Prototype Feedback Examples: A Comprehensive Guide for Effective Iteration
Prototyping is essential to product development, allowing designers and developers to test their ideas and gather feedback before finalizing their designs. However, without proper feedback, prototyping can become an exercise in futility. This comprehensive guide will explore the importance of prototype feedback and provide practical examples to help you iterate effectively.
🔩 The Nuts and Bolts:
- Feedback Validates Design Choices: Prototype feedback is invaluable for validating assumptions and ensuring design choices resonate with the target audience, which is critical for developing a market-successful product.
- Unveils Usability Challenges: User interactions with prototypes reveal usability issues, offering a unique opportunity to enhance user experience before finalizing the design.
- Fosters Stakeholder Collaboration: Involving stakeholders in the feedback process builds buy-in and enriches product development with diverse perspectives and expertise.
- Prioritizing Feedback is Crucial: Effective iteration requires prioritizing feedback based on its impact and feasibility, ensuring that significant improvements are made where they matter most.
- Feedback Gathering Techniques Vary: Employing a mix of interviews, surveys, and usability testing provides a comprehensive understanding of user perceptions, guiding more informed design iterations.
- Regular Feedback Drives Continuous Improvement: The iteration process should involve continuous feedback collection and analysis, aligning the evolving product with user needs and preferences.
- Organizing Feedback Streamlines Iteration: Systematically categorizing and prioritizing feedback ensures that development efforts focus on first addressing the most critical design aspects.
Understanding the Importance of Prototype Feedback
Prototype feedback is crucial in the product development process as it provides valuable insights into the strengths and weaknesses of your design. By gathering feedback early on, you can identify potential issues, make informed decisions, and improve your prototype before investing significant time and resources.
Understanding the importance of prototype feedback cannot be overstated when creating a successful product. Prototype feedback plays a vital role in product development by guiding design decisions and ensuring that the final product meets the target audience’s needs. It helps you bridge the gap between your initial concept and the final product, ensuring you create a solution that solves real problems.
One key benefit of effective prototype feedback is the ability to validate your assumptions and gain confidence in your design choices. When you receive feedback from users and stakeholders, you can test your ideas and see if they resonate with the intended audience. This validation is essential in building a product that will be successful in the market.
Another advantage of prototype feedback is its ability to uncover usability issues. By putting your prototype in the hands of users, you can observe how they interact with it and identify any areas that may cause confusion or frustration. This feedback allows you to make necessary improvements and create a user-friendly experience.
Furthermore, prototype feedback is not limited to improving the design itself. It also plays a crucial role in building stakeholder buy-in and fostering collaboration. Involving stakeholders in the feedback process creates a sense of ownership and investment in the product. This collaboration leads to more successful outcomes as everyone’s perspectives and expertise are taken into account.
In conclusion, prototype feedback is an essential component of the product development process. It provides valuable insights, validates assumptions, uncovers usability issues, and fosters collaboration. By embracing prototype feedback, you can create a product that not only meets the needs of your target audience but also exceeds their expectations.
The Art of Gathering Prototype Feedback
Gathering feedback is an art that requires careful planning and consideration. To ensure you collect the most helpful feedback, you need to identify the right audience and employ effective techniques.
Make your design decisions count.
Subscribe to Design Under Pressure. Get insights, UX metrics, and tools for bold, informed design.
We respect your inbox. Just insights. No fluff. Privacy Policy.
Identifying the Right Audience for Feedback
When seeking prototype feedback, it is essential to target individuals who represent your intended users or stakeholders. These individuals can offer valuable perspectives and insights into how well your prototype addresses their needs. Selecting the right audience ensures that the feedback you receive is relevant and actionable.
For example, if you are designing a new mobile app for fitness enthusiasts, it would be beneficial to gather feedback from individuals who are passionate about fitness and regularly use fitness apps. Their experiences and preferences will provide valuable guidance on improving your prototype to meet the needs of your target audience better.
Additionally, consider involving stakeholders with a vested interest in the success of your prototype. These may include project managers, designers, developers, and other key team members. Their feedback can help ensure that the prototype aligns with the project goals and objectives.
Techniques for Collecting Useful Feedback
Collecting valuable feedback involves employing various techniques tailored to your specific needs. Conducting user interviews and observations can help you gain qualitative insights, while surveys and questionnaires enable you to collect quantitative data. By combining these techniques, you can gather a well-rounded perspective on your prototype’s strengths and areas for improvement.
