Examples of Qualitative Research: A Comprehensive Guide
Qualitative research is a valuable approach that allows researchers to gain in-depth insights into complex phenomena. This comprehensive guide will explore the various aspects of qualitative research, including its definition, importance, and critical characteristics. We will also delve into different qualitative research methods and discuss how to design and analyze a qualitative research study. So, let’s begin our journey of understanding qualitative research!
🔩 The Nuts and Bolts:
- Rich Data Beyond Numbers: Qualitative research offers nuanced insights that quantitative methods miss, capturing the depth of human emotions and experiences essential for comprehensive analysis.
- Diverse Methods for Diverse Questions: Utilizing various qualitative methods, such as interviews, focus groups, and ethnographic studies, enables researchers to approach complex questions from multiple angles, enriching the research outcomes.
- Contextual Understanding Enhances Relevance: By focusing on the context in which behaviors occur, qualitative research reveals the influences of cultural, social, and personal factors on decision-making and actions.
- Interactive Data Collection Builds Trust: Techniques like in-depth interviews and participant observations build trust and rapport, leading to more honest and detailed responses from participants.
- Adaptable Frameworks for Dynamic Research: Qualitative research’s flexible nature allows researchers to adapt their methods as studies progress, responding to new findings and insights in real time.
- Detailed Analysis Uncovers Hidden Patterns: Through methods like thematic analysis, qualitative research decodes complex data sets to uncover patterns and themes that are not immediately apparent.
- Impactful for Policy and Practice: The detailed insights from qualitative research have profound implications for policy-making, educational practices, and business strategies, directly impacting societal progress.
Understanding Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is an approach to understanding the subjective experiences, perspectives, and contexts of individuals or groups. Unlike quantitative research, which focuses on numerical data and statistical analysis, qualitative research aims to explore the richness and depth of human experiences.
Researchers delve into the intricacies of human behavior, motivations, and emotions when conducting qualitative research. Using methods such as interviews, focus groups, and observations, they gather data that allows for a more nuanced understanding of the subject matter. This approach goes beyond numbers and statistics, uncovering the underlying factors that shape our thoughts, actions, and interactions.
Definition and Importance of Qualitative Research
At its core, qualitative research is about exploring the “whys” and “hows” rather than the “what” and “how many.” It allows researchers to explore complex social phenomena and better understand human behavior. By using methods such as interviews, focus groups, and observations, qualitative research provides insights that quantitative methods alone might miss.
Qualitative research is crucial in psychology, sociology, anthropology, and education, where understanding human experiences and social processes is essential. It helps researchers uncover nuanced insights that can inform policies, develop theories, and improve practices.
For example, in psychology, qualitative research can explore the lived experiences of individuals with mental health disorders. By conducting in-depth interviews, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of the challenges faced by these individuals, the impact of their condition on their daily lives, and the coping mechanisms they employ. This knowledge can then inform the development of more effective interventions and support systems.
Make your design decisions count.
Subscribe to Design Under Pressure. Get insights, UX metrics, and tools for bold, informed design.
We respect your inbox. Just insights. No fluff. Privacy Policy.
Critical Characteristics of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research has several key characteristics that distinguish it from quantitative research. First, it is exploratory, allowing researchers to generate new hypotheses and theories. By immersing themselves in the subject matter, researchers can comprehensively understand the topic and identify new avenues for investigation.
Second, qualitative research focuses on understanding social and cultural contexts, acknowledging the influence of these factors on individuals’ experiences and behaviors. It recognizes that our actions and perceptions are shaped by the society and culture in which we live. Qualitative research provides a more holistic understanding of human behavior by considering these contextual factors.
Another characteristic is that qualitative research is typically conducted in natural settings. This enables researchers to observe people in their natural environments and capture real-life experiences. This approach allows for a more authentic representation of individuals’ behaviors and interactions, as they are not influenced by artificial laboratory conditions.
Moreover, qualitative research emphasizes participants’ subjective interpretations, recognizing the significance of individual perspectives in shaping their experiences. By valuing participants’ unique viewpoints, researchers can gain insights into the complexities and nuances of human experiences, shedding light on the diversity of human thought and behavior.
In summary, qualitative research offers a valuable approach to understanding individuals’ or groups’ subjective experiences, perspectives, and contexts. Through its exploratory nature, focus on social and cultural contexts, and emphasis on subjective interpretations, qualitative research provides a deeper understanding of human behavior and enriches our knowledge in various fields.
Types of Qualitative Research Methods
Qualitative research methods are widely used to gather data and gain insights into human experiences. These methods provide researchers with a deeper understanding of various phenomena and allow them to explore the complexities of human behavior and perspectives. Let’s explore some of the most common qualitative research methods in more detail:
In-Depth Interviews
In-depth interviews are a fundamental qualitative research method involving detailed and extensive conversations with participants. These interviews aim to explore participants’ perspectives, experiences, and beliefs deeply. By engaging in one-on-one discussions, researchers can establish a rapport with participants, creating a safe and comfortable environment for them to share their thoughts and feelings openly. In-depth interviews provide researchers with rich and detailed data, allowing them to understand the topic being studied comprehensively.
