A Comprehensive Guide to Qualitative Research Approaches
Qualitative research offers a deep understanding of phenomena from the participants’ perspective. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the various aspects of qualitative research, from understanding its definition and importance to exploring different approaches and designing a research study. We will also delve into qualitative data analysis and how to make sense of the rich information gathered throughout the research process.
🔩 The Nuts and Bolts:
- Phenomenology Reveals Human Experiences: Phenomenology focuses on understanding individuals’ lived experiences, offering insights into the essence of phenomena through personal narratives.
- Ethnography Uncovers Cultural Contexts: Ethnography immerses researchers in specific cultural environments, providing a comprehensive view of societal behaviors and practices.
- Grounded Theory Develops New Theories: This approach generates theory from data, allowing researchers to build new conceptual frameworks closely tied to empirical evidence.
- Case Studies Offer Detailed Analysis: Focusing on specific instances within real-life contexts provides depth and detail that support broader research findings and theories.
- Narrative Research Highlights Personal Stories: This approach values the power of storytelling, emphasizing how personal narratives shape individuals’ perceptions and worldviews.
- Flexibility in Research Design: Qualitative research approaches are adaptable, enabling researchers to modify their strategies as new insights emerge, ensuring more comprehensive data collection.
- Inductive Reasoning Enhances Theory Formation: Qualitative methods often use inductive reasoning, where theories emerge organically from the data, providing grounded and practical insights.
Understanding Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is a fascinating and multifaceted approach that delves into the complexity of human experiences, behaviors, and social phenomena. It goes beyond mere numbers and statistics, valuing subjective interpretations and seeking to capture the rich context in which these experiences occur. Through interviews, observations, and textual analysis, qualitative research uncovers a wealth of information that contributes to our understanding of the world.
Qualitative research is vital in numerous fields, including sociology, psychology, anthropology, education, and healthcare. Its ability to provide rich and detailed insights into individuals’ perspectives and realities makes it an invaluable tool for researchers. By exploring the intricacies of human behavior and societal dynamics, qualitative research helps to uncover new knowledge, challenge existing theories, and inform practical interventions and policies.
Definition and Importance of Qualitative Research
At its core, qualitative research is an exploration of the human experience. It seeks to understand the intricate tapestry of thoughts, emotions, and actions that shape our lives. By focusing on the subjective interpretations of individuals, qualitative research provides a unique lens through which to view the world.
One of qualitative research’s critical strengths is its ability to capture the context in which experiences occur. It recognizes that our understanding of a phenomenon is deeply intertwined with the social and cultural environment in which it occurs. By immersing themselves in participants’ lives, researchers gain a holistic understanding of the complexities.
Unlike quantitative research, which relies on numerical data and statistical analysis, qualitative research employs various methods to collect data. Interviews allow researchers to engage in meaningful conversations with participants, delving into their thoughts, beliefs, and experiences. Observations allow one to witness behavior in its natural setting, uncovering nuances that may be missed through other methods. Textual analysis will enable researchers to explore written or recorded materials, such as diaries, letters, or speeches, to gain further insights.
Critical Characteristics of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research possesses several key characteristics that set it apart from other research methodologies:
- Subjectivity: Qualitative research recognizes that the researcher’s presence and interpretations significantly shape the research process and findings. It acknowledges that the researcher is not a detached observer but an active participant in the research journey.
- Flexibility: Unlike rigid research designs, qualitative research allows flexibility and adaptability. As new insights emerge, the research design can evolve, enabling researchers to explore unexpected avenues and delve deeper into the subject matter.
- Contextualization: Understanding the social and cultural context in which the phenomena are studied is fundamental to qualitative research. By recognizing the influence of the environment, qualitative researchers gain a more comprehensive understanding of the complexities at play.
- Inductive approach: Qualitative research takes an inductive approach, meaning that theories and hypotheses are generated based on the data collected rather than testing pre-existing hypotheses. This allows for a more open and exploratory exploration of the research topic.
- Rich data: Qualitative research gathers detailed and descriptive information through interviews, observations, and textual analysis. This rich data provides a nuanced understanding of the research topic, capturing the intricacies and subtleties that quantitative methods may miss.
These characteristics make qualitative research a powerful tool for uncovering the depth and complexity of human experiences. By embracing subjectivity, flexibility, and contextualization, qualitative researchers can shed light on the intricacies of our world and contribute to the advancement of knowledge.
Make your design decisions count.
Subscribe to Design Under Pressure. Get insights, UX metrics, and tools for bold, informed design.
We respect your inbox. Just insights. No fluff. Privacy Policy.
Different Approaches to Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is a valuable method for exploring and understanding the complexities of human experiences. It allows researchers to delve into the rich and intricate details of individuals’ lives, providing insights that quantitative research may need to capture. There are various approaches to qualitative research, each with its unique focus and methodology. Let’s explore some of these approaches in more detail.
