Ever wonder why you choose one product over another? Whether you’re picking out a new phone or deciding where to grab lunch, there’s a fascinating process happening behind the scenes. This process, known as the consumer decision-making process, guides every purchase you make. Understanding these steps can help businesses tailor their strategies to meet your needs more effectively.
In this post, we’ll break down the consumer decision-making process so you can see how it works. We’ll look at each stage and provide some Helio user research techniques that help you recognize a need to evaluate your choices and finally make a purchase. You’ll have a clear picture of how decisions are made and how businesses can influence them. Let’s dive into the five key steps that shape your buying journey.
We will demonstrate how to uncover buyer behavior by testing consumers’ decision-making and actions. Buyer behavior refers to consumers’ decision-making processes and actions when purchasing products or services. It includes understanding the reasons behind their purchases, brand loyalty, and the factors influencing their decisions.
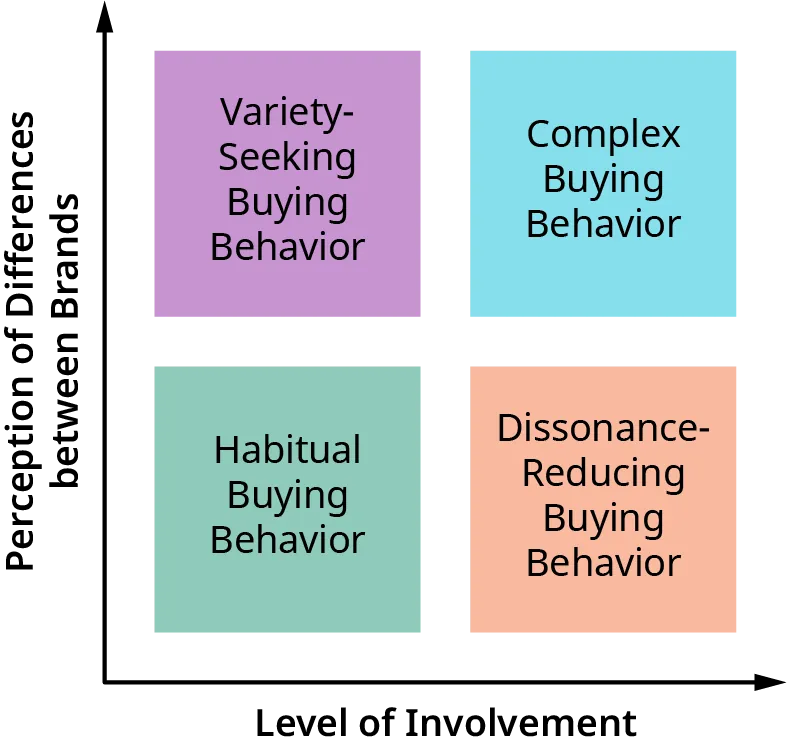
There are four types of buyer behavior:
- Complex
- Dissonance-reducing
- Habitual
- Variety-seeking
Understanding buyer behavior by LibreTexts
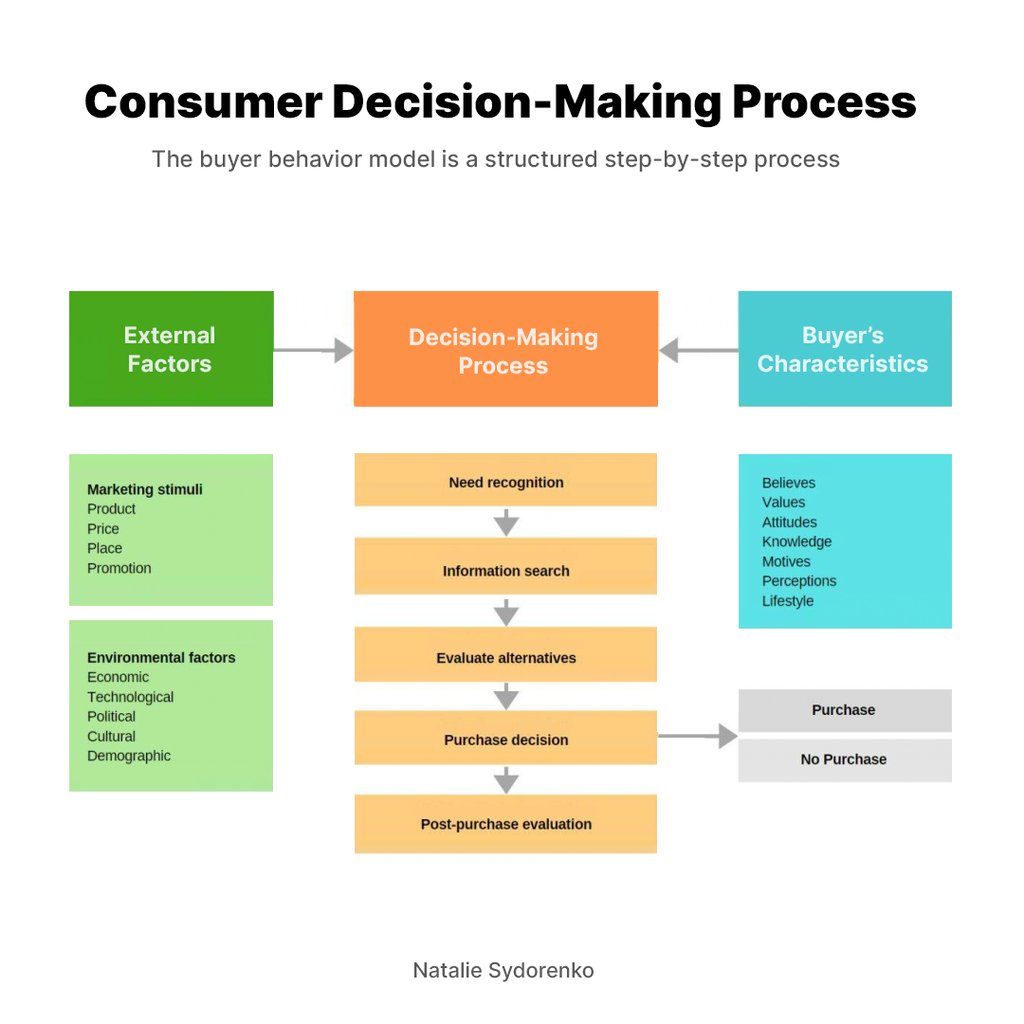
Analyzing buyer behavior helps companies tailor their marketing strategies effectively. The buyer behavior model involves need recognition, information search, evaluation of alternatives, purchase decisions, and post-purchase evaluation.
The consumer decision-making process usually begins with some sort of problem. The consumer then develops a need or a want that they pursue until they satisfy it. Generally, the process follows these five steps, although longer decision-making processes (six or seven steps) sometimes occur.

External Factors Influencing the Decision-Making Process
