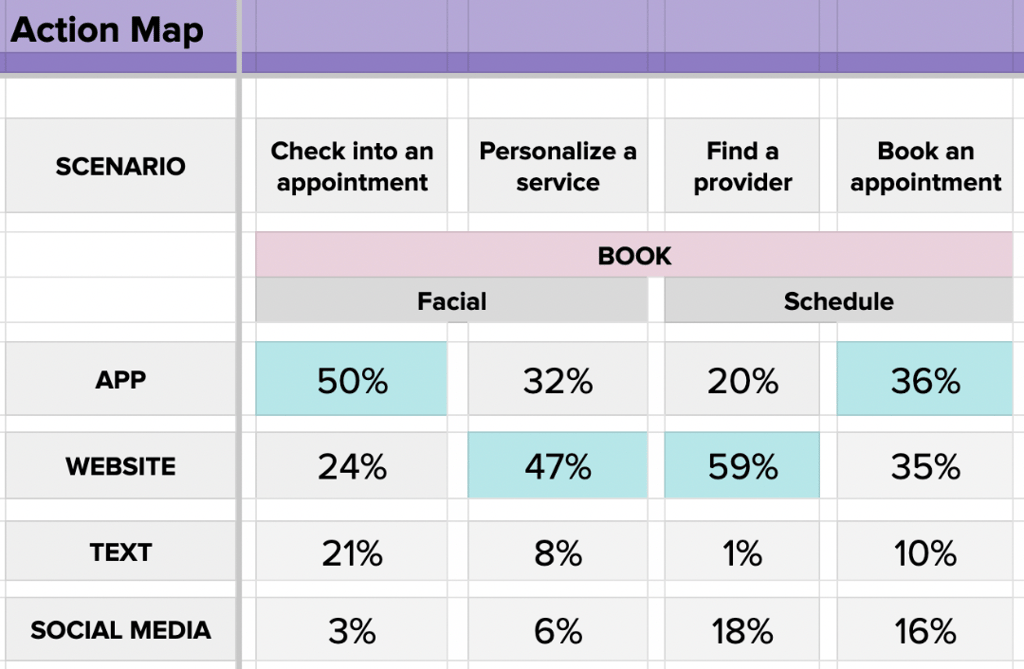
We employed our action map testing to learn which of these channels SkinSavvy’s consumers preferred to use in key situations across the web experience, such as finding a skincare provider or browsing through beauty products.
Each box in the image above represents the percentage of participants who would choose that channel for completing their goal, and the most prominent choice is highlighted in blue for each scenario.
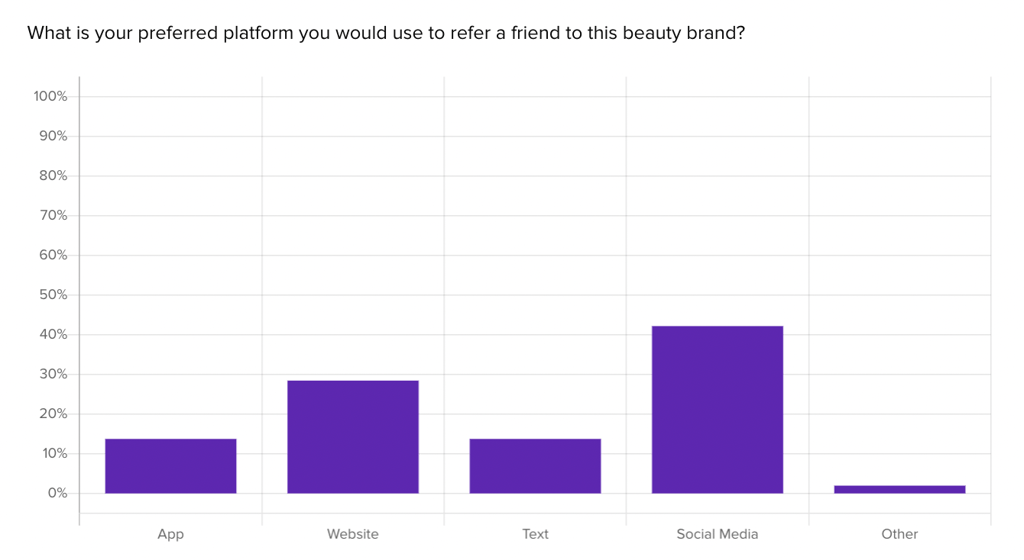
For instance, activities around appointments are preferred to be handled in the mobile app where users can easily access their personal information, while decisions about what services a consumer wants to receive are more comfortable on the website.
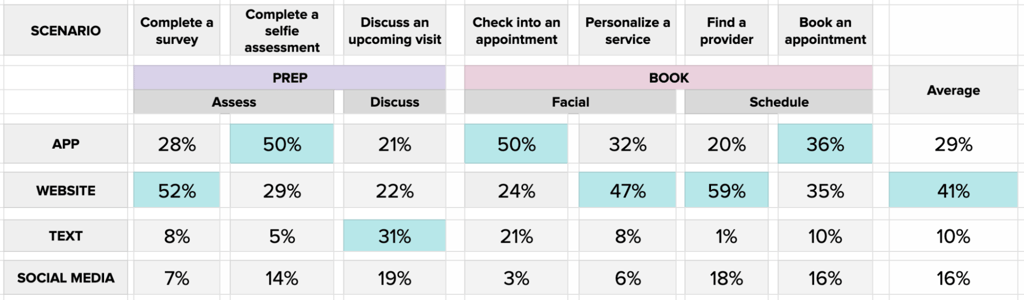
Once responses had been collected on up to 13 different scenarios across key parts of the experience like booking and treatment prep, the average percentage of each channel was calculated.
Across each of their preferred channels of communication, SkinSavvy found that their consumers prefer to use the website experience rather than the mobile app, though there was significant engagement with the app for time-sensitive booking activities. Moving forward, the SkinSavvy team focused on polishing the website and app experiences for smooth user journeys.
By setting strategic goals based on user feedback, involving users in the roadmap creation process, and prioritizing features that meet user needs, you create a strategic and user-centric roadmap. This approach ensures that your product development efforts are focused on delivering maximum value to your users, which is the ultimate goal of any effective product management workflow.
3. Idea Management
Managing ideas effectively is a vital part of the product management workflow. It involves collecting, organizing, and prioritizing ideas to ensure that the best ones rise to the top. By engaging users in this process, you can gather valuable insights and create a product that truly meets their needs.
Collecting and Organizing Ideas
You need a steady stream of fresh ideas to build a successful product. Here’s how to collect and organize them:
- Open Channels for Ideas: Create multiple channels where team members, stakeholders, and users can submit their ideas. This could be through email, dedicated forms on your website, or feedback tools.
- Categorize and Tag Ideas: Once ideas start coming in, categorize them based on themes or features. Tagging ideas makes it easier to sort and prioritize them later.
- Regular Review Meetings: Hold regular meetings to review and discuss new ideas. This ensures that no good idea gets overlooked and helps keep the idea pool fresh and relevant.
Engaging Users in Idea Submission
Users are a goldmine of ideas because they interact with your product daily. Engaging them in the idea submission process not only generates great ideas but also makes them feel valued.
- User Feedback Surveys: Use surveys to ask users for their ideas and suggestions. Questions like “What features would you like to see?” or “How can we improve your experience?” can yield insightful responses.
- Idea Submission Portals: Set up an easy-to-use portal where users can submit their ideas directly. Make sure it’s accessible and regularly monitored.
- Incentivize Participation: Encourage users to submit ideas by offering incentives like discounts, free trials, or even just recognition. People are more likely to contribute if they feel appreciated.
Using Tools Like Helio to Manage and Prioritize Ideas
Managing and prioritizing a large number of ideas can be challenging. Tools like Helio can streamline this process and ensure that the best ideas are brought to the forefront.
- Centralized Idea Repository: Use Helio to create a centralized repository where all ideas are stored and easily accessible. This prevents ideas from getting lost and makes them available for everyone to see.
- Prioritization Frameworks: Implement frameworks within Helio to rank ideas based on criteria like feasibility, impact, and user demand. This structured approach ensures that you focus on ideas that offer the most value.
- Stakeholder Collaboration: Helio allows for seamless collaboration among stakeholders. Everyone can vote, comment, and rank ideas, making the prioritization process more democratic and inclusive.
Helio Example
To effectively manage ideas across an org, we use an Opportunity Index to gather ideas, collect user feedback, and incorporate input from business stakeholders and tech decision makers into the prioritization of these product opportunities.We used this method to build a ranked list of opportunities for a theoretical ad management company called Advent:
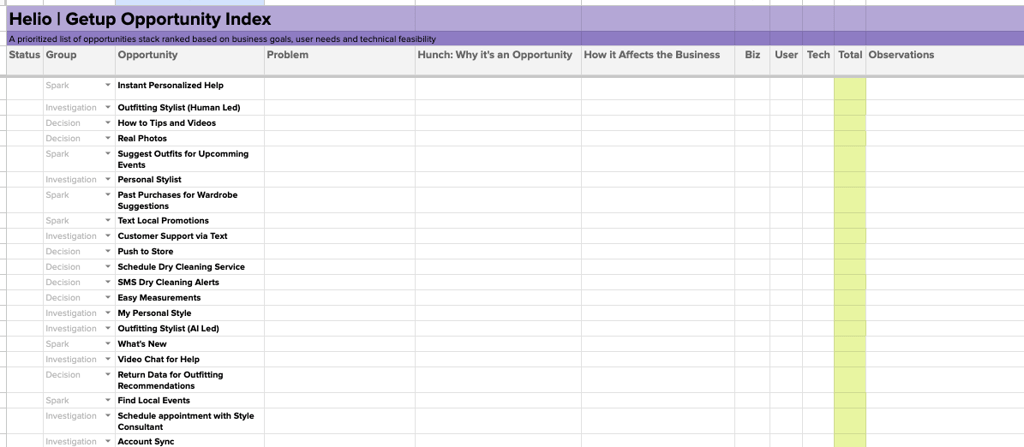
These ideas were listed into the Opportunity Index framework, with areas for the team to expand on what problem each concept is solving, why it’s important, and how it can be beneficial for the business.