Phenomenology
Phenomenology is a qualitative research approach that seeks to understand individuals’ lived experiences. It focuses on exploring the meaning that individuals attribute to their experiences and aims to uncover the essence and structure of the phenomenon being studied. Researchers engage in in-depth interviews with participants, encouraging them to share their thoughts, emotions, and perceptions. Through careful analysis of the participants’ descriptions, researchers identify commonalities and variations in individual experiences, shedding light on the complexities of human existence.
Ethnography
Ethnography is a qualitative research approach that involves immersing oneself in the cultural context of a specific group or community. Researchers spend extended periods in the field, observing and participating in social activities. By adopting a holistic perspective, ethnographers aim to portray the group and its dynamics authentically. They study the community’s behaviors, beliefs, and practices, seeking to understand the cultural meanings and social interactions that shape their lives. Ethnography allows researchers to gain a deep understanding of the complexities of human culture and society.
Grounded Theory
Grounded theory is an inductive approach to qualitative research that develops theories grounded in collected data. Researchers start the research process without preconceived theories or hypotheses, allowing themes and concepts to emerge from the data. Through constant comparative analysis, they iteratively refine the theory until reaching theoretical saturation – the point at which new data no longer generates new insights. Grounded Theory is a flexible and dynamic approach that allows researchers to directly uncover new perspectives and theories from the data, contributing to advancing knowledge in a particular field.
Case Study Research
Case study research is a qualitative approach focusing on in-depth investigations of a particular case or phenomenon within its real-life context. Researchers select a specific case, such as an individual, a group, an organization, or a community, and gather multiple data sources, such as interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts. By examining the case from various angles, researchers aim to provide a rich and holistic understanding of complex issues. Case studies often highlight the interplay between multiple factors and the case’s uniqueness, offering valuable insights to inform theory and practice.
Narrative Research
Narrative research is a qualitative approach that aims to explore and understand individuals’ stories and personal narratives. It recognizes the power of storytelling in shaping our understanding of the world. Researchers analyzed participants’ narratives, paying attention to underlying themes, plot structures, and meanings attributed to events and experiences. Narrative research allows researchers to capture the complexity and richness of individual experiences, uncovering the nuances and intricacies that may not be apparent through other research methods.
These are just a few examples of the diverse approaches to qualitative research. Each approach offers a unique lens through which researchers can explore and understand the complexities of human experiences. By employing these methods, researchers can gain valuable insights that contribute to our understanding of the world and inform theory, practice, and policy.
Designing a Qualitative Research Study
Conducting a qualitative research study requires careful planning and consideration. In this expanded HTML text, we will explore the various aspects of designing a qualitative research study.
Formulating a Research Question
Formulating a well-defined research question is crucial for conducting a successful qualitative study. The research question serves as a guide, directing the selection of appropriate research methods, data collection techniques, and data analysis strategies. It should be concise, relevant, and aligned with the research objectives.
When formulating a research question, it is essential to consider the scope of the study. Researchers must determine the specific aspects they wish to explore and the population or phenomenon they intend to study. This process involves reviewing existing literature, identifying gaps in knowledge, and clarifying the purpose of the research.
Selecting a Suitable Research Approach
Choosing the most appropriate research approach is critical in designing a qualitative study. The selection depends on the nature of the research question and the phenomena being studied. Researchers must carefully consider the strengths and limitations of each qualitative approach, as well as the resources available, including time, budget, and expertise.
Qualitative research approaches can vary widely, including phenomenology, grounded theory, ethnography, case study, and narrative inquiry, among others. Each approach offers unique perspectives and methods for data collection and analysis. In some cases, a combination of multiple approaches can provide a richer and more comprehensive understanding of the research topic.
Sampling and Data Collection
In qualitative research, sampling differs from quantitative research. Rather than aiming for statistical representativeness, qualitative researchers use purposive sampling. This approach involves intentionally selecting individuals who can provide rich and diverse information related to the research question.
Data collection methods in qualitative research are varied and flexible, allowing researchers to gather in-depth insights. Standard procedures include interviews, focus groups, observations, and document analysis. Each method has its own advantages and considerations, and researchers must carefully choose the most appropriate methods for their study.
When collecting data, researchers should establish rapport with participants, ensuring they feel comfortable and willing to share their experiences and perspectives. Ethical considerations are paramount, and researchers must obtain informed consent, protect the privacy and anonymity of participants, and ensure the confidentiality of collected data.
By carefully considering these aspects and incorporating them into the design of a qualitative research study, researchers can enhance the validity and reliability of their findings. The expanded HTML text provides a more comprehensive overview of the key considerations involved in designing a qualitative research study.
🚀 If you’re using Helio
Data collection methods in qualitative research are varied and flexible, allowing researchers to gather in-depth insights.
