User Testing vs Usability Testing: What’s the Difference?
In the design field, testing plays a crucial role in ensuring that products are user-friendly, intuitive, and meet the needs of their target audience. Two commonly used methods for testing a product’s usability are user testing and usability testing. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they have distinct differences that are important to understand.
🔩 The Nuts and Bolts:
- Distinct Goals Shape Testing Approaches: User testing aims to gather user feedback and insights, focusing on how individuals interact with a product. In contrast, usability testing evaluates a product’s usability against predefined criteria. This differentiation guides designers in choosing the appropriate method for their testing needs.
- Methodology Matters in Testing: User testing employs qualitative methods like observations and interviews to deeply understand user behavior and preferences. In contrast, usability testing uses quantitative and qualitative methods to objectively assess usability, emphasizing the importance of method selection based on project goals.
- Participant Selection and Sample Size Differ: User testing typically involves a smaller, more focused group of participants, allowing for in-depth analysis of individual experiences. Usability testing, however, requires a larger sample size to ensure statistical significance, highlighting the need for tailored participant recruitment strategies.
- Both Testing Types are Crucial for Design Success: Integrating user and usability testing into the design process ensures products are both intuitive and meet specific usability standards. This dual approach helps identify pain points and validate design decisions, underlining the importance of a comprehensive testing strategy.
- Continuous Testing Leads to Incremental Improvements: Viewing user and usability testing as ongoing processes allows designers to improve continually, ensuring products adapt to user needs and stay ahead in competitive markets. This insight stresses the importance of iterative testing throughout the product lifecycle.
- Balancing Qualitative and Quantitative Insights: Combining user testing’s qualitative feedback with usability testing’s quantitative data offers a holistic view of user experience, allowing for informed design optimizations. This balanced approach ensures products are both user-friendly and meet usability benchmarks.
- Misconceptions Can Undermine Testing Efficacy: Clearing up common misconceptions about user and usability testing being identical or prohibitively expensive encourages a more nuanced understanding and application of these methods, ensuring they are leveraged effectively to enhance design outcomes.
Understanding the Basics of Testing in Design
Before delving into the differences between user testing and usability testing, it’s essential to have a solid understanding of the basics of testing in design. Testing is a systematic approach to evaluating a product’s performance, usability, and overall user experience. Through testing, designers can gather valuable insights and feedback to inform the design process, identify areas for improvement, and validate design decisions.
Various methodologies and techniques can be employed in design testing. These include user testing, usability testing, A/B testing, beta testing, and more. Each method has its own unique purpose and benefits, but they all share the goal of improving a product’s design and user experience.
User testing, as the name suggests, focuses on testing a product or service with real users. It involves observing users interacting with the product and collecting feedback on their experiences. This type of testing often occurs in a controlled environment, such as a usability lab, where participants are given specific tasks to complete while their actions and feedback are recorded.
During user testing, designers can gain valuable insights into how users navigate a product, their challenges, and how they perceive the overall user experience. By observing users in real time, designers can identify pain points, usability issues, and areas for improvement. This feedback can then be used to iterate on the design and make informed decisions that enhance the user experience.
On the other hand, usability testing focuses on assessing the usability of a product or service based on a defined set of usability criteria. It involves evaluating users’ effectiveness, efficiency, and satisfaction when performing specific tasks. Usability testing can be conducted through various methods, such as remote tests, heuristic evaluations, or expert reviews.
Usability testing allows designers to evaluate a product’s usability from a more objective standpoint. By defining specific usability criteria and measuring user performance against those criteria, designers can identify areas where the product may fall short and make improvements accordingly. Usability testing can also help designers understand how users perceive the product’s ease of use, efficiency, and overall satisfaction, providing valuable insights for further design iterations.
Both user testing and usability testing play crucial roles in the design process. While user testing focuses on gathering feedback from real users in a more naturalistic setting, usability testing provides a more structured and objective evaluation of a product’s usability. By combining these two approaches, designers can comprehensively understand how their design performs in real-world scenarios and make informed decisions to enhance the user experience.