The consumer decision-making process doesn’t happen in a vacuum. Several external factors influence each step of this process, shaping how decisions are made. Before we discuss each step, let’s review the external factors.
Marketing Stimuli
- Product: A product’s features, quality, and design play a crucial role in attracting consumers. A well-designed product that meets consumer needs can significantly influence their decision.
- Price: Pricing strategies, discounts, and perceived value for money are critical. Competitive pricing can make a product more attractive than others in the market.
- Place: The availability and convenience of purchasing the product matter. Products that are easy to find and purchase online and offline have a higher chance of being chosen.
- Promotion: Advertising, sales promotions, and other marketing communications influence consumer perceptions and decisions. Effective promotion creates awareness and generates interest.
Environmental Factors
- Economic Factors: Consumer purchasing power and economic conditions like inflation and unemployment rates affect buying decisions. In tough economic times, consumers might opt for more affordable options.
- Technological Factors: Advances in technology can change how consumers search for information and make purchases. For example, the rise of e-commerce has made online shopping a norm.
- Political Factors: Government policies, regulations, and political stability can impact consumer confidence and purchasing behavior.
- Cultural Factors: Cultural norms and values influence consumer preferences and buying behavior. What is considered desirable or necessary varies from culture to culture.
- Demographic Factors: Age, gender, income, education, and family size all shape consumer decisions. Different demographics have varying needs and preferences.
1. Need Recognition
The first step in the consumer decision-making process is need recognition. This is when you realize you have a problem or a need that requires a solution. Think of it as that lightbulb moment when you say, “I need this!”