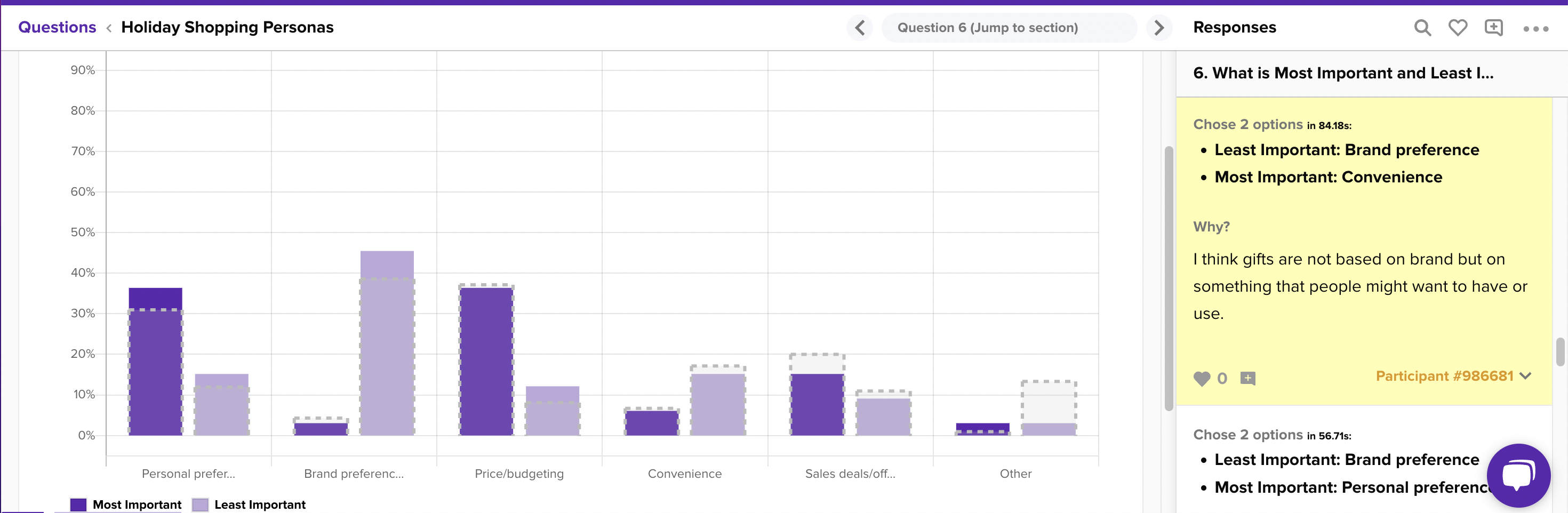
Each method has its own advantages and considerations, and researchers must carefully choose the most appropriate methods.
Analyzing Qualitative Data
Coding and Categorizing Data
Coding is the process of systematically organizing data into meaningful elements or categories. Researchers read and reread the data, applying labels or tags to capture recurring themes, concepts, or ideas. Through constant comparison and refinement, coding helps identify connections and patterns within the data. Computer-assisted qualitative data analysis software (CAQDAS) can be beneficial in managing large datasets.
Identifying Themes and Patterns
Identifying themes involves synthesizing codes to identify broader patterns or concepts that emerge from the data. Themes should be coherent and reflective of the participants’ perspectives and experiences. Researchers may use mind maps, concept maps, or diagrams to visualize the relationships between themes and sub-themes.
Interpreting and Making Sense of Data
Interpreting qualitative data requires researchers to engage in a reflective and reflexive process. They critically analyze the data, contextualize it within relevant theoretical frameworks, and consider alternative explanations. Drawing upon their own experiences, biases, and perspectives, researchers generate insights, construct arguments, and provide meaningful interpretations of the data gathered.
In conclusion, qualitative research offers a unique lens through which researchers can deepen their understanding of the complexities of human experiences and social phenomena. By embracing different approaches, conducting rigorous research designs, and employing robust data analysis techniques, qualitative researchers can bring valuable insights and contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of the world around us.
Qualitative Research Approaches FAQs
Qualitative research approaches involve detailed methodologies focusing on understanding human experiences and societal dynamics. They are essential because they provide depth and context, allowing researchers to grasp the nuances of complex issues.
Phenomenology helps researchers understand the subjective experiences of individuals, focusing on the meanings people attribute to their experiences. This approach is crucial for studies that delve deep into personal perceptions and emotional responses.
Ethnography is unique because it requires researchers to immerse themselves in the community or culture they are studying. This deep immersion allows for a comprehensive understanding of the social and cultural factors that influence behavior.
Grounded theory is popular because it allows theories to emerge from the data itself rather than testing existing hypotheses. This approach is beneficial in areas where little is known, as it builds theoretical frameworks directly from the research findings.
Yes, combining multiple qualitative research approaches can enrich a study by providing various perspectives on the same issue. This mixed-methods approach can enhance the depth and breadth of the findings.
Challenges include managing subjective biases, ensuring the reliability and validity of interpretations, and the intensive nature of data collection and analysis. Researchers must employ rigorous methods and maintain ethical standards throughout the study.
Findings from qualitative research can inform policy-making, improve educational and healthcare practices, and enhance business strategies by providing deep insights into human behavior and societal trends. They help decision-makers address real-world problems based on a comprehensive understanding of complex issues.