When conducting user interviews, it is important to create an open and comfortable environment where participants feel encouraged to share their thoughts and opinions. This can be achieved by asking open-ended questions and actively listening to their responses. Observing users as they interact with your prototype can also provide valuable insights into their behavior and preferences.
Surveys and questionnaires, on the other hand, allow you to collect feedback from a larger sample size. They can be distributed online or in person, depending on the accessibility of your target audience. When designing surveys, include a mix of closed-ended and open-ended questions to gather quantitative and qualitative data. This will provide a comprehensive understanding of user perceptions and preferences.
Furthermore, consider incorporating usability testing into your feedback-gathering process. This involves observing users as they complete specific tasks using your prototype. Usability testing can uncover any usability issues or pain points that may need to be apparent through interviews or surveys alone.
Lastly, take into account the power of your team members’ feedback. They bring a unique perspective and can provide valuable insights based on their expertise and experience. Encourage open and honest discussions within your team to gather feedback that can help refine and enhance your prototype.
Combining these techniques and involving the right audience ensures that the feedback you gather is comprehensive, relevant, and actionable. This will ultimately lead to a more refined and successful prototype that meets the needs of your users and stakeholders.
Prototype Testing
Analyzing Prototype Feedback
Analyzing feedback is an essential step in the iteration process. You can identify patterns and trends that inform your design decisions by interpreting feedback effectively.
Several key factors must be considered when analyzing prototype feedback. One important aspect is to pay attention to recurring comments, suggestions, and concerns. These recurring themes can provide valuable insights into areas needing improvement or further exploration.
Another crucial element to consider is the context in which the feedback was given. Different users may have unique perspectives and needs, so it is essential to consider these when interpreting the input. Understanding the context can help you better understand the user’s experience and identify potential areas for enhancement.
Interpreting Feedback: What to Look For
When analyzing prototype feedback, looking for actionable insights that can guide your iteration process and help you make informed design decisions is important. These actionable insights can be found by examining the feedback for specific patterns or trends.
For example, if multiple users mention difficulties navigating a particular feature, it may indicate a usability issue that needs to be addressed. On the other hand, if users consistently praise a specific aspect of the prototype, it may suggest a successful design element that should be emphasized and expanded upon.
Furthermore, it is crucial to prioritize the feedback and categorize it accordingly. By grouping similar feedback, you can identify the most critical areas for improvement. This categorization process lets you focus on addressing the most pressing issues first.
Turning Feedback into Actionable Insights
Transforming feedback into actionable insights involves a systematic approach. Once you have categorized the input, you can analyze each category individually and determine the appropriate actions.
For instance, if the feedback highlights a need for improved user onboarding, you can prioritize this area and explore different strategies to enhance the onboarding experience. This could involve creating more explicit instructions, adding tooltips, or simplifying the registration process.
By turning feedback into actionable insights, you can map out the next steps in your iteration process. This ensures that your design evolves with a clear purpose and addresses your users’ needs and expectations.
It is important to note that analyzing prototype feedback is an ongoing process. As you iterate and make changes to your design, it is crucial to continue gathering feedback and analyzing it to ensure that your design decisions are effective and aligned with user expectations.
🚀 If you’re using Helio
Gather feedback and analyze it to ensure that your design decisions are effective.
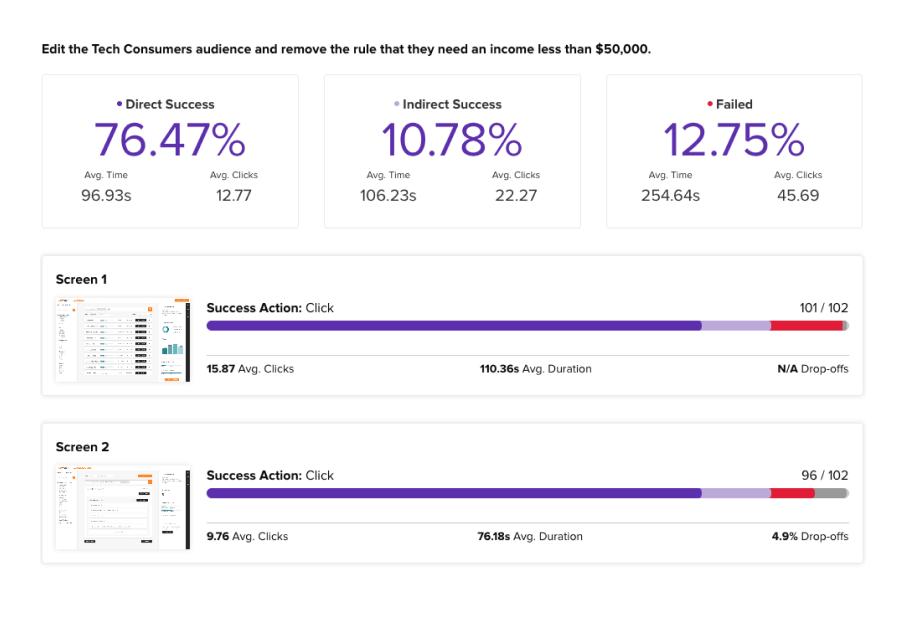
Refine your design and move closer to creating a successful product.
