The Ultimate Guide to User Testing a Prototype
User testing is a crucial step in the development process of any prototype. It allows designers and developers to gather valuable feedback from real users, ensuring that the final product meets their needs and expectations. In this ultimate guide, we will explore the basics of user testing, how to prepare, create a user testing plan, conduct the test, and analyze the results. So, let’s dive in and uncover the secrets to successful user testing!
🔩 The Nuts and Bolts:
- Foundation for Informed Design Decisions
User testing prototype is crucial for collecting firsthand feedback ensuring products are developed in alignment with user needs and preferences. - Diverse User Participation Enhances Feedback Quality
Engaging a representative sample of users in prototype testing provides a broad perspective, identifying usability issues across different demographics. - Iterative Feedback Loop Refines Product Usability
Continuous user feedback during the prototype phase enables ongoing refinement, ensuring usability issues are addressed before product launch. - Direct Link Between User Satisfaction and Prototype Adjustments
Implementing changes based on user testing prototype feedback directly impacts user satisfaction, enhancing the overall product experience. - Quantitative and Qualitative Insights Drive Improvement
The user testing prototype gathers statistical and narrative feedback, offering a comprehensive understanding of user experience challenges. - Testing Environment Influences Feedback Accuracy
Creating a comfortable setting for prototype testing encourages honest, detailed user feedback, revealing critical insights for product development. - Feedback Implementation Validates Design Choices
Adjusting prototypes based on user testing validates design decisions with empirical evidence, increasing the likelihood of product success.
Understanding the Basics of User Testing
User testing, simply put, is the process of evaluating a prototype by observing how users interact with it. It involves gathering first-hand feedback to determine the product’s usability, functionality, and overall user experience. This feedback is invaluable as it helps identify areas that need improvement and ensures that the final product is user-friendly and meets the intended goals.
When conducting user testing, it is important to select a group of representative users who match the prototype’s target audience. These users should have diverse backgrounds, experiences, and skill levels to provide a comprehensive perspective. By involving real users in testing, designers and developers can gain insights into how the product performs in real-world scenarios.
Defining User Testing
Before we delve deeper into the process, let’s define user testing. User testing involves selecting a group of representative users who match the prototype’s target audience. These users are given specific tasks on the prototype while their interactions and feedback are observed and recorded.
During user testing, creating a comfortable and natural environment for participants is essential. This can be done by clearly explaining the test’s purpose, assuring participants that their feedback is valuable, and encouraging them to think aloud as they interact with the prototype. By creating a relaxed atmosphere, participants are more likely to provide honest and insightful feedback.
Importance of User Testing in Prototype Development
User testing plays a pivotal role in prototype development. It helps uncover usability issues, identifies confusion or frustration, and highlights gaps between user expectations and the actual product. By incorporating user feedback early on, designers and developers can make informed decisions to enhance the prototype and address potential problems before the final launch.
One of the critical benefits of user testing is its ability to provide actionable insights. By observing users in real-time, designers and developers can identify pain points and areas of improvement that may have been overlooked during the design phase. This iterative approach allows for continuous refinement and optimization of the prototype, resulting in a more user-friendly and intuitive final product.
Furthermore, user testing helps validate design decisions. By involving users in the testing process, designers can gather evidence to support their design choices and make data-driven decisions. This not only enhances the credibility of the design but also increases the chances of creating a successful product that meets the needs and expectations of the target audience.
In conclusion, user testing is a critical component of prototype development. It provides valuable insights into a product’s usability, functionality, and overall user experience. By involving representative users in the testing process, designers and developers can identify areas for improvement, address user concerns, and create a final product that is intuitive, user-friendly and meets the target audience’s needs.
Make your design decisions count.
Subscribe to Design Under Pressure. Get insights, UX metrics, and tools for bold, informed design.
We respect your inbox. Just insights. No fluff. Privacy Policy.
Preparing for User Testing
Before you jump into user testing, laying the groundwork and ensuring you’re well-prepared is crucial. Here are a few essential steps to consider:
Identifying Your Target Users
Understanding your target users is key to conducting effective user testing. Take the time to identify your intended audience’s characteristics, preferences, and needs. This information will help you select appropriate participants for the test and ensure that their feedback aligns with your target demographic.
Consider conducting user research to gather insights into your target users’ behaviors, motivations, and pain points. This can involve techniques such as surveys, interviews, and observation. By deeply understanding your users, you can tailor your testing approach to address their specific needs and expectations.
Additionally, it’s important to consider the diversity within your target user group. Ensure you include participants with different backgrounds, experiences, and skill levels. This will provide a more comprehensive perspective on your prototype’s performance across various user segments.
Setting Clear Testing Objectives
Defining your testing objectives ensures a focused and productive testing session. What specific aspects of the prototype are you looking to evaluate? Are you primarily interested in usability, functionality, or both?