What Triggers Need Recognition?
Need recognition can be triggered by both internal and external factors. Internal triggers come from within you, like hunger or realizing that your old phone isn’t cutting it anymore. External triggers, on the other hand, come from outside influences. This could be an ad you saw on Instagram, a recommendation from a friend, or even a change in your lifestyle.
Examples of Need Recognition
- Internal Triggers:
- Feeling hungry and deciding you need to eat.
- Noticing your shoes are worn out and deciding it’s time for a new pair.
- External Triggers:
- Seeing an advertisement for a new smartphone and realizing your current one lacks the features you want.
- A friend is raving about a new restaurant, making you want to try it out.
The Role of Marketing in Need Recognition
Businesses can significantly influence the need recognition stage through effective marketing. By highlighting problems you didn’t even know you had, they create a perceived need for their products or services. For example, a skincare brand might show you the signs of aging you hadn’t noticed, prompting you to consider buying their anti-aging cream.
Tools for Identifying Consumer Needs
Understanding what triggers need recognition in consumers is crucial for businesses. Companies like Helio offer tools to conduct visual surveys and identify emerging customer needs and pain points. These surveys help businesses understand what makes you realize a need and how they can effectively position their products to meet those needs.
Imagine you’re scrolling through your social media feed, and you come across a post about the latest fitness tracker. You hadn’t thought about tracking your workouts before, but now you’re intrigued. This is a classic example of need recognition triggered by external factors. Suddenly, you need to monitor your fitness levels, and you’re ready to learn more about this new gadget.
Need recognition is the starting point of the consumer decision making process. It’s all about realizing you have a need or a problem that requires a solution. Businesses that understand how to trigger this recognition can effectively guide you towards their products and services, setting the stage for the next steps in your buying journey.
Helio Example:
User polls and surveys are the bread and butter of Helio, so determining what an audience’s needs are and how to meet is just a factor of what questions you want to ask.
For instance, we ran testing to understand the target audience of a theoretical online banking platform called Banko. The goal was to identify needs, motivations, and considerations for different types of consumers within the audience.
To do so, we ran a survey asking questions of 200 participants in an audience of banking consumers in the US:
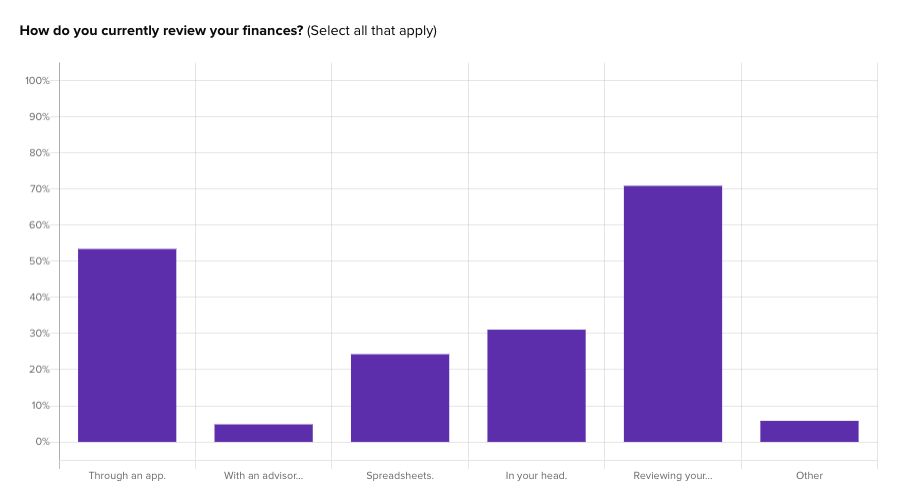
This survey question aimed to understand what behaviors banking consumers are currently exhibiting, and what gaps there are in their experiences that a new financial platform might be able to fill.
Check out our segment below on how we build Personas out of the needfindings surveys!
2. Information Search
Once you recognize a need, the next step in the consumer decision-making process is the information search. This is where you start looking for ways to satisfy your newly recognized need. It’s all about gathering information to make an informed decision.
Types of Information Search
There are two main types of information search: internal and external.