The Iteration Process: From Feedback to Improvement
Once you have gathered and analyzed feedback, it’s time to incorporate it into your prototype iteration process. This iterative cycle helps you refine your design and move closer to creating a successful product.
Steps to Incorporate Feedback into Prototype Iteration
Integrating feedback into your prototype iteration process involves several steps. Start by prioritizing the input based on its impact and feasibility. Then, implement the necessary changes and test the updated prototype with your target audience. Repeat this process until you have addressed the critical areas for improvement identified through feedback.
Common Challenges in the Iteration Process and How to Overcome Them
The iteration process can pose challenges, but with careful planning, you can overcome them. One common challenge is managing conflicting feedback. By prioritizing feedback based on your project goals and user needs, you can navigate conflicting opinions and make informed decisions. Additionally, engaging stakeholders and involving them in the iterative process fosters collaboration and ensures a shared understanding of the desired outcomes.
Best Practices for Managing Prototype Feedback
Managing prototype feedback effectively requires organization and continuous improvement. Implementing these best practices can streamline your feedback management process and drive successful iterations.
Organizing and Prioritizing Feedback
To manage feedback efficiently, establish a systematic method for organizing and prioritizing it. Categorize feedback based on common themes and prioritize based on the impact on your design goals and user needs. This approach ensures you address the most critical input and improve significantly.
Ensuring Continuous Improvement Through Regular Feedback
Prototype feedback is not a one-time event; it should be an ongoing process throughout the development lifecycle. Regularly seek feedback from stakeholders and users, even after initial iterations. This continuous improvement mindset allows you to stay aligned with the evolving needs of your target audience and deliver a product that exceeds expectations.
In conclusion, prototype feedback is an integral part of the product development process. By understanding its importance, mastering the art of gathering and analyzing feedback, and following best practices, you can iterate effectively and create products that meet users’ needs. Incorporate these examples into your design process, and watch your prototypes evolve into successful, user-centric solutions.
Prototype Feedback Examples FAQs
Prototype feedback is crucial for identifying design strengths and weaknesses, validating design decisions, and ensuring the final product meets user expectations. It guides the iteration process, allowing for necessary adjustments based on user and stakeholder insights.
Gather feedback from a targeted audience that represents your end-users or stakeholders using varied techniques like user interviews, surveys, and usability testing. This multi-faceted approach ensures a depth of qualitative and quantitative insights for guiding design improvements.
Managing conflicting feedback and prioritizing changes are common challenges. Address these by aligning feedback with project goals and user needs, ensuring decisions support the product’s overall vision and usability. Engage stakeholders in the iteration process for broader consensus and collaborative problem-solving.
Prioritizing feedback ensures that development efforts are concentrated on making impactful improvements. By focusing on changes that significantly enhance user experience and align with project objectives, you can efficiently use resources and accelerate the development timeline.
Organize feedback by categorizing it based on common themes and prioritizing it according to its impact on design goals and user needs. This structured approach helps address critical feedback first, streamlining the iteration process.
Continuously seek and analyze feedback from users and stakeholders, even beyond the initial development phases. This approach fosters an ongoing improvement cycle, ensuring the product evolves in alignment with user expectations and market trends.
Establish a systematic method for organizing feedback, prioritize based on impact, and involve stakeholders in the feedback loop. Based on this structured feedback, regularly update and iterate on your prototype, maintaining a focus on continuous improvement to meet and exceed user expectations.