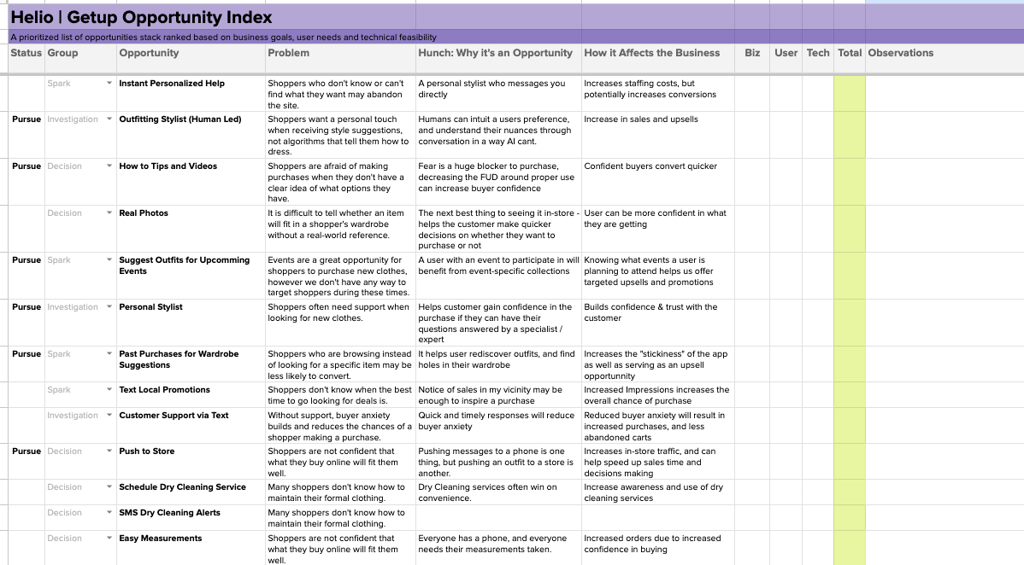
Advent used their Opportunity Index to track each concept their team came up with, and then compare the business value, technical feasibility, and user need for each idea.
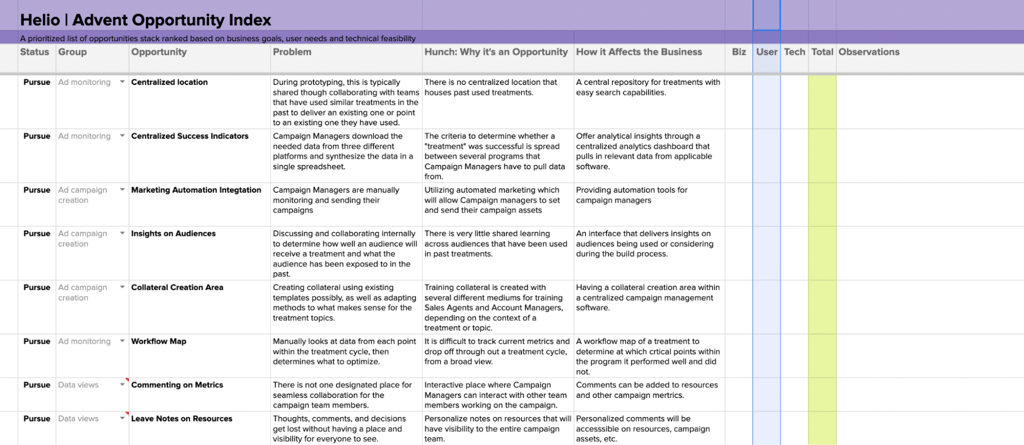
The biz and tech columns were completed by the Advent team, who rated a 5 as valuable or easy and 1 as unnecessary or difficult.
The user value is influenced through audience testing, in which we asked participants in Advent’s audience of marketing and advertising professionals about their experiences and reactions to different ideas.
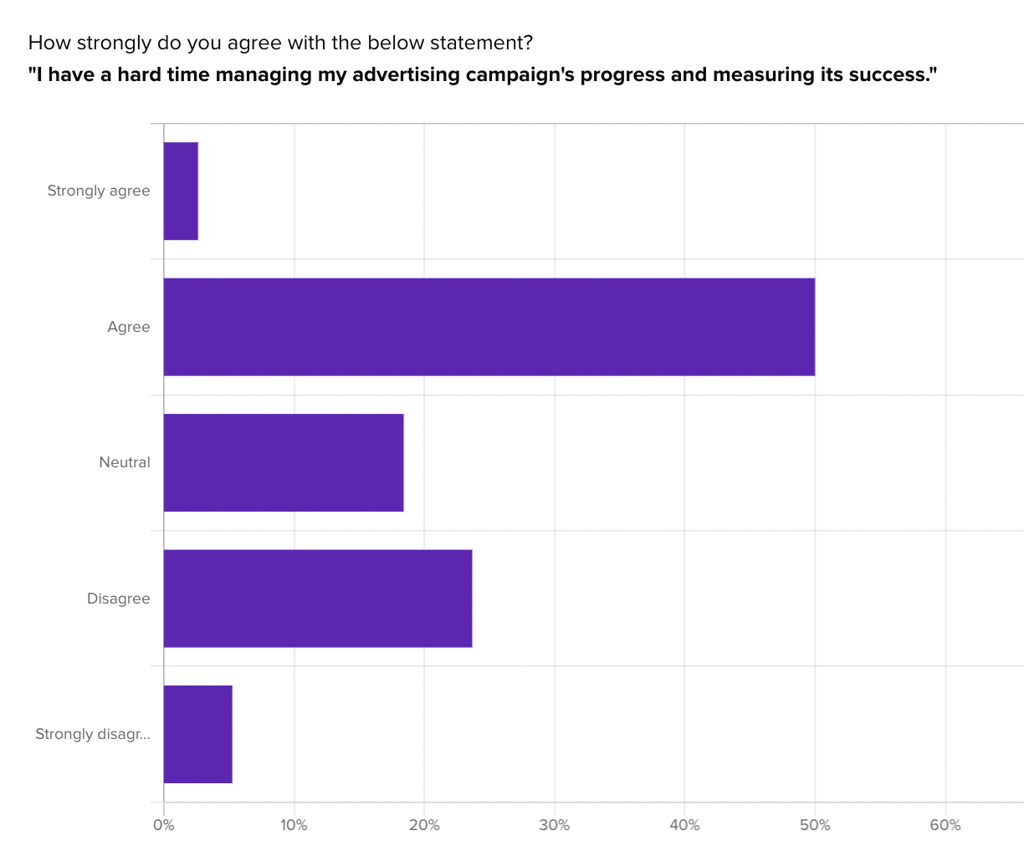
Once data has been collected on each feature idea, the value of that idea is translated into a 1 – 5 rating based on how important it would be to an Advent user. This progress tracker idea received a fair amount of disagreement from participants (28%), so it would be rated on the lower end of the 5-point scale (2/5).
The data observation supporting each user rating is listed to the right, as well as a link leading to the raw data itself. Now, with a user rating for each opportunity in hand, the Biz and Tech ratings could also be applied to each idea based on input from the product team.
View the Advent Opportunity Index
You can ensure that your product management workflow remains dynamic and user-focused by effectively managing ideas, engaging users in the submission process, and utilizing tools like Helio for organization and prioritization. This approach not only enhances the quality of your product but also fosters a community of engaged and loyal users who feel invested in your product’s success.
4. Prioritization
Prioritization is a critical step in the product management workflow. It ensures that your team focuses on the most valuable and feasible ideas first, aligning your product development efforts with user needs and business goals. Here’s how to approach prioritization effectively.
Evaluating Ideas Based on User Impact and Feasibility
Not all ideas are created equal. To decide which ones to pursue, you need to evaluate them based on their potential impact on users and their feasibility.
- User Impact: Determine how significantly an idea will improve the user experience. Will it solve a major pain point? Will it add substantial value? Gathering direct feedback from users can help gauge the potential impact.
- Feasibility: Assess the technical and resource feasibility of each idea. Do you have the necessary skills, technology, and budget to implement it? How long will it take to develop? Balancing impact with feasibility ensures you’re not biting off more than you can chew.
Techniques for Prioritizing User Needs
To prioritize user needs effectively, you can employ several techniques that help make informed and strategic decisions.
- MoSCoW Method: Categorize ideas into four groups: Must have, Should have, Could have, and Won’t have. This method helps you focus on what’s essential for the product and what can be deferred or dropped.
- Value vs. Effort Matrix: Plot ideas on a matrix based on their value to users and the effort required to implement them. This visual representation makes it easier to identify quick wins (high value, low effort) and avoid high-effort, low-value initiatives.
- Kano Model: Classify features such as basic needs, performance needs, and delighters. This helps in understanding which features are fundamental, which will improve satisfaction, and which will wow your users.
Rank and Likert Scales for User Feedback
Gathering quantitative data from users is crucial for objective prioritization. Rank and Likert scales are effective tools for this purpose.
- Rank Scales: Ask users to rank a list of features or ideas in order of importance. This provides a clear picture of what users value most. For example, a survey could ask users to rank potential new features from most to least important.
- Likert Scales: Use Likert scales to measure user attitudes towards specific ideas. These scales typically range from “Strongly Disagree” to “Strongly Agree.” For instance, you could ask, “How important is feature X to you?” with response options ranging from “Not at all important” to “Extremely important.”
Helio Example
Once all ratings from the user surveys have been attributed to each opportunity, and your business stakeholders and tech decision have a chance to give their ratings for each idea, that Opportunity Index produces a ranked list of ideas for your team to pursue.
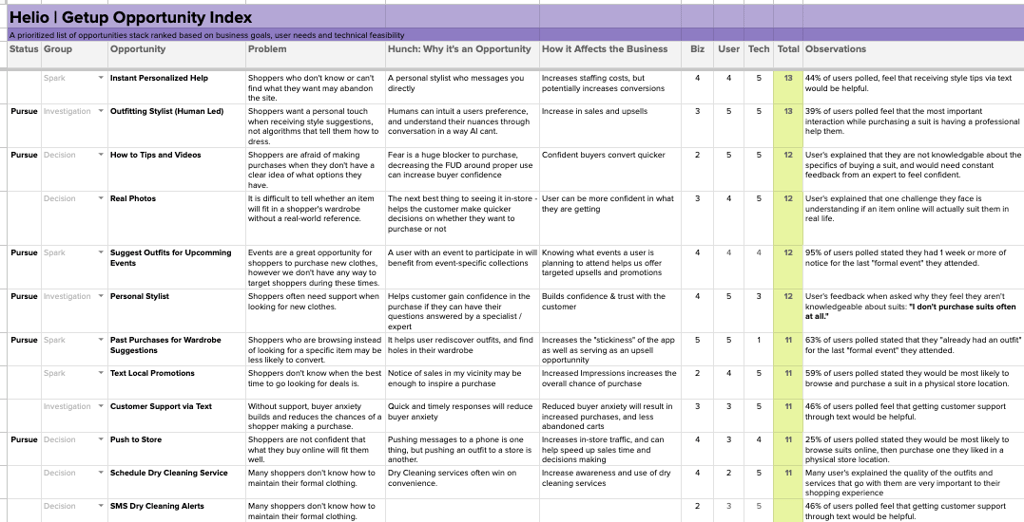
The final total out of 15 is evaluated for each opportunity, with the highest-ranking opportunities representing a combination of importance to the business and users and simplicity to build from a technical standpoint.