- Internal Search involves relying on memory and past experiences. For instance, remember places you’ve enjoyed if you’re looking for a restaurant.
- External Search: When your internal search doesn’t provide enough information, you turn to external sources. These can include:
- Personal Sources: Friends, family, and colleagues who can offer recommendations.
- Public Sources: Reviews and ratings on websites, consumer reports, and forums.
- Commercial Sources: Advertisements, brochures, and salespeople.
Modern Information Search Methods
In today’s digital age, the information search stage has evolved significantly. Consumers now have access to a wealth of information at their fingertips. Here are some modern methods people use:
- Search Engines: Google is often the first stop. A quick search can provide much information, from product details to reviews.
- Social Media: Platforms like Instagram, Facebook, and Twitter can influence your decision. Seeing what others are buying and using can provide valuable insights.
- Online Reviews: Websites like Yelp, Amazon reviews, and other review platforms help you see what others think about a product or service.
How Businesses Can Leverage This Stage
Businesses need to optimize their presence where consumers are searching for information. Here are some strategies:
- SEO (Search Engine Optimization): Ensure your website ranks high on search engines. Use keywords like “consumer decision making process,” “buying decision process,” and “consumer purchase behavior” to attract searchers.
- Content Marketing: Create valuable content that answers consumers’ common questions during their search. Blog posts, how-to guides, and videos can position your brand as a helpful resource.
- Social Proof: Encourage satisfied customers to leave reviews and share their experiences on social media. Positive testimonials can significantly influence potential buyers.
Tools and Techniques
Businesses can use various tools to understand and influence the information search process:
- User Testing and Feedback Collection: Platforms like Helio allow businesses to gather feedback on where and how customers search for information. This helps in optimizing content and improving the customer experience.
- Comparative Analysis: Understanding how consumers evaluate different options can guide businesses in highlighting their strengths and differentiators.
Let’s say you’ve decided you need a new laptop. Your first step might be to recall the brands you trust (internal search). Next, you go online to read reviews, compare features, and check prices (external search). You might ask friends for their opinions or watch unboxing videos on YouTube. Each source provides you with pieces of information that help shape your decision.
The information search is a crucial step in the consumer decision-making process. It’s where you gather the knowledge needed to make an informed choice. Businesses that understand this stage can effectively position themselves to provide the information consumers seek, guiding them toward their products and services.
Helio Example:
Helio allows you to map out how consumers will find information and what pathways they will pursue in certain scenarios. To do this, we use an Action Map method which asks participants to indicate what actions they would most likely take given a specific scenario. We conducted this type of testing for a theoretical skincare company called SkinSavvy, and tapped into an audience of beauty product consumers in the US to map their actions.
In our work with beauty brand & skincare provider SkinSavvy, we needed to understand where to focus our design and development efforts across their website, mobile app, and social media platforms. With many visitors coming through each of those channels, the team needed validation as to which platform would be their testing grounds for developing patterns that would trickle down into the others.
We employed our Action Map testing to learn which channels SkinSavvy’s consumers preferred to use in key situations across the web experience, such as finding a skincare provider or browsing beauty products.
To test each scenario, we clearly outlined what goal participants are trying to accomplish, and then presented four key actions that represent different flows the user could take:
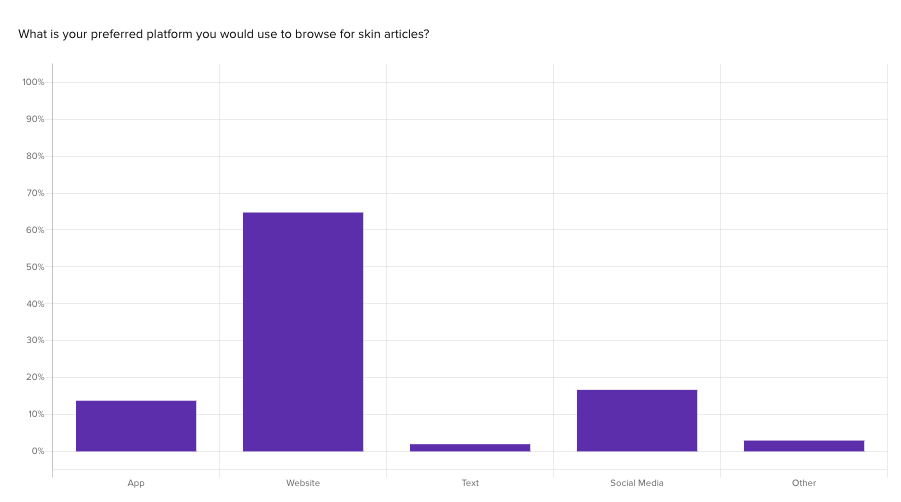
The Action Map framework provided a place to collect all of the data across our surveys and compare what pathways consumers would take in different scenarios.