Consider breaking down your objectives into specific tasks or scenarios participants will be asked to complete during the test. This will help you measure your design’s effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
Additionally, aligning your testing objectives with your overall project goals is essential. Are you aiming to increase user engagement, improve conversion rates, or enhance the overall user experience? By keeping your objectives in line with your broader goals, you can ensure that the insights gained from user testing are actionable and contribute to the success of your project.
Furthermore, consider setting measurable metrics to evaluate the success of your testing objectives. These could include metrics such as task completion rates, time on task, or user satisfaction ratings. Quantifiable data will provide concrete evidence of the impact of your design decisions and help prioritize future improvements.
Prototype Testing
Creating a User Testing Plan
Now that you have laid the foundation, creating a comprehensive user testing plan is time. This plan will serve as your roadmap throughout the testing process and ensure everything runs smoothly. Here are a few crucial steps:
Deciding on the Testing Method
Various testing methods are available, including moderated or unmoderated testing, remote testing, or in-person testing. Consider the advantages and disadvantages of each method and choose the one that best suits your needs and resources. Remember, every prototype and target audience may have unique requirements, so choose wisely!
When deciding on the testing method, it’s important to consider factors such as the level of control you want over the testing environment, the geographical distribution of your target audience, and the budget available for conducting the tests. Moderated testing allows for real-time participant interaction, providing valuable insights into their thoughts and experiences. On the other hand, unmoderated testing offers flexibility and scalability, enabling you to test with more participants in a shorter period.
Remote testing has gained popularity recently due to its convenience and cost-effectiveness. It allows participants to complete the tests from their environment, providing more natural and authentic feedback. On the other hand, in-person testing offers the advantage of observing participants directly and capturing non-verbal cues that may be missed in remote testing.
Preparing Your Prototype for Testing
Before the test, it’s essential to ensure your prototype is ready for the users. Double-check for any technical issues or bugs that might hinder the testing process. Clear instructions should be provided to participants, explaining the tasks they need to perform and any specific areas of interest that should be explored in detail.
When preparing your prototype, consider the level of fidelity appropriate for the development stage. Low-fidelity prototypes, such as paper sketches or wireframes, are helpful for early-stage testing to gather feedback on the overall concept and functionality. High-fidelity prototypes, which closely resemble the final product in terms of design and interactivity, are more suitable for testing specific features and user interactions.
It’s also important to consider the target audience when preparing your prototype. Ensure the prototype reflects their characteristics and preferences if your product is intended for a specific demographic. This will help you gather more relevant and actionable feedback during testing.
In addition to technical preparation, it’s crucial to create a comfortable and welcoming environment for participants. Make sure the testing location is quiet and free from distractions. Provide any necessary equipment, such as computers or mobile devices, and ensure they are in good working condition. Consider offering incentives to participants as a token of appreciation for their time and feedback.
🚀 If you’re using Helio
It’s also important to consider the target audience when preparing your prototype.