This opportunity ranking technique produced a highly detailed ranking of each idea that Advent had on the table for their e-commerce MVP, using data-backed decision-making and input from multiple teams across Advent’s org.
View the Advent Opportunity Index
By evaluating ideas based on user impact and feasibility, employing effective prioritization techniques, and using rank and Likert scales to gather user feedback, you can make informed decisions that align your product development with user needs and business objectives. This structured approach to prioritization ensures that your product management workflow remains focused and efficient, leading to the development of features that truly resonate with your users.
5. Product Discovery
Product discovery is a critical phase in the product management workflow. This stage involves conducting thorough user research to validate assumptions and deeply understand user needs. Leveraging various research methods and tools, like Helio, can help you gather valuable insights that inform your product development process.
Conducting Thorough User Research to Validate Assumptions
Before you start building features, you must ensure that your user needs assumptions are accurate. Thorough user research helps you validate these assumptions and avoid costly mistakes.
- Start with Hypotheses: Formulate hypotheses about your users’ needs, preferences, and pain points. These hypotheses will guide your research.
- Diverse Research Methods: Use qualitative and quantitative research methods to get a holistic view of your users. This includes surveys, interviews, and usability tests.
- Iterative Approach: Conduct research iteratively. Start with broad questions to understand the general landscape, then narrow down your focus as you gather more data.
Using Surveys, Interviews, and Usability Tests
Different research methods provide different types of insights. Combining them ensures you cover all bases and get a comprehensive understanding of your users.
- Surveys: Surveys are great for gathering quantitative data from a large number of users. Use them to collect information about user demographics, preferences, and behaviors. Ensure your questions are clear and unbiased to get reliable data.
- Interviews: Conduct one-on-one interviews to dive deeper into specific user experiences and uncover insights that surveys might miss. Interviews allow you to ask follow-up questions and explore topics in detail.
- Usability Tests: Usability tests help you see how users interact with your product. By observing users as they complete tasks, you can identify usability issues and areas for improvement. This method provides direct insights into how user-friendly your product is.
Gathering Insights with Helio’s Tools
Helio offers a suite of tools that make it easier to gather and analyze user feedback. Here’s how you can leverage these tools during the product discovery phase.
- Surveys and Polls: Use Helio’s survey tools to create and distribute surveys to your target audience. Collect detailed responses about their needs, preferences, and pain points. Helio’s intuitive interface makes it easy to design surveys that get meaningful responses.
- User Testing: Conduct user tests through Helio to gather real-time feedback on your product’s usability. Helio provides a platform where you can set up tests, invite users, and collect their feedback efficiently.
- Data Analysis: Helio’s analytics tools help you make sense of the data you collect. Use these tools to identify patterns, trends, and key insights that inform your product decisions. This analytical approach ensures you’re making data-driven decisions that align with user needs.
Helio Example
We helped a beauty brand, called SkinSavvy for the purposes of this study, determine the user interest and early product opportunities for a customer loyalty program they wanted to implement for their business.
Leveraging Helio, we surveyed their target audience, beauty consumers, in the US in order to understand their current experiences with customer loyalty programs as well as willingness to engage:
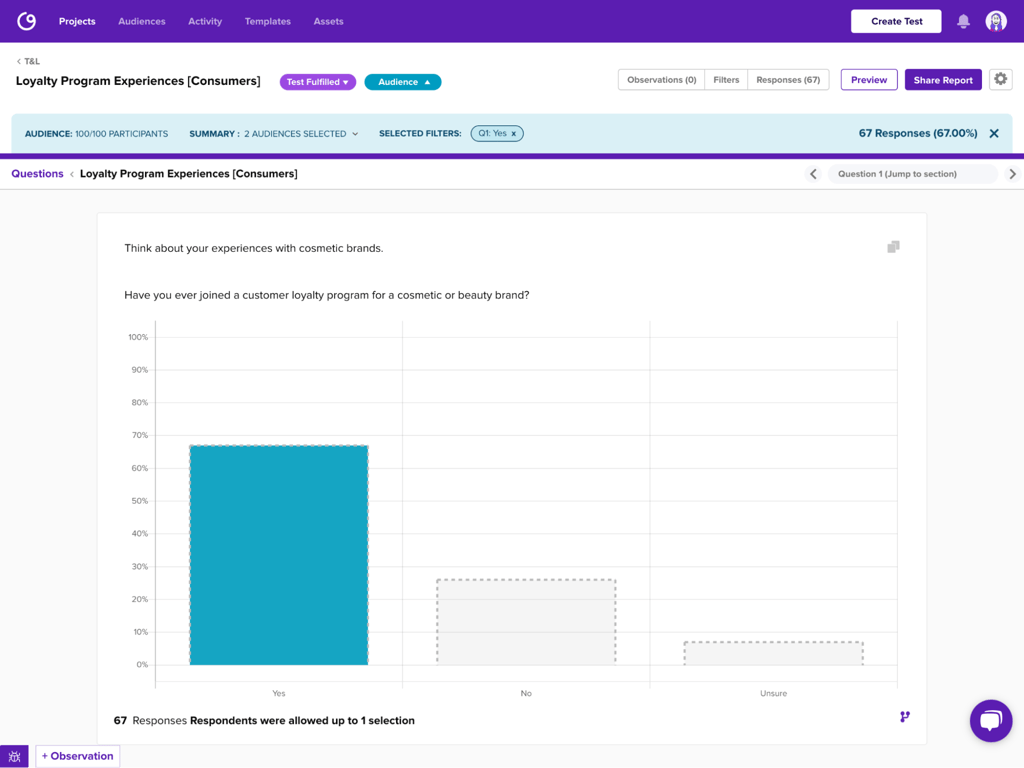
We found that most of their consumers (67%) have joined a loyalty program before, though the majority (36%) only take advantage of these offers occasionally.
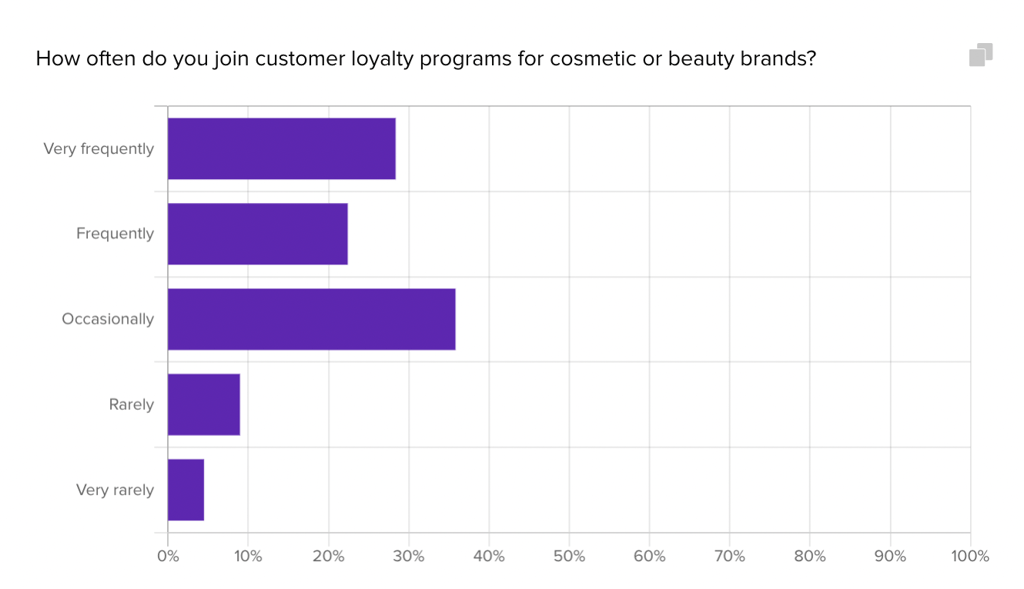
“I usually do sign up if they offer a perk quickly enough or with low entry cost (like free shipping, $5 off or an extra freebie). If they have really high thresholds (like spend $500 for little perks), I won’t sign up.”
– Helio Participants, Beauty Product Consumer (US)
Helio helped SkinSavvy understand that interest for a loyalty program is high, with most participants (50%) saying their interest level is a 10/10. However, participants admit that they don’t always sign up for these programs with new brands, so providing enticing perks and few barriers to entry will be key to building engagement with their new loyalty program.
View the Helio Example
By conducting thorough user research, utilizing surveys, interviews, and usability tests, and leveraging tools like Helio, you can ensure that your product discovery phase is robust and insightful. This approach helps you validate your assumptions, understand your users deeply, and build a product that truly meets their needs. Integrating these practices into your product management workflow sets the foundation for a user-centered product development process.
6. Design
Design is a crucial stage in the product management workflow where you bring your ideas to life. It’s about developing solutions that address user requirements, prototyping them, and iterating based on user feedback. This user-centered approach ensures that your product is functional and delightful to use.
Developing Design Solutions That Address User Requirements
Creating effective design solutions starts with a deep understanding of user needs and requirements. Here’s how to ensure your designs hit the mark:
- User-Centered Design Principles: Always put the user at the center of your design process. Use insights from your research to guide your design decisions.
- Collaborate with Stakeholders: Engage with cross-functional teams, including product managers, developers, and marketers, to ensure that your designs align with business goals and technical feasibility.
- Sketch and Wireframe: Start with low-fidelity sketches and wireframes to quickly visualize ideas and get early feedback. This helps in identifying potential issues before investing time in high-fidelity designs.