Make your design decisions count.
Subscribe to Design Under Pressure. Get insights, UX metrics, and tools for bold, informed design.
We respect your inbox. Just insights. No fluff. Privacy Policy.
Key Differences Between User Testing and Usability Testing
While user testing and usability testing share a common goal of assessing the user experience, the two methods have several key differences. Understanding these differences can help designers determine the most suitable approach for their specific testing needs.
Purpose and Goals
User testing primarily gathers feedback and insights to understand how users interact with a product or service. It aims to uncover usability issues, identify areas for improvement, and validate design decisions. This process involves observing users navigating through the product, conducting interviews to understand their thoughts and preferences, and using thinking-aloud protocols to gain deeper insights into their behavior.
For example, in a user testing session for a mobile app, participants may be asked to complete specific tasks while the researcher observes and takes notes. The researcher may also ask follow-up questions to understand the user’s thought process and gather feedback on their overall experience.
Usability testing, on the other hand, is more focused on evaluating the product’s overall usability based on predefined criteria. Its goal is to assess how well users can accomplish specific tasks and determine if the product meets their needs effectively and efficiently. This process involves setting predefined tasks for participants to complete and measuring their performance and satisfaction.
For instance, in a usability testing session for a website, participants may be asked to find a specific product and complete a purchase. The researcher would measure the time taken, the number of errors made, and the participant’s subjective satisfaction with the process.
Methodology and Approach
User testing typically involves direct interaction with users in person or remotely. It often utilizes qualitative research methods, such as observations, interviews, and thinking-aloud protocols, to gain deeper insights into user behavior and preferences.
During a user testing session, the researcher may observe how users navigate the product, take notes on their actions and comments, and ask follow-up questions to understand their thoughts and preferences. This qualitative approach provides a rich understanding of the user experience and valuable insights for improving the design.
Usability testing, on the other hand, can be conducted using various quantitative and qualitative research methods. It often relies on predefined tasks and measures to objectively assess the product’s usability. This may involve collecting quantitative data, such as completion rates, task success rates, and time taken, and qualitative data through participant feedback and observations.
For example, in a usability testing session, participants may be asked to complete predefined tasks while the researcher measures their performance and collects feedback. The researcher may also use questionnaires or surveys to gather additional quantitative data on the user’s satisfaction and perceived product usability.
Participants and Sample Size
When it comes to participants and sample size, user testing typically involves a smaller number of participants, ranging from 5 to 10, depending on the complexity of the product and the research goals. This allows for more in-depth interactions and a deeper understanding of user experiences.
With a smaller sample size, user testing can provide valuable insights into individual users’ specific needs, preferences, and pain points. This qualitative approach allows for a more personalized understanding of the user experience, which can be particularly useful in the early stages of product development.
Usability testing, on the other hand, often requires a larger sample size to ensure the reliability and statistical significance of the findings. This can range from 15 to 30 participants, depending on the research goals and the desired confidence level in the results.
A larger sample size allows for more robust statistical analysis and generalizability of the findings to a broader user population. It helps identify common usability issues and patterns affecting a larger user base, providing insights to guide design decisions and improvements.
Usability Testing
The Importance of User and Usability Testing
User testing and usability testing both play crucial roles in the design process. By incorporating these testing methods, designers can ensure that their products are usable, intuitive, and meet the needs of their target audience.
User testing allows designers to gain valuable insights into how real users interact with their products. This type of testing helps identify pain points, usability issues, and areas for improvement. By observing users in action, designers can understand their behavior, preferences, and motivations, enabling them to create more user-centric designs. User testing also allows for early identification of potential problems, reducing the risk of costly design changes later.
On the other hand, usability testing provides a systematic approach to evaluating a product’s usability based on predefined criteria. This testing method allows designers to assess users’ efficiency, effectiveness, and satisfaction when performing specific tasks. By conducting usability tests, designers can identify and address usability issues early in the design process, ultimately improving the overall user experience.