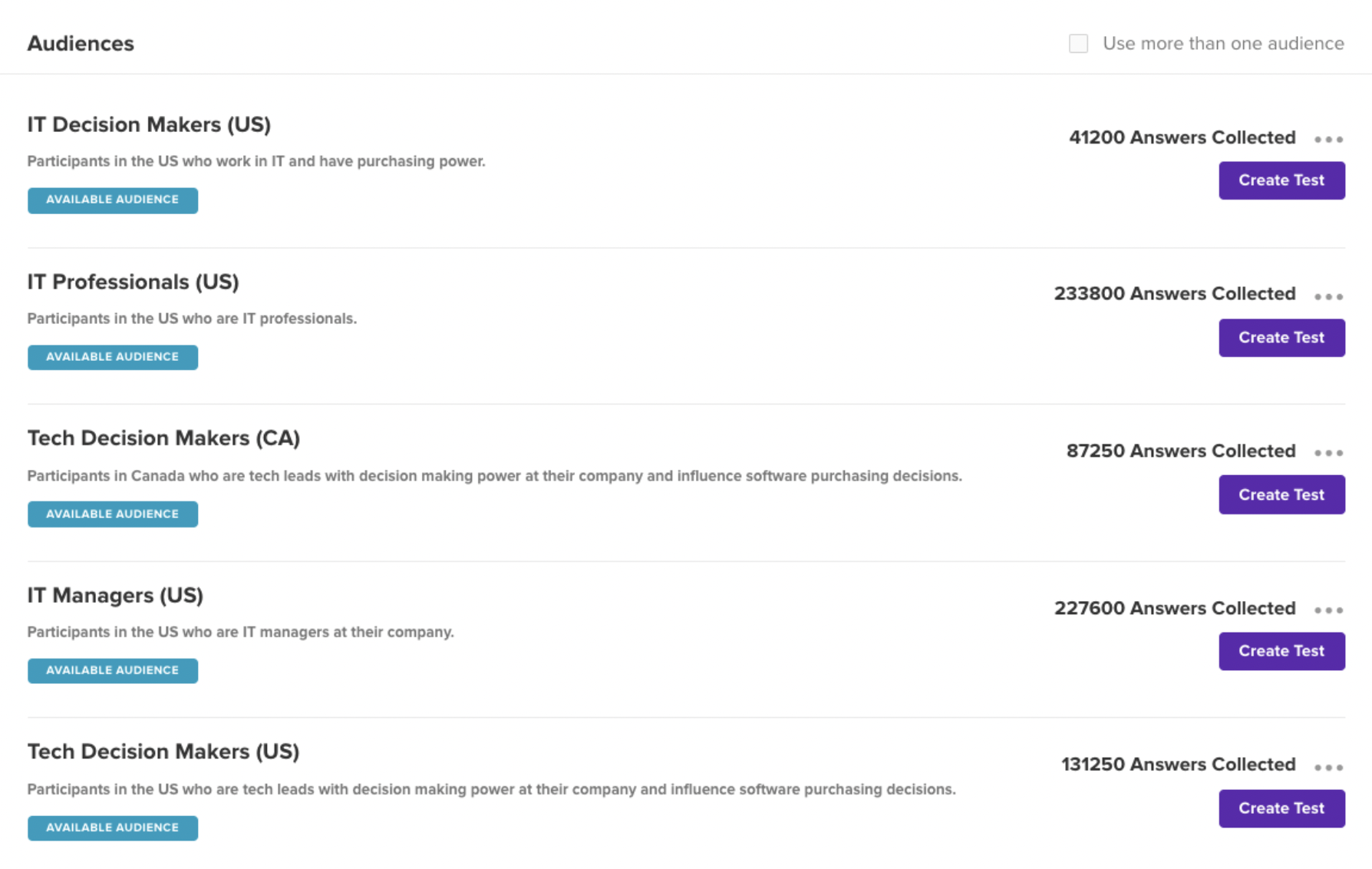
This will help you gather more relevant and actionable feedback during testing.
Conducting the User Test
Now comes the exciting part – conducting the user test itself! Here’s how to ensure a successful and productive testing session:
Best Practices for User Testing
During the testing session, creating a comfortable and non-threatening environment for the participants is essential. Encourage them to think aloud and share their thoughts as they interact with the prototype. Be an active listener, take notes, and ask follow-up questions to understand their experience better. Remember, the user is at the center of this process!
Common Mistakes to Avoid During User Testing
While conducting user testing, it’s essential to be aware of common mistakes that can compromise the validity and reliability of the results. Avoid leading participants, providing hints, or influencing their responses. The goal is to gather unbiased feedback that accurately reflects the user’s experience and uncover potential issues or opportunities for improvement.
Analyzing User Testing Results
Once the user testing is complete, it’s time to analyze the results and extract meaningful insights. Here’s how you can make the most of the feedback received:
Interpreting User Feedback
To interpret user feedback effectively, look for patterns, common themes, and recurring issues. Categorize the feedback and prioritize the areas that require immediate attention. Use this information to make data-driven decisions and iterate on the prototype to enhance its usability and user experience.
Making Necessary Adjustments to Your Prototype
The final step in the user testing process is implementing the necessary adjustments based on the feedback received. Address the identified issues, refine the design, and make the prototype more intuitive and user-friendly. Remember, the goal is to create a product that meets and exceeds user expectations.
By following these guidelines, you are well on your way to conducting effective user testing for your prototype. User testing is an iterative process, and continuous feedback is essential for ongoing improvements. So go ahead, gather those user insights, and create a prototype that considers your users’ needs!
User Testing Prototype FAQs
User testing involves evaluating a product prototype by observing real users interact with it to gather feedback on usability, functionality, and overall experience. This process helps identify improvements, ensuring the final product meets user expectations.
This testing phase is vital as it uncovers usability issues, gathers user preferences, and validates design decisions, ensuring the product is user-friendly and meets the target audience’s needs. It’s a critical step to avoid costly revisions post-launch and enhance user satisfaction.
Businesses should choose participants who closely match the product’s target audience, including diverse backgrounds, experiences, and skill levels, to ensure the feedback is comprehensive and representative of the broader user base.
Preparation includes defining clear testing objectives, identifying target users, creating a detailed testing plan, selecting the appropriate testing method, and ensuring the prototype is fully functional and representative of the final product.
Analyzing feedback involves identifying patterns and common themes in user responses, prioritizing areas for improvement based on feedback severity and frequency, and translating these insights into actionable changes in the prototype.
Businesses should avoid leading questions, influencing participant responses, and ignoring negative feedback. Ensuring an unbiased approach and valuing all types of feedback are crucial for gaining genuine insights.
Insights should be systematically categorized and prioritized. Teams should develop an action plan to address feedback, making iterative adjustments to the prototype based on user input and continually testing these adjustments to refine the product.