Prototyping and User Testing
Prototyping and user testing are essential steps to validate your designs and ensure they meet user needs. Here’s how to approach these steps:
- Create Interactive Prototypes: Use tools like Figma, Sketch, or Adobe XD to create interactive prototypes. These prototypes should simulate the user experience and allow users to interact with the product as they would with the final version.
- Conduct Usability Tests: Test your prototypes with real users to gather feedback on usability and functionality. Observe how users interact with the prototype and note any issues or areas of confusion.
- Iterate Quickly: Based on the feedback from usability tests, make necessary adjustments to your designs. Quick iterations help you refine the product efficiently and ensure it aligns with user expectations.
Iterating Designs Based on User Feedback
Iteration is a continuous process that involves refining your designs based on user feedback. Here’s how to do it effectively:
- Gather Feedback Continuously: Use tools like Helio to collect ongoing user feedback. This can be through surveys, direct comments, or usability test results.
- Analyze and Prioritize Feedback: Not all feedback will be equally valuable. Analyze the feedback to identify common themes and prioritize changes that will significantly impact user satisfaction.
- Implement Changes: Make the necessary design adjustments based on the prioritized feedback. Ensure that each iteration moves the product closer to meeting user needs and business goals.
- Repeat the Cycle: Design is an iterative process. After implementing changes, test the designs again with users and gather more feedback. Repeat this cycle until your design is polished and fully meets user requirements.
Helio Example
We helped Indiana University improve the experience of their degree index page, where visitors search for the degree they want to pursue.
One of the team’s ideas was to prioritize how features are displayed on the degree listing page rather than maintaining the current alphabetical order.
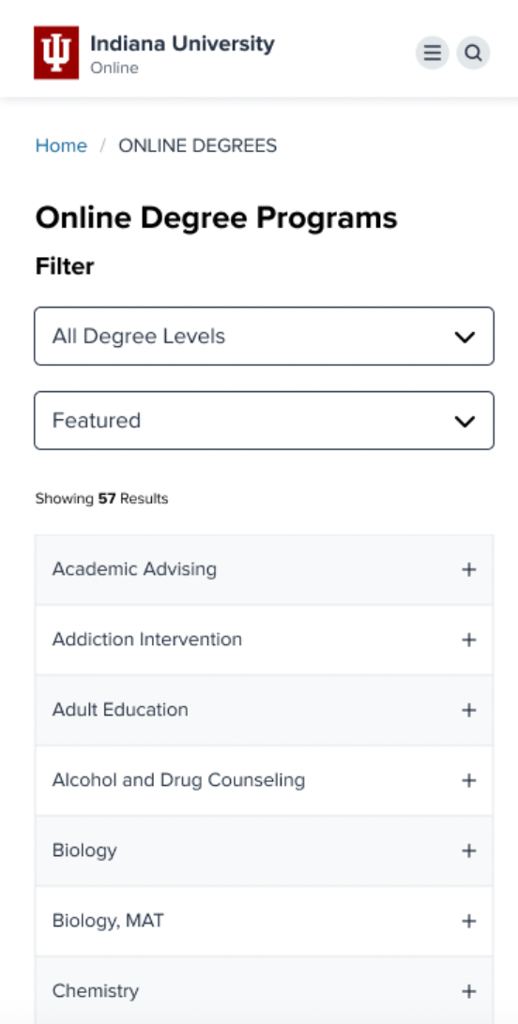
The Indiana University team’s goal was to encourage the exploration of different degrees on the index page and increase engagement with 10 of their key school programs.
One hundred participants from IU’s audience of undergrad and grad students interacted with each version of the page, answering the same questions to compare their responses across variations. Once the data had been collected, the responses were copied into a data comparison framework for quick design evaluation.
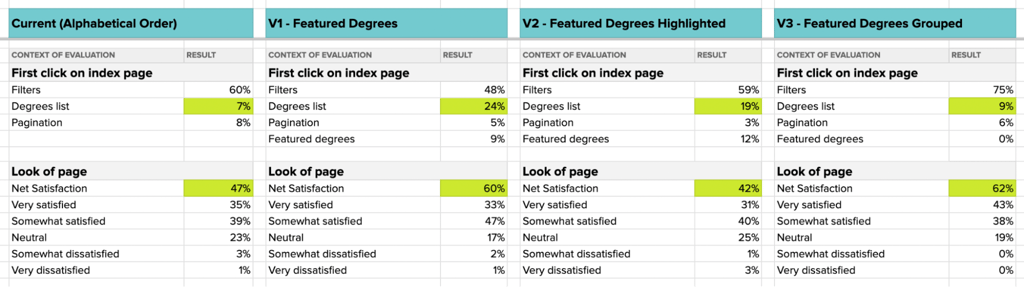
Once the data had been collected and loaded into the comparison framework, the picture of how users reacted to each different version became more clear:
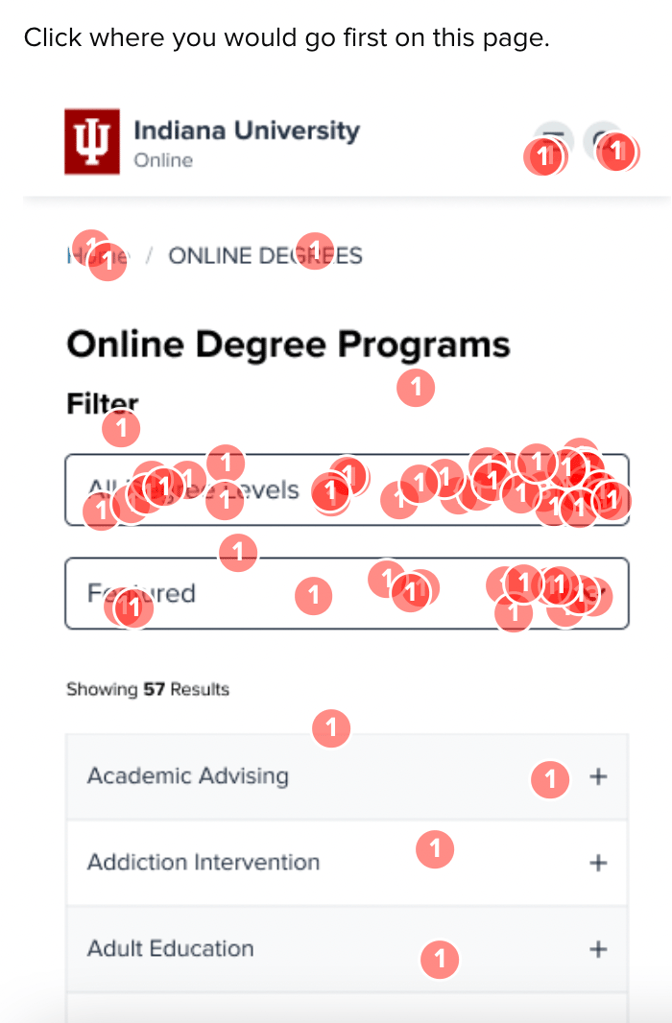
In the current page version, with the degrees in alphabetical order, only 7% of participants engaged with the list, instead opting to go directly to the filters and search bar.
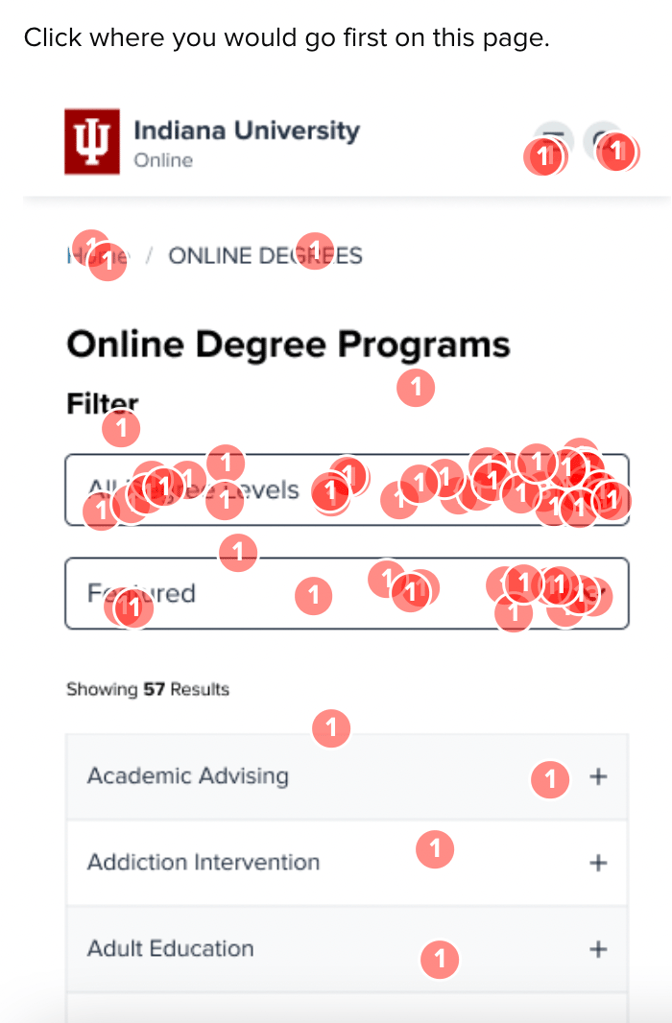
When the degrees list was reorganized to show featured degrees up top, engagement with the list jumped to 19-24%, showing a desire to interact with the page rather than resort to the search features.