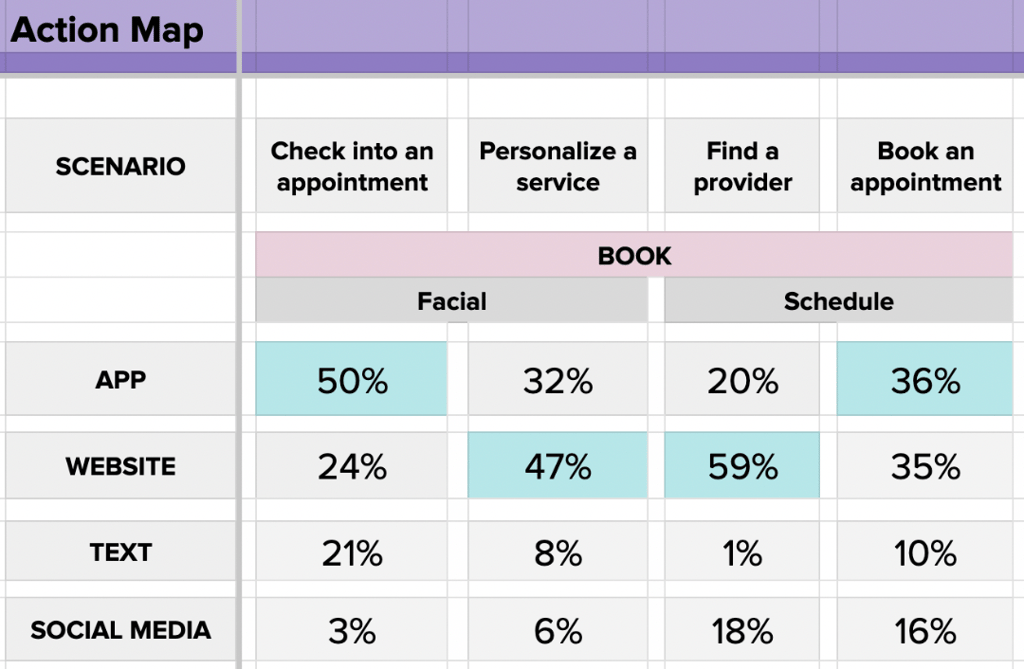
Each box in the image above represents the percentage of participants who would choose that channel to complete their goal; the most prominent choice is highlighted in blue for each scenario.
We found that the app and website were by far the most preferred channels to complete different goals across booking and appointment scenarios.On average, the majority of consumers (41%) prefer to use the website across these key scenarios.
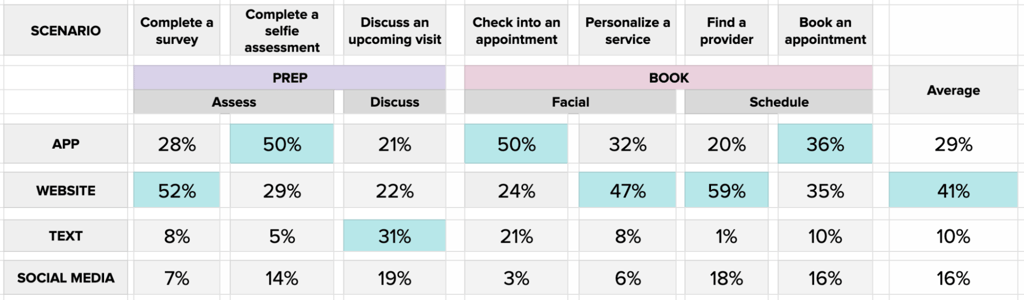
This type of Action Map testing provides clear patterns for how consumers search for information and what pathways they will take when engaging with certain products.