During usability testing, designers often create scenarios or tasks for users to complete while observing their interactions. This process helps designers understand how easily users can navigate the product, whether they encounter any difficulties or confusion, and how satisfied they are with the overall experience. By gathering this data, designers can make informed decisions about design changes and enhancements.
Moreover, user and usability testing can also help designers validate their design decisions. By involving real users in the testing process, designers can gather feedback and ensure their design solutions align with user expectations. This iterative approach allows designers to refine their designs based on user feedback, leading to more successful and user-friendly products.
It is important to note that user and usability testing should not be seen as a one-time event, but rather as an ongoing process throughout the design lifecycle. By continuously testing and gathering feedback, designers can make incremental improvements to their products, ensuring they remain relevant and effective.
In conclusion, user and usability testing are essential components of the design process. These testing methods provide designers with valuable insights, help identify and address usability issues, and enable the creation of user-centric designs. By incorporating user and usability testing into their workflow, designers can ensure that their products meet the needs and expectations of their target audience.
🚀 If you’re using Helio
By incorporating user and usability testing into their workflow, designers can ensure that their products meet the needs and expectations of their target audience.
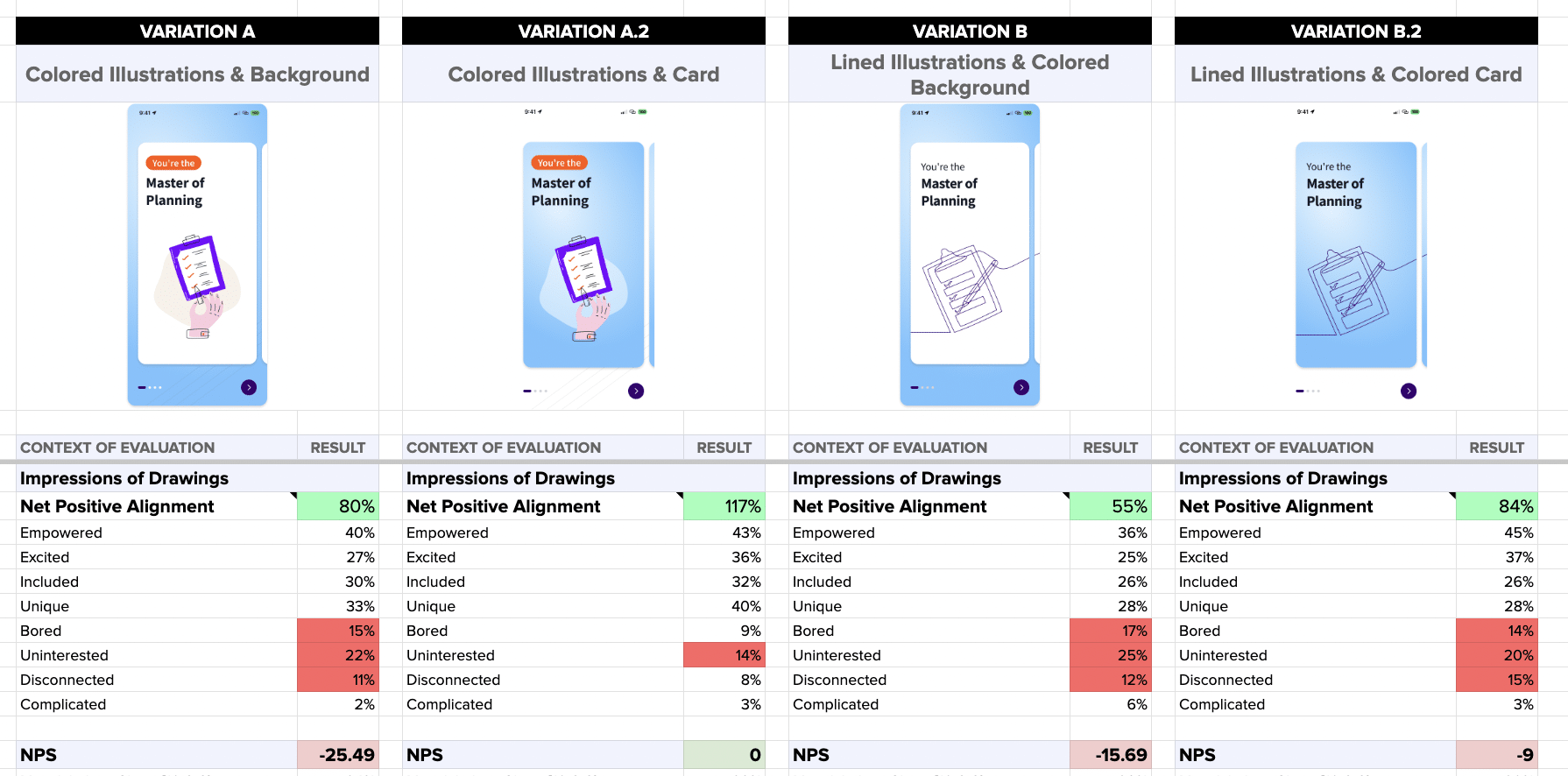
Consider various factors to determine the most appropriate method for their needs.