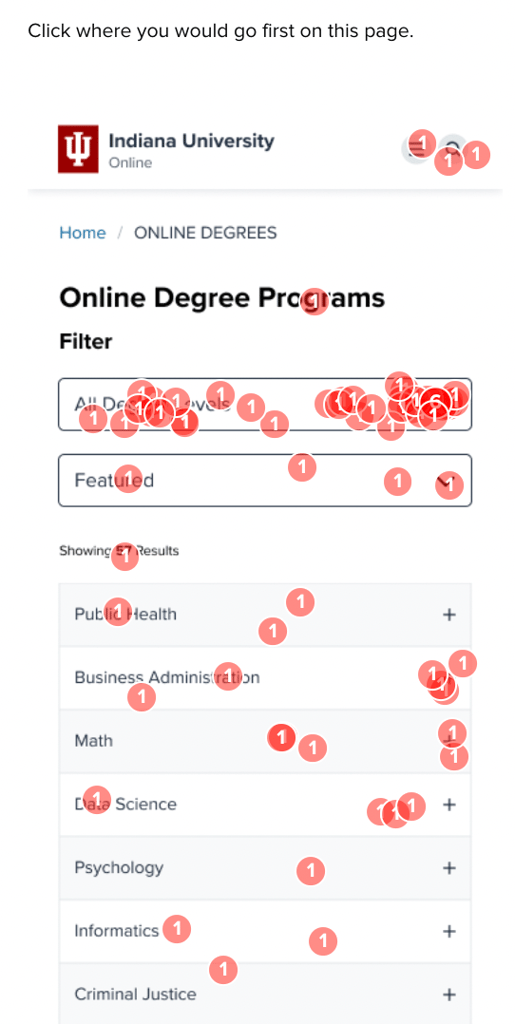
The versions where we tried out highlights in the degrees list both reduced satisfaction with the look of the page (V2), and reduced engagement on the list when hidden under a dropdown (V3). The team decided to move forward simply with the idea of re-ordering the degree list without trying to introduce visual highlights.

Once the data had been collected and loaded into the comparison framework, the picture of how users reacted to each different version became more clear:
In the current page version, with the degrees in alphabetical order, only 7% of participants engaged with the list, instead opting to go directly to the filters and search bar.
When the degrees list was reorganized to show featured degrees up top, engagement with the list jumped to 19-24%, showing a desire to interact with the page rather than resort to the search features.
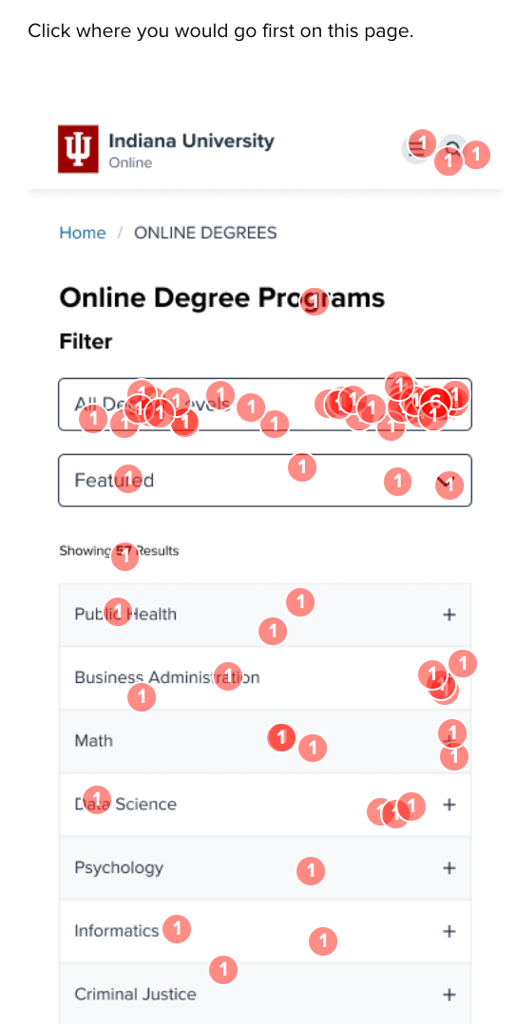
The versions where we tried out highlights in the degrees list both reduced satisfaction with the look of the page (V2), and reduced engagement on the list when hidden under a dropdown (V3). The team decided to move forward simply with the idea of re-ordering the degree list without trying to introduce visual highlights.

Experimentation like this allows your designs to reach the highest rates of satisfaction and user engagement through user-validated opportunities.
View the Idea Validation Case Study
You ensure your product is user-centered and well-designed by developing design solutions that address user requirements, creating interactive prototypes, conducting thorough user testing, and iterating based on feedback. Integrating these practices into your product management workflow helps you build products that function well and provide an excellent user experience. This user-focused approach is key to creating successful products that resonate with your audience.
7. Development
The development phase in the product management workflow is where your user-tested designs come to life. This stage involves translating designs into a working product, maintaining continuous feedback loops, and ensuring smooth collaboration among cross-functional teams.
Translating User-Tested Designs into Development
Once your designs have been validated through user testing, it’s time to hand them off to the development team. Here’s how to ensure a smooth transition:
- Detailed Documentation: Provide developers with comprehensive documentation that includes design specifications, user flows, and any insights from user testing. This ensures everyone is on the same page.
- Design Handoff Tools: Use tools like Zeplin or Figma to facilitate the design handoff. These tools allow designers to seamlessly share assets, style guides and interact with developers.
- Clear Communication: Maintain open lines of communication between designers and developers. Regular check-ins and meetings help address any questions or issues during development.
Continuous Feedback Loops During Development
Establish continuous feedback loops during development to ensure the product stays true to user needs. This iterative approach helps catch and resolve issues early.
- Regular User Testing: Conduct usability tests on early builds or prototypes. This can help identify usability issues that might not have been apparent in the design phase.
- Internal Testing and Reviews: Set up regular internal testing sessions where team members from different departments can use the product and provide feedback.
- Agile Methodologies: Implement agile development practices such as sprints and stand-up meetings. This encourages frequent testing and iteration, allowing the team to adapt quickly to feedback.
Collaborating with Cross-Functional Teams
Successful product development relies on effective collaboration across various teams. Here’s how to foster a collaborative environment:
- Cross-Functional Meetings: Hold regular meetings with representatives from design, development, marketing, and other relevant departments. These meetings ensure everyone is aligned and aware of the project’s progress.
- Shared Goals and KPIs: Establish shared goals and key performance indicators (KPIs) for the project. This alignment helps keep all teams focused on the same objectives.
- Collaboration Tools: Use tools like Jira, Trello, or Asana to manage tasks and track progress. These tools provide visibility into the project’s status and facilitate communication among team members.
Helio ExampleShared data is the foundation for a unified vision for the product. When everyone, from designers to developers, looks at the same user feedback, crafting a cohesive product narrative that seamlessly blends form and function becomes easier. This unity benefits the product and team morale, as it fosters a sense of shared achievement.
To create this unity, we used Helio testing for the ad management platform Advent to establish design principles for their landing pages based on user data:

Each design principle is accompanied by an explanation of the data that led to that decision. For Advent’s second design principle, the team established that the videos tested out on different versions of their landing page would be necessary for visitor engagement:
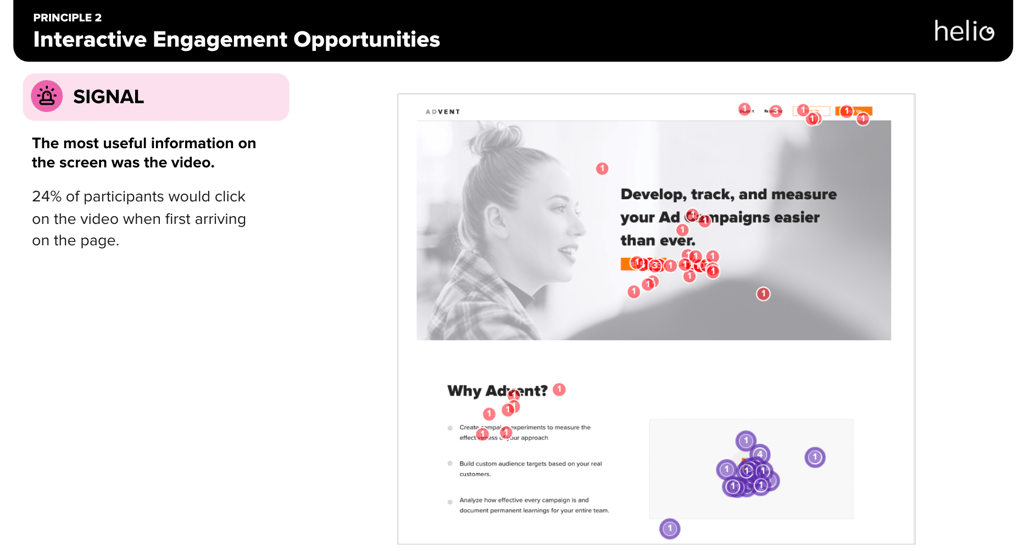
Almost a quarter of participants started on the landing page by clicking the video, a very high amount of engagement for an action below the fold. Typically, any actions attracting more than 10% of first clicks are high traction points, so this 24% engagement is proof that the video is desired on the landing page.
By translating user-tested designs into development with detailed documentation and clear communication, establishing continuous feedback loops, and fostering collaboration among cross-functional teams, you can ensure that your product development process is efficient and user-centered. This approach helps build a product that meets user needs and creates a cohesive workflow that integrates smoothly into your overall product management workflow.
8. User Testing
User testing is a critical stage in the product management workflow. It’s your opportunity to ensure that your product meets user expectations and works as intended before its official launch. By conducting thorough user testing, using effective methods and tools, and analyzing feedback to identify issues, you can significantly enhance the quality and success of your product.
Importance of Thorough User Testing Before Launch
Thorough user testing is essential for several reasons:
- Catch Issues Early: User testing helps identify usability issues, bugs, and other problems that might not be obvious during development. Catching these issues early prevents costly fixes later.
- Validate User Experience: Ensure that the product provides a smooth and enjoyable user experience. Testing with real users allows you to see how they interact with the product and whether it meets their needs.
- Increase Confidence: Thorough testing builds confidence among your team and stakeholders that the product is ready for launch. It minimizes the risk of negative user feedback post-launch.
Methods and Tools for Effective User Testing
There are various methods and tools you can use to conduct effective user testing:
- Usability Testing: Conduct usability tests to observe users interacting with your product. Note any difficulties they encounter and areas where they hesitate or make errors.
- Moderated Usability Testing: A researcher guides the user through tasks, asking questions and probing for deeper insights. This method is excellent for understanding the reasons behind user actions.
- Unmoderated Usability Testing: Users complete tasks independently, without a moderator. This method is scalable and can provide a large volume of feedback quickly.
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Use surveys to gather quantitative data on user satisfaction, ease of use, and other relevant metrics. Tools like Google Forms, SurveyMonkey, and Typeform are useful.
- A/B Testing: Compare two versions of a feature or interface to see which performs better. This method helps in making data-driven decisions about design changes.
- Beta Testing: Before the official launch, release the product to a select group of users. Collect feedback on their experiences and make any necessary adjustments.