3. Evaluation of Alternatives
After gathering all the necessary information, the next step in the consumer decision making process is the evaluation of alternatives. This is where you compare different options to determine which one best meets your needs and preferences.
How Consumers Evaluate Alternatives
During this stage, consumers assess the available options using various criteria. Here are some common factors:
- Price: The cost of the product or service is often a major consideration. Consumers compare prices to find the best value for their money.
- Quality: Features, durability, and overall performance play a crucial role. Consumers want to ensure they are getting a high-quality product.
- Brand Reputation: Trust in a brand can heavily influence decisions. Brands with strong reputations for quality and customer service often have an edge.
- Reviews and Testimonials: Opinions and experiences of other customers provide valuable insights. Positive reviews can tip the scales in favor of a particular option.
Decision-Making Models
Consumers might use different models to evaluate their choices. Some common models include:
- SWOT Analysis: Assessing the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of each option.
- Pros and Cons Lists: Listing the benefits and drawbacks of each choice to make a balanced decision.
- Decision Matrix: Using a grid to rate each option based on various criteria helps quantitatively compare the alternatives.
Several factors can influence how consumers evaluate alternatives:
- Psychological Factors: Personal preferences, biases, and perceptions can affect evaluation. For instance, consumers might favor a brand they have used before, even if another option is objectively better.
- Social Factors: Opinions and recommendations from friends, family, and social media can sway decisions. Social proof, like seeing a product used by influencers, can be compelling.
- Situational Factors: The context in which the decision is made can also play a role. For example, urgency might lead to a quicker decision with less thorough evaluation.
How Businesses Can Influence This Stage
To positively influence consumers during the evaluation of alternatives, businesses can:
- Highlight Unique Selling Points (USPs): Communicate what differentiates your product. This could be superior quality, better pricing, exceptional customer service, or innovative features.
- Leverage Customer Testimonials: Showcase positive reviews and success stories from satisfied customers. This builds trust and provides social proof.
- Offer Comparisons: Provide detailed comparisons with competitors to help consumers see your product’s advantages. This can be done through comparison charts, infographics, or side-by-side feature lists.
Tools and Techniques
Understanding how consumers evaluate alternatives is crucial for businesses. Here are some tools and techniques:
- Comparative Analysis: Use tools like Helio to conduct comparative studies. This helps understand what factors are most important to consumers and how they weigh different options.
- Surveys and Feedback: Collecting feedback through surveys can reveal which aspects of your product are most valued by consumers and where you might need improvements.
You need a new smartphone. After gathering information about different models, you start comparing them. You look at prices, read reviews, check out the features, and ask friends for their opinions. You might create a pros and cons list to help you decide which phone offers the best balance of price, quality, and features for your needs.
Evaluating alternatives is a critical step in the consumer decision-making process. It involves comparing different options to make the best possible choice. Businesses that understand this stage can effectively position their products to stand out, influencing consumers to purchase.
Helio Example:
To evaluate what alternatives might be available in the market, competitor analysis testing shows you where you can learn from your competition, and where you’re already excelling in the industry. Helio enables you to conduct competitor analysis by comparing user feedback on different homepages. This comparison helps you identify areas for improvement and differentiate your site from the competition.
To illustrate how you can use Helio to test landing pages, we analyzed five prominent CRM providers—HubSpot, Zoho, Zendesk, Salesforce, and Monday.com. We conducted five independent tests focused on user motivation, ability, and clarity of prompts.

Distinct patterns emerged, highlighting the strengths and weaknesses of each platform. The image below shows the framework we used to evaluate the results from each test.