Choosing the Right Testing Method
When deciding between user and usability testing, designers must consider various factors to determine the most appropriate method for their needs.
Factors to Consider
Some factors to consider include the research objectives, the stage of the design process, the target audience, the budget and resources available, and the timeline for the project. It’s essential to evaluate these factors and weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each testing method to make an informed decision.
Balancing User and Usability Testing
Sometimes, a combination of user and usability testing might be the most effective approach. By combining both methods, designers can gain comprehensive insights into the user experience, including qualitative feedback and measurable data. This balanced approach allows for a more holistic evaluation of the product’s usability and user satisfaction.
Common Misconceptions About User and Usability Testing
Despite the importance and benefits of user and usability testing, several misconceptions surround these testing methods.
Clearing Up Confusion
One common misconception is that user and usability testing are the same. As we have discussed, while they both evaluate the user experience, they have distinct differences. Another misconception is that testing is time-consuming and expensive. While comprehensive testing does require time and resources, various methods and techniques can be used to optimize the testing process.
It’s important to dispel these misconceptions and recognize the value that user and usability testing bring to the design process. By understanding the differences between these testing methods and leveraging their strengths, designers can ultimately create user-centric, intuitive, and successful products.
User Testing vs Usability Testing FAQs
User testing focuses on observing real users to gather feedback on their experiences with a product, aiming to understand how they interact with it and identify any usability issues. Usability testing, however, evaluates a product’s usability against specific criteria, assessing how well users can accomplish predefined tasks, thereby offering a more structured and objective analysis of a product’s user interface.
User testing is crucial because it provides direct insights into how real users interact with a product, revealing pain points, usability issues, and areas for improvement. This feedback is invaluable for making informed design decisions that enhance user experience, ensuring the product effectively meets users’ needs and expectations.
Usability testing contributes by objectively evaluating a product’s usability, focusing on effectiveness, efficiency, and satisfaction in task completion. It helps identify where a product falls short of usability standards, guiding designers in making necessary improvements to enhance the user experience and meet users’ needs more effectively.
Combining user testing and usability testing can be highly effective, providing qualitative insights from real user interactions and quantitative data on usability metrics. This comprehensive approach allows designers to create more user-centric, intuitive, and successful products by leveraging the strengths of both testing methods.
When deciding between user and usability testing, consider the research objectives, design process stage, target audience, available budget, resources, and project timeline. Evaluating these factors helps determine the most suitable testing method to achieve the desired outcomes.
Effective user testing involves recruiting participants that match the target audience, creating realistic scenarios or tasks, observing and recording user interactions, and gathering feedback through interviews or questionnaires. This process requires a careful balance of qualitative research methods to gain deep insights into user behavior and preferences.
Common misconceptions include believing that user and usability testing are the same or that testing is always time-consuming and expensive. Dispelling these myths is crucial, as both types of testing play unique and valuable roles in the design process, and various methods can optimize testing efficiency and cost.