Analyzing User Feedback to Identify Issues
Once you’ve gathered feedback from user testing, it’s crucial to analyze it effectively:
- Categorize Feedback: Organize feedback into usability issues, feature requests, and bugs. This helps prioritize what needs to be addressed first.
- Identify Patterns: Look for common themes and patterns in the feedback. Issues mentioned by multiple users should be prioritized.
- Prioritize Fixes: Not all feedback will be equally important. Prioritize fixes based on their impact on user experience and the feasibility of implementing them.
- Iterate and Test Again: Make the necessary changes and test the product to ensure the issues have been resolved. User testing is an iterative process until the product is ready for launch.
Helio Example
We track interaction success of key actions in a design using the Interaction Matrix framework, a method for measuring usability through remote user testing.
In this case, we put the dashboard of a theoretical online banking platform called Banko to the test. Banko’s dashboard was tested in the same way, with the baseline data being logged and then analyzed to determine how they can be improved:
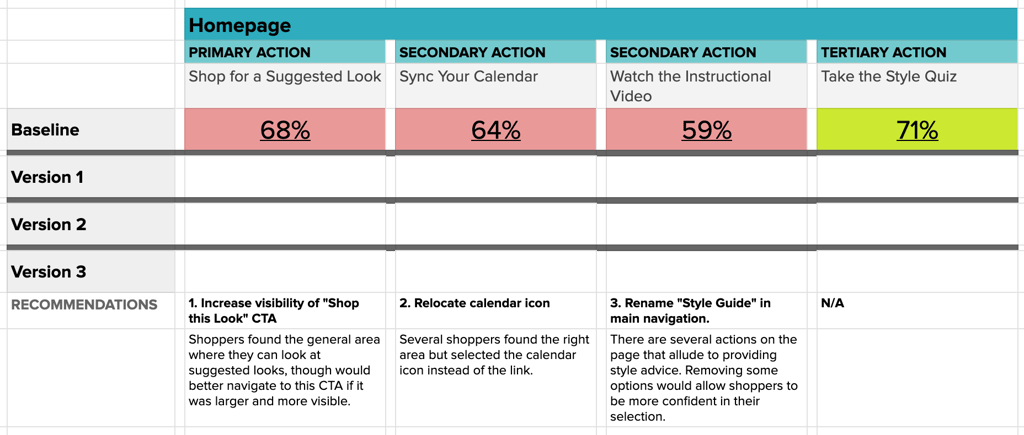
Primary actions such as a viewing account balance or recent transactions are expected to have over 80% success on participants’ first click. Secondary actions, like accessing credit score information, are expected to land above 70%, and all other tertiary actions should show at least 55% successful interactions on first click.
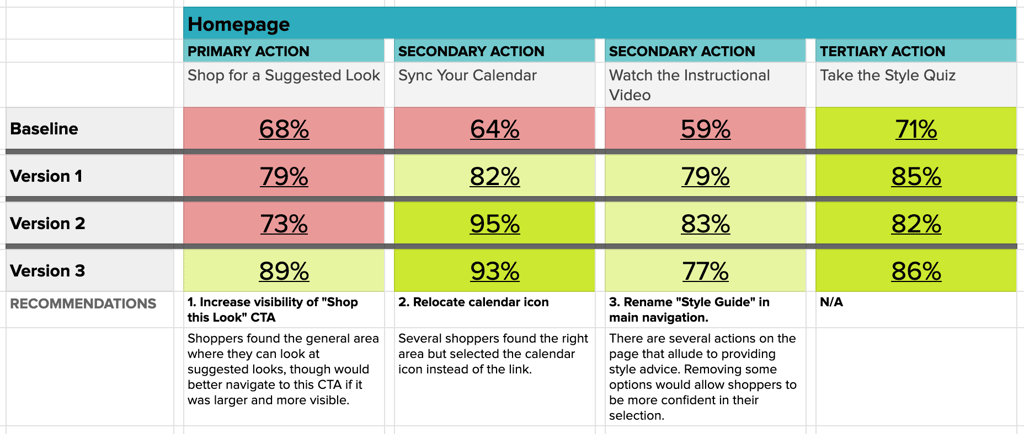
As the problem actions in each round of testing are revealed, new designs are created to resolve the issue and work towards a row of all green interactions in the matrix.
View the Interaction Matrix Guide
By conducting thorough user testing, using various effective methods and tools, and analyzing feedback to identify and address issues, you can ensure that your product meets user expectations and performs well in the real world. This stage is crucial for delivering a polished, user-friendly product that aligns with your product management workflow and achieves your business goals.
9. Launch
The launch phase in the product management workflow is where all your hard work comes together. A successful launch is user-centered, gathers valuable feedback, and measures product performance and user satisfaction. Here’s how to ensure your product launch goes smoothly and continues to meet user needs.
Preparing for a User-Centered Launch
A user-centered launch focuses on making sure your product is ready for your users and that they have a great experience from day one.
- Pre-Launch Testing: Conduct final rounds of user testing to ensure all major issues are resolved. This helps catch any last-minute bugs or usability problems.
- Clear Communication: Communicate clearly with your users about what to expect. Use emails, social media, and in-app notifications to inform them about new features, improvements, and how to use them.
- Support Readiness: Ensure your support team is ready to handle any queries or issues. Provide them with detailed documentation and training on the new features and changes.
- Marketing and PR: Coordinate with your marketing and PR teams to create buzz around the launch. Use blog posts, press releases, and social media campaigns to reach your target audience.
Collecting and Analyzing User Feedback Post-Launch
Post-launch feedback is crucial for understanding how users perceive your product and identifying areas for improvement.
- User Surveys: Send out surveys to users to gather their initial impressions and any issues they might have encountered. Ask specific questions about their experience with new features.
- Feedback Tools: Use tools like Helio to collect ongoing user feedback. Set up in-app feedback prompts to make it easy for users to share their thoughts.
- Monitor Social Media and Reviews: Keep an eye on social media platforms, app stores, and review sites. Users often share their experiences and issues publicly, providing valuable insights.
- Customer Support Interactions: Analyze customer support tickets and interactions to identify common problems and areas for improvement.
Measuring Product Performance and User Satisfaction
Measuring how well your product performs and how satisfied users are is essential for ongoing success.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Define and track KPIs that align with your business goals. This could include metrics like user engagement, retention, and conversion rates.
- User Satisfaction Scores: Use metrics like Net Promoter Score (NPS) and Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT) to gauge user satisfaction with your product.
- Usage Analytics: Analyze usage data to see how users interact with your product. Look for patterns that indicate which features are popular and which might need improvement.
- Feedback Analysis: Review user feedback regularly to identify trends and prioritize areas for development. This ongoing process ensures that you continue to meet user needs and expectations.
Helio Example
For a final assessment, Helio’s Gravity Score Testing offers a holistic analysis of the user experience based on feedback. Similar to SUS testing, participants respond to a series of evaluative questions after interacting with designs. The resulting data feeds into a formula to generate a single data point representing the UX score of the page.
After participants complete the most important actions on the page, a series of 10 Likert scale questions begins.
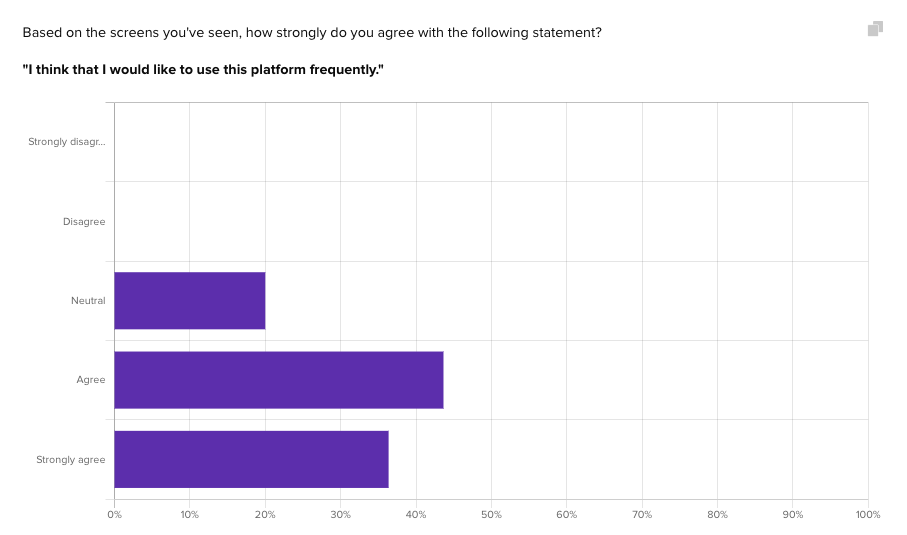
These questions alternate between positive and negative inquiries to gauge the success of the product in eliciting positive emotions and avoiding user pain points. The data from these questions undergoes the same formula as the tried and tested SUS method.
The Gravity Score method produces a single data point for comparison in future iterations, such as the 66 achieved in the first round of testing on the Audience page.
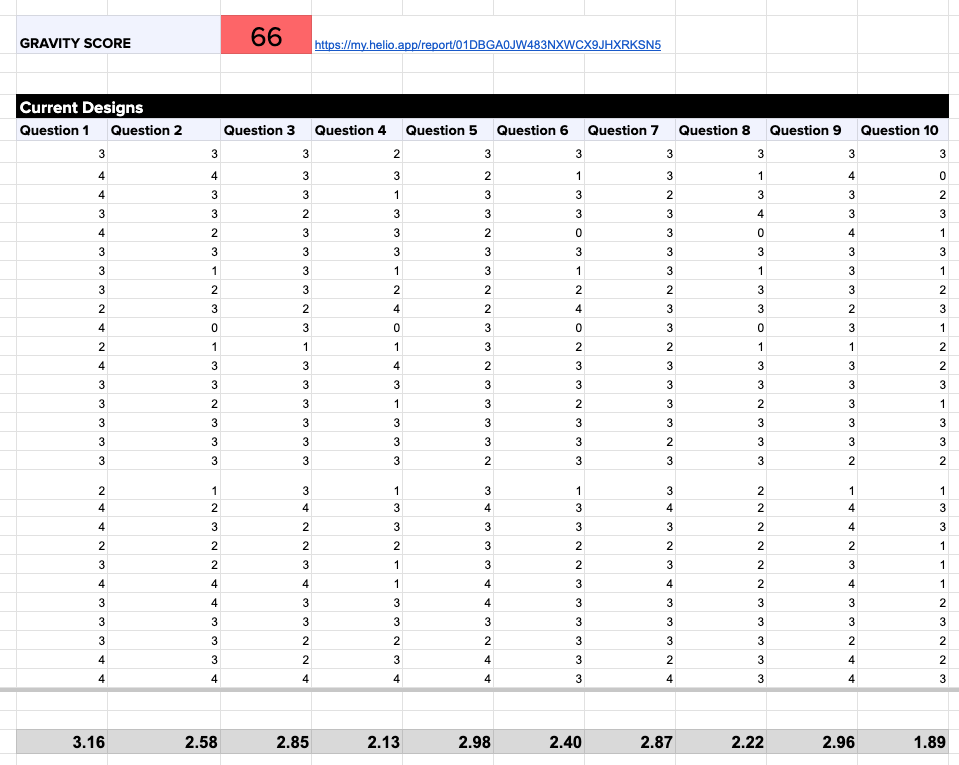
On average, a Helio Gravity Score is 68, indicating that the first iteration of this page did not meet the team’s or participants’ expectations. To see how the team built on these data findings, check out the Iteration phase of product management below!