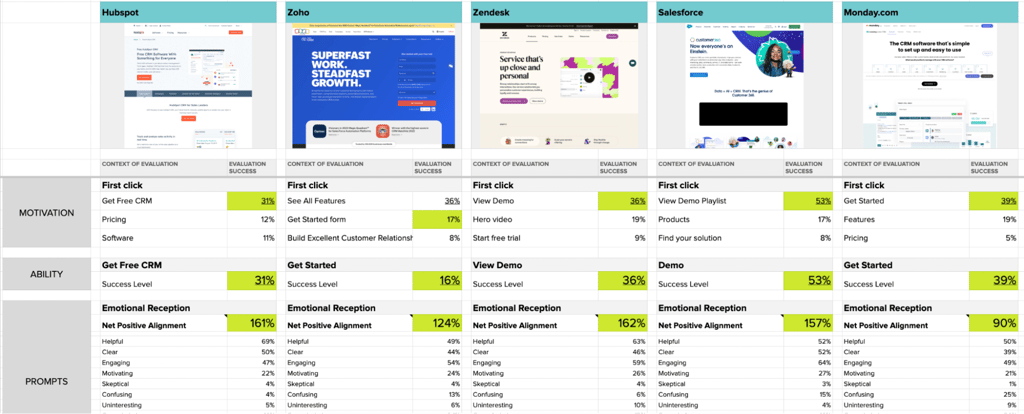
Hubspot proved to have the overall highest customer satisfaction and landing page engagement, while Monday.com’s confusing use of white-space led to the lowest impressions among their competitors.
This type of competitive review testing can significantly affect a company’s market fit score, which quantifies the alignment between product features and identified market needs. It helps determine how well the proposed product fits into the existing market landscape.
View the Competitive Review Case Study
4. Purchase Decision
Now comes the exciting part: making the purchase decision. You’re ready to choose after recognizing a need, gathering information, and evaluating alternatives. This step in the consumer decision-making process is where all your research and comparisons culminate in a final decision.
Factors Affecting the Purchase Decision
Several factors influence the final purchase decision:
- Marketing Strategies: Discounts, promotions, and special offers can tip the scales to favor a particular product. Limited-time offers create a sense of urgency, pushing you to decide.
- Emotional and Rational Considerations: Your decision is often a mix of emotional and rational factors. While the logical side weighs the features and benefits, the emotional side considers how the purchase makes you feel.
- Social Influences: Recommendations from friends, family, and influencers can significantly impact your choice. Social proof can reassure you that you’re making the right decision.
Key Decision Points
During this stage, certain aspects become critical in swaying your decision:
- Product Pages: Detailed product descriptions, high-quality images, and user reviews on product pages help make an informed decision.
- Sales Strategies: Effective sales strategies, like personalized recommendations and exceptional customer service, play a vital role.
- Trust and Credibility: Brands that build trust through transparent practices and reliable products are likelier to win your business.
Overcoming Barriers to Purchase
Sometimes, you might hesitate despite all the information and positive evaluations. Here are common barriers and how businesses can address them:
- Price Concerns: If the price is a barrier, offering flexible payment options, financing, or discounts can help.
- Risk Aversion: To reduce perceived risk, businesses can provide money-back guarantees, free trials, or robust return policies.
- Lack of Information: Ensure all necessary information is readily available. Clear FAQs, detailed product descriptions, and easy access to customer support can ease last-minute doubts.
Conversion Techniques
Businesses use various techniques to convert leads into customers at this stage:
- Personalized Marketing: Tailoring messages and offers based on previous interactions and preferences can increase the likelihood of purchase.
- Follow-Up Emails: Abandoned cart emails or reminders about items left in the cart can nudge customers to complete their purchases.
- Loyalty Programs: Offering rewards for making a purchase can incentivize a decision and foster long-term loyalty.
Consider you’re buying a new laptop. After comparing different models, you finally decide on one. The decision might be influenced by a limited-time discount, a recommendation from a friend who recently bought the same model or a positive review you read online. You feel confident in your choice and proceed to make the purchase.
In summary, the purchase decision is the culmination of the consumer decision-making process. It’s influenced by rational and emotional factors, marketing strategies, and social influences. Businesses that understand this stage can employ effective techniques to overcome barriers and guide you toward making a purchase, ensuring a smooth transition from consideration to action.
Helio Example:
Skincare company SkinSavvy wanted to evaluate the purchase decisions of their customers and determine their purchase likelihood through pricing elasticity testing. This type of testing aims to determine the spectrum of pricing that a business can present to consumers and still receive a positive response and engagement from their target audience.
The SkinSavvy team had several price points and treatment combinations in mind to test. We presented one price point each to a different group of beauty product consumers, with the goal of learning how well they react to their purchase offer.