Researchers often use open-ended questions during in-depth interviews to encourage participants to express themselves freely. This method allows participants to share personal stories, anecdotes, and reflections, providing researchers valuable insights into their lived experiences. Researchers may also use probing techniques to delve deeper into specific topics or clarify ambiguous responses. In-depth interviews are beneficial when exploring sensitive or complex issues requiring more nuanced understanding.
Focus Groups
Focus groups are another popular qualitative research method that involves bringing together participants with similar characteristics or experiences. The group dynamic in focus groups allows for a dynamic interaction among participants, which can reveal insights that individual interviews might not capture. Through facilitated discussions, researchers can explore a wide range of perspectives, opinions, and experiences within a relatively short period.
During focus group sessions, researchers act as moderators, guiding the discussion and ensuring that all participants have an opportunity to share their thoughts. The group setting encourages participants to build upon each other’s ideas, challenge assumptions, and engage in a lively exchange of viewpoints. This method is beneficial when exploring topics that benefit from collective insights or when researchers want to understand how group dynamics influence individuals’ perspectives.
Ethnographic Research
Ethnographic research is a qualitative research method that involves immersing the researcher in the natural settings of the participants. By spending an extended period in the field, researchers gain a deep understanding of the culture, social norms, and practices of the group or community being studied. This method allows researchers to observe participants’ behaviors and interactions firsthand, providing valuable insights into their daily lives.
During ethnographic research, researchers often adopt a participant observation approach, actively participating in the community’s activities and rituals. This immersive experience allows researchers to develop a contextual understanding of the participants’ lives, uncovering the underlying meanings and motivations behind their actions. Ethnographic research often involves building relationships and trust with participants, which can lead to a more comprehensive and nuanced understanding of their experiences.
Content Analysis
Content analysis is a systematic qualitative research method that involves analyzing texts, such as interviews, documents, or media, to identify patterns, themes, or meanings. Researchers categorize and interpret the content to gain insights into the underlying messages or representations being conveyed. This method allows researchers to uncover hidden meanings, explore social constructs, and understand the cultural context in which the texts are produced.
Content analysis can be conducted using various techniques, such as thematic, narrative, or discourse analysis. Researchers may use coding schemes to categorize the content into meaningful units, which are then analyzed for patterns and themes. This method allows for a rigorous and systematic examination of textual data, giving researchers a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
It is important to note that these are just a few examples of qualitative research methods, and many other approaches and variations are available to researchers. The choice of method depends on the research question, the nature of the phenomenon being studied, and the resources available to the researcher. By employing a combination of qualitative research methods, researchers can comprehensively understand complex human experiences and contribute to the body of knowledge in their respective fields.
🚀 If you’re using Helio
Qualitative research is crucial education, where understanding human experiences and social processes is essential.
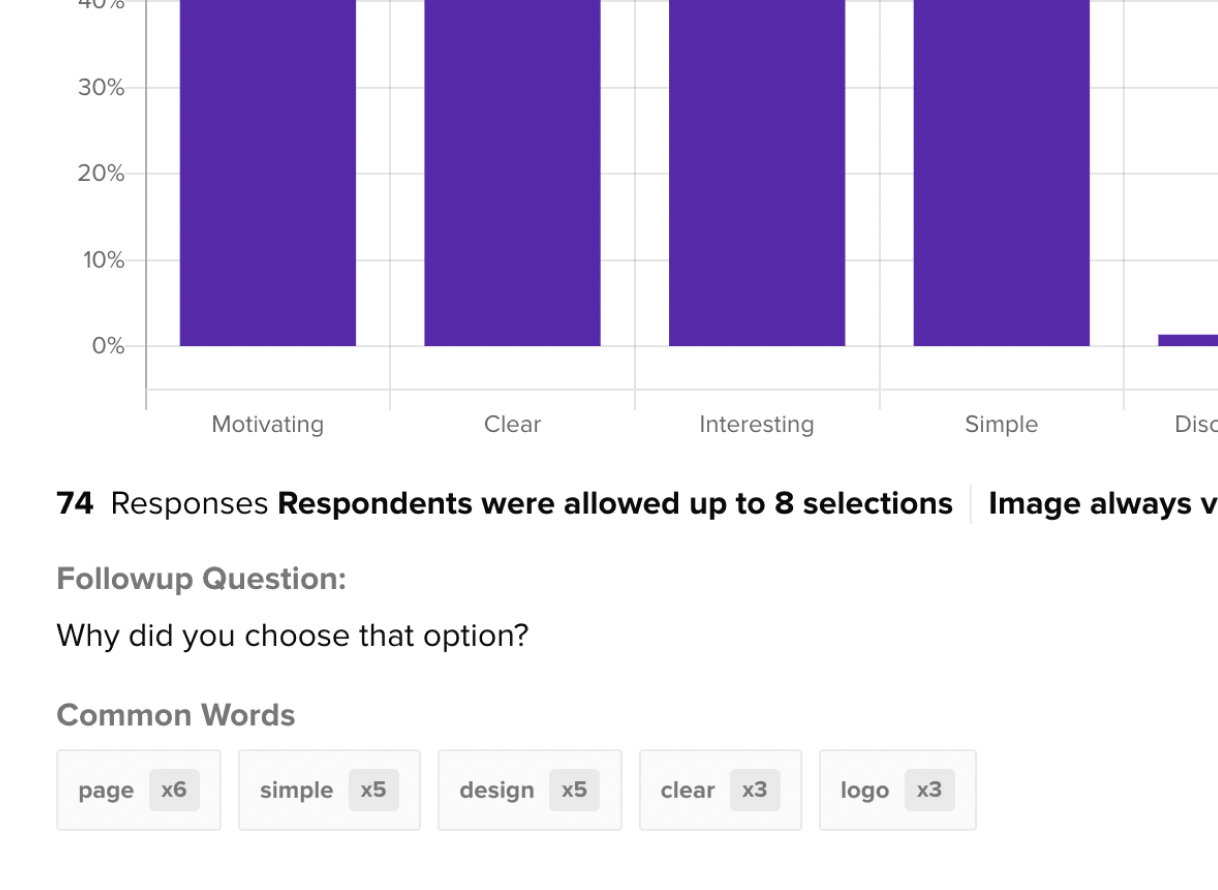
A well-defined question helps guide the study and ensures the data collected will address the intended goals.
Designing a Qualitative Research Study
Designing a qualitative research study involves several crucial steps. Let’s take a closer look:
Formulating a Research Question
Before beginning a study, it is essential to formulate a straightforward research question that aligns with the purpose and objectives of the research. A well-defined research question helps guide the study and ensures the data collected will address the intended goals.