By preparing for a user-centered launch, collecting and analyzing user feedback post-launch, and measuring product performance and user satisfaction, you can ensure that your product meets initial expectations and continues to evolve and improve. This approach is essential for maintaining a successful product management workflow and achieving long-term success.
10. Feedback Gathering & Analysis
Feedback gathering and analysis are essential components of the product management workflow. They help you understand user experiences, identify improvement areas, and measure your product’s success. Here’s how to set up effective feedback channels, analyze the feedback, and use analytics to drive your product forward.
Setting Up Channels for Continuous User Feedback
To gather continuous feedback, you need to set up multiple channels where users can easily share their thoughts and experiences.
- In-App Feedback: Integrate feedback forms directly into your app or website. This allows users to share their experiences in real-time without leaving your product.
- Surveys: Regularly send out surveys to your users. Use tools like Helio, SurveyMonkey, or Google Forms to create and distribute surveys that ask targeted questions about user satisfaction and feature preferences.
- Social Media Monitoring: Monitor social media platforms for mentions of your product. Users often share their opinions and feedback on platforms like Twitter, Facebook, and LinkedIn.
- Customer Support Interactions: Collect feedback through customer support channels. Encourage your support team to ask users for feedback after resolving their issues.
- User Communities: Create and engage with user communities, such as forums or social media groups. These communities can provide a wealth of feedback and suggestions.
Analyzing Feedback to Identify Trends and Areas for Improvement
Once you have collected feedback, it’s important to analyze it to identify common trends and pinpoint areas that need improvement.
- Categorize Feedback: Organize feedback into usability issues, feature requests, and bug reports. This helps manage and prioritize feedback efficiently.
- Identify Patterns: Look for recurring themes and patterns in the feedback. Are multiple users experiencing the same issue? Are there common requests for new features? These patterns can guide your product development priorities.
- Sentiment Analysis: Use sentiment analysis tools to gauge the overall tone of user feedback. This can help you understand how users feel about your product and identify areas where they might be frustrated or dissatisfied.
- Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis: Combine qualitative feedback (comments and suggestions) with quantitative data (survey ratings and usage metrics) to comprehensively understand user needs and preferences.
Using Analytics to Measure Success
Analytics provide valuable insights into how users interact with your product and its success in meeting their needs.
- Key Metrics: Define and track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as user engagement, retention rates, and customer satisfaction scores. These metrics help you measure your product’s success and identify areas for improvement.
- Usage Patterns: Analyze usage data to see how users navigate your product. Identify which features are most used and which ones are underutilized. This can inform decisions about where to focus development efforts.
- A/B Testing: Conduct A/B tests to compare different versions of features or interfaces. This helps in making data-driven decisions about which changes positively impact user experience.
- User Cohorts: Segment your users into cohorts based on their behavior or demographics. Analyze how different cohorts interact with your product to identify specific needs and tailor your product accordingly.
Helio Example
We helped the skincare company SkinSavvy conduct post-purchase testing on their new skincare mobile app, from booking an appointment, to receiving an in-person treatment, and using the app to earn loyalty rewards.
We organized a limited launch of their SkinSavvy’s app to skincare providers who already carry their products. Upon release of the app, we sent 5 of our Helio advocates to engage in secret shopping and uncover early pain points in the usage of their MVP.
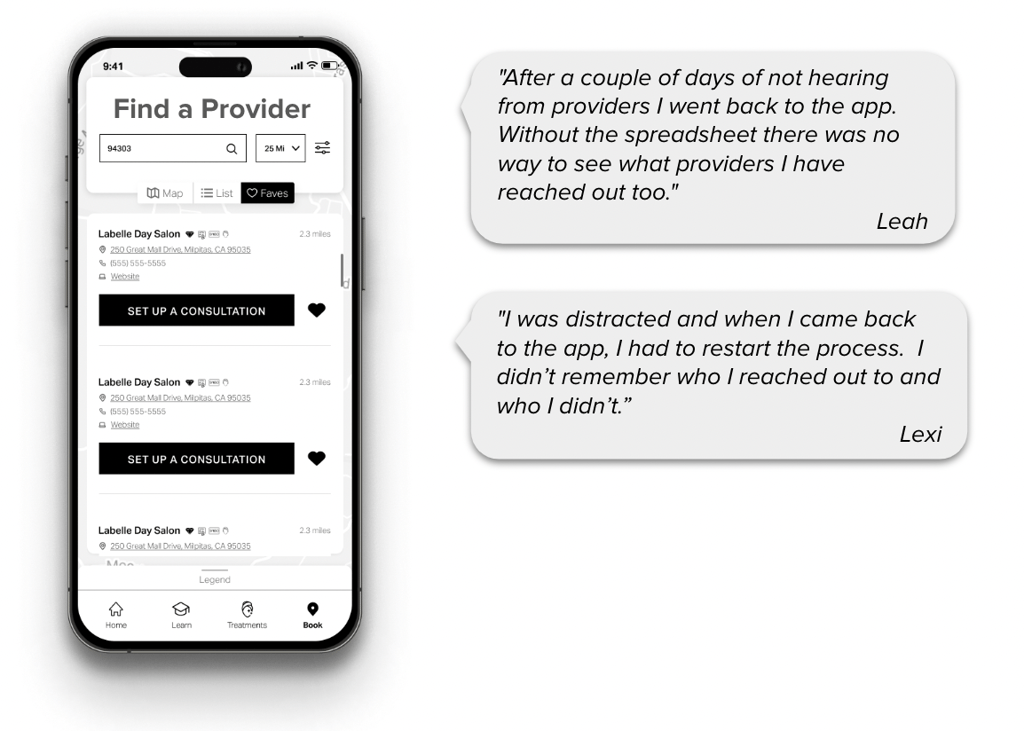
Our Helio advocates put the new SkinSavvy app to the test by scheduling appointments through the new platform, following through with in-person treatments, and observing interactions around the app between providers and customers.
After reaching out to 30 beauty providers each through the app, and following through with a treatment, Helio advocates conducted interviews with each participant to understand their user experiences:
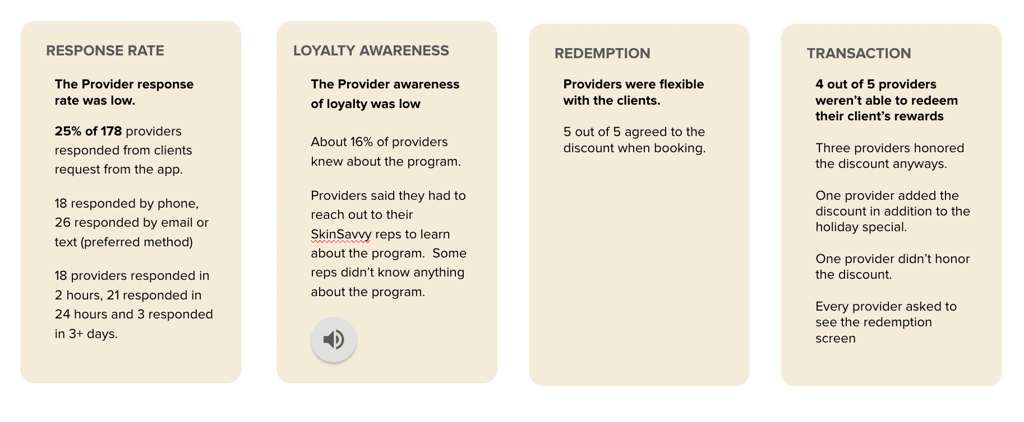
The most impactful insight in this ethnographic study came in the form of hard data, with only 25% of beauty providers contacted through the app actually providing a response.
Interviews with the participants also revealed that the process of completing customer transactions through the app was anything but smooth, with 4 out of 5 providers handling loyalty discounts outside of the platform after treatment.
The difficulty with SkinSavvy’s MVP release can be alleviated through consistent communication to their customer base. With pre-launch feedback like this, teams building products like SkinSavvy can elevate their user experience and provide a smoother decision making process for their consumers.
By setting up channels for continuous user feedback, analyzing feedback to identify trends and areas for improvement, and using analytics to measure success, you can ensure that your product remains user-centric and continuously improves. This approach integrates seamlessly into your product management workflow, driving ongoing enhancements and ensuring that your product meets and exceeds user expectations.
11. Iteration
Iteration is a crucial part of the product management workflow, enabling you to continuously refine and improve your product. By making data-driven decisions, prioritizing changes based on user needs and feedback, and planning and executing updates quickly, you ensure your product evolves in line with user expectations.
Making Data-Driven Decisions for Product Iterations
To make informed decisions about product iterations, rely on data rather than intuition. Here’s how to do it:
- Collect and Analyze Data: Gather data from various sources, including user feedback, analytics, and usability tests. Use tools like Helio to streamline data collection and analysis.
- Identify Key Metrics: Focus on key performance indicators (KPIs) that reflect your product’s success. Metrics such as user engagement, retention, and conversion rates provide valuable insights into how well your product meets user needs.
- Data-Driven Hypotheses: Develop hypotheses based on your data. For example, if analytics show a drop-off at a particular step in the user journey, hypothesize why this is happening and test potential solutions.
Prioritizing Changes Based on User Needs and Feedback
Not all feedback will be equally important. To ensure your iterations have the maximum impact, prioritize changes based on user needs and feedback.
- Categorize Feedback: Organize user feedback into usability issues, feature requests, and bugs. This helps you see the most common and critical areas needing attention.
- Impact vs. Effort Matrix: Prioritized changes by using an impact vs. effort matrix. Focus on high-impact, low-effort changes first to quickly enhance the user experience.
- User-Centric Prioritization: Always prioritize changes that address user needs and pain points directly. Use surveys, interviews, and usability test feedback to guide your prioritization.
Planning and Executing Updates Quickly
Once you’ve identified and prioritized changes, planning and executing updates efficiently is important. Here’s how to keep the iteration process smooth and effective:
- Agile Methodology: Adopt agile practices to facilitate rapid iterations. Break down changes into manageable tasks and plan them in short sprints. This allows for quick adjustments based on feedback.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Ensure close collaboration between designers, developers, and other stakeholders. Regular stand-up meetings and progress reviews help keep everyone aligned and the iteration process on track.
- User Testing of Iterations: Conduct user tests to validate the updates after implementing changes. This ensures that the iterations solve the identified issues effectively and meet user expectations.
- Release Management: Plan releases carefully to minimize disruption. Use feature flags to roll out changes gradually and gather user feedback before a full-scale launch.
Helio Example
Successful product management includes testing changes to your designs over time. The Gravity Score method discussed in the Launch phase is a very popular tool for teams to use in order to measure overall usability of their site across design iterations.
For instance, our testing on the first iteration of the Advent audience targeting page produced a sub-optimal Gravity Score, two points below an average score of 68:

Notably, the reactions to questions 8 and 10 were particularly detrimental to the overall score, indicating widespread agreement among participants that the design feels cumbersome and requires significant upfront learning to use.
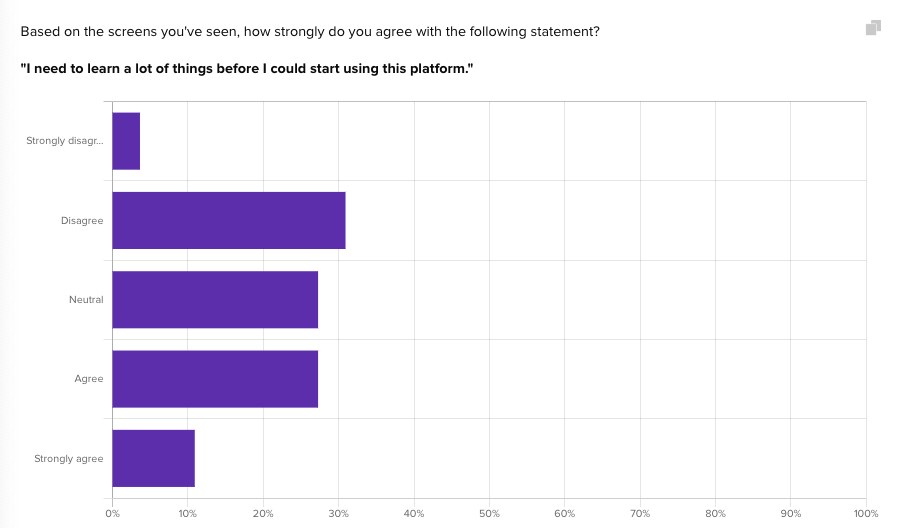
Over the following week, changes were made to Advent’s Audience page design to increase fidelity and address these issues, followed by another Gravity Score test.
The updated prototype received a new score of 69, affirming the team’s direction with the Audience page and allowing them to proceed confidently toward the final iteration.
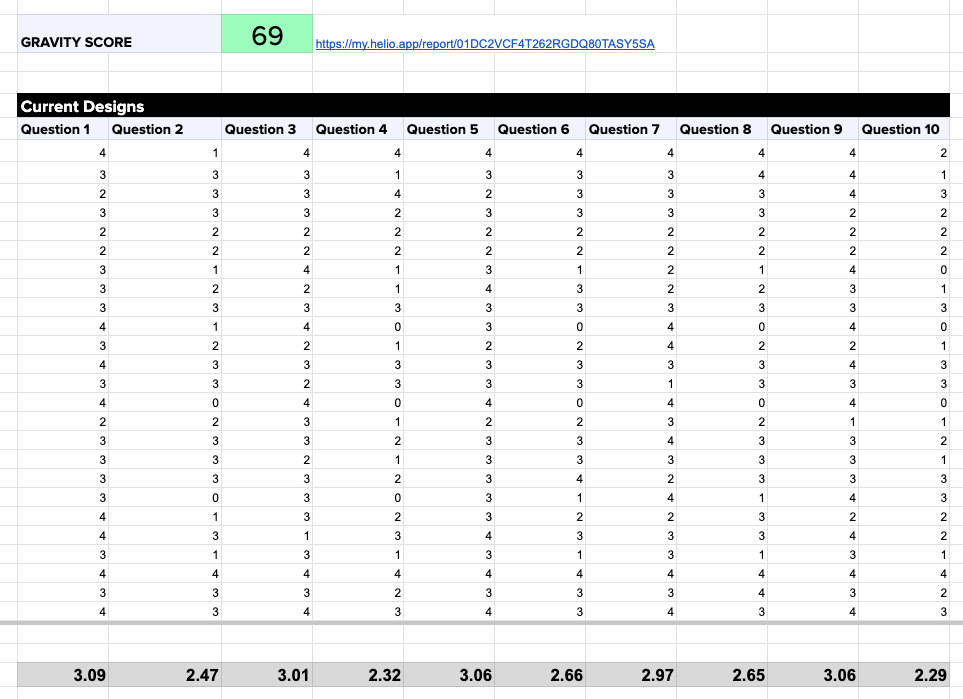
With the wireframe layout finalized, Advent completed the Audience page design in full visual fidelity within the next week and conducted another test to validate their decisions.
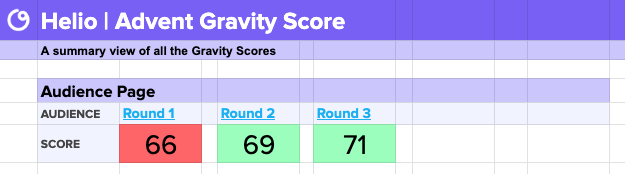
With a steady increase in the Gravity Score up to 71, the Advent team concluded the Audience page designs and confidently presented them to stakeholders, supported by user data.
By making data-driven decisions for product iterations, prioritizing changes based on user needs and feedback, and planning and executing updates quickly, you create a product that continually improves and remains aligned with user expectations. This iterative approach is integral to a successful product management workflow, ensuring that your product stays relevant and valuable to your users.
Best Practices for Conducting User Research
Conducting effective user research is key to a successful product management workflow. Engaging with users regularly, asking the right questions, avoiding bias, and using insights to drive decisions ensure your product development is user-centric and data-driven.
Engaging with Users Regularly
Regular engagement with your users keeps you attuned to their needs and preferences. Use various channels like surveys, interviews, and feedback forms to maintain an ongoing dialogue with your users. Tools like Helio can facilitate this process by providing easy-to-use platforms for gathering and analyzing user feedback.
Asking the Right Questions
The quality of your user research depends on the questions you ask. Focus on open-ended questions that encourage detailed responses, and be specific about the aspects of the product you want feedback on. For example, instead of asking, “Do you like this feature?” ask, “How does this feature help you achieve your goals?” This approach yields more actionable insights.
Avoiding Bias in User Research
To get genuine feedback, it’s crucial to avoid bias in your research. Ensure your questions are neutral and avoid leading the user towards a particular answer. Diversify your user base to get a wide range of perspectives, and be open to feedback that challenges your assumptions.
Using Insights to Drive Decisions
The ultimate goal of user research is to inform your product decisions. Regularly review and analyze the feedback you collect, and use it to guide your product development. Prioritize changes based on user needs and the potential impact on user satisfaction. By integrating these insights into your product management workflow, you ensure that your product evolves in line with user expectations and delivers real value.
By following these best practices for conducting user research, you create a robust, user-centered product management workflow. Engaging with users regularly, asking insightful questions, avoiding research bias, and using data to drive decisions are all essential steps to building products that truly resonate with your audience. This approach enhances user satisfaction and ensures your product’s long-term success in the market.
Product Management Workflow FAQ
A product management workflow encompasses all the stages of bringing a product to market. It includes steps like vision and strategy, road mapping, idea management, prioritization, product discovery, design, development, testing, launch, feedback gathering, and iteration. This structured approach helps teams stay organized, prioritize tasks, and ensure that every aspect of the product development process is covered.
User research is crucial because it provides insights for making informed decisions and ensures the product aligns with user needs and expectations. It helps understand user behaviors, preferences, and pain points, reducing risks and increasing the likelihood of product success. Continuous user feedback and data-driven decisions lead to a product that meets business goals and delights users.
To collect and organize ideas, create multiple channels for idea submission, such as email, dedicated forms, or feedback tools. Categorize and tag ideas based on themes or features, and hold regular review meetings to discuss new ideas. Engaging users in the idea submission process through surveys and easy-to-use portals, and using tools like Helio for prioritization, ensures a steady stream of valuable insights.
Techniques for prioritizing user needs include the MoSCoW method (categorizing ideas into must-have, should-have, could-have, and won’t-have), value vs. effort matrix (plotting ideas based on their value and effort required), and the Kano model (classifying features into basic needs, performance needs, and delighters). These methods help focus on essential features and prioritize changes that offer the most value to users.
Effective methods for user testing include usability testing (moderated and unmoderated), surveys and questionnaires, A/B testing, beta testing, and using eye-tracking and heatmaps. Tools like Helio, Google Forms, SurveyMonkey, and Typeform can facilitate these tests, helping gather quantitative and qualitative data to validate user experience and identify issues.
To measure product performance and user satisfaction, define and track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as user engagement, retention rates, and customer satisfaction scores. Use metrics like Net Promoter Score (NPS) and Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT) to gauge satisfaction. Analyze usage data to see how users interact with the product and regularly review feedback to identify trends and areas for improvement.
Best practices for conducting user research include engaging with users regularly through surveys, interviews, and feedback forms, asking the right questions that encourage detailed responses, avoiding bias by ensuring questions are neutral, and using a diverse user base. Use insights from this research to drive decisions, ensuring the product evolves in line with user expectations and delivers real value.