Selecting a Suitable Research Method
Once the research question is identified, researchers must choose an appropriate qualitative research method that aligns with the research question and objectives. The selected method should provide the most effective way to gather the desired data and generate insights.
Sampling and Data Collection
In qualitative research, researchers use purposeful sampling to select participants who can provide valuable insights related to the research question. Data collection methods, such as interviews or observations, are then employed to gather the necessary information. Rigor and ethical considerations are crucial throughout the sampling and data collection process.
Analyzing Qualitative Data
Analyzing qualitative data involves carefully examining the collected data to identify patterns, themes, and meanings. Let’s explore the critical steps of analyzing qualitative data:
Coding and Categorizing Data
Researchers begin by coding the data, which involves labeling and categorizing data segments that relate to specific themes or concepts. This coding process helps identify patterns and connections within the data.
Identifying Themes and Patterns
Researchers then analyze the coded data to identify recurring themes, patterns, or ideas that emerge from the data. This process involves looking for similarities, differences, and relationships between the coded segments to understand the data holistically.
Interpreting and Presenting Findings
Finally, researchers interpret the findings by critically analyzing the themes and patterns identified. They explore the implications of the findings, relate them to existing theories, and offer insights that contribute to the field. The findings are often presented through narratives, visual representations, or quotes to make them accessible and engaging for the target audience.
Conclusion
In conclusion, qualitative research is a robust methodology that offers a comprehensive understanding of human experiences, perspectives, and behaviors. By exploring various qualitative research methods, designing a research study, and analyzing the collected data, researchers can uncover valuable insights that contribute to knowledge and create positive impacts in various fields. So, whether you are a researcher or someone interested in understanding the human world in greater depth, qualitative research is undoubtedly a valuable approach to explore and embrace.
Examples of Qualitative Research FAQs
Qualitative research is a methodological approach that focuses on understanding the qualities of human behavior and the reasons that govern such behavior. It’s important because it provides depth and context to the human aspects of study subjects, which quantitative research can only sometimes adequately address.
Different methods, such as in-depth interviews, focus groups, and ethnographic studies, offer varied perspectives on a subject, enhancing the richness of the data collected and ensuring a well-rounded understanding of the research topic.
In fields that study complex human behaviors and societal structures, qualitative research is crucial because it delves deep into personal experiences and cultural contexts, providing insights that are essential for developing theories and practices that truly reflect human nature.
By providing detailed insights into consumer behavior, employee satisfaction, or public opinion, qualitative research helps businesses and policymakers make informed decisions more likely to be effective and accepted by the target populations.
Challenges include managing subjective interpretations, ensuring the reliability and validity of data, and the extensive time required for data collection and analysis. These can be mitigated through rigorous methodological design and thorough researcher training.
Data is typically analyzed through coding and thematic analysis, where researchers identify patterns and themes that emerge from the data. This process requires a detailed and systematic approach to capture and interpret all relevant data accurately.
Ethical considerations include ensuring confidentiality and informed consent, respecting participants’ privacy, and being sensitive to the research’s impact on them. These considerations are critical to maintaining trust and integrity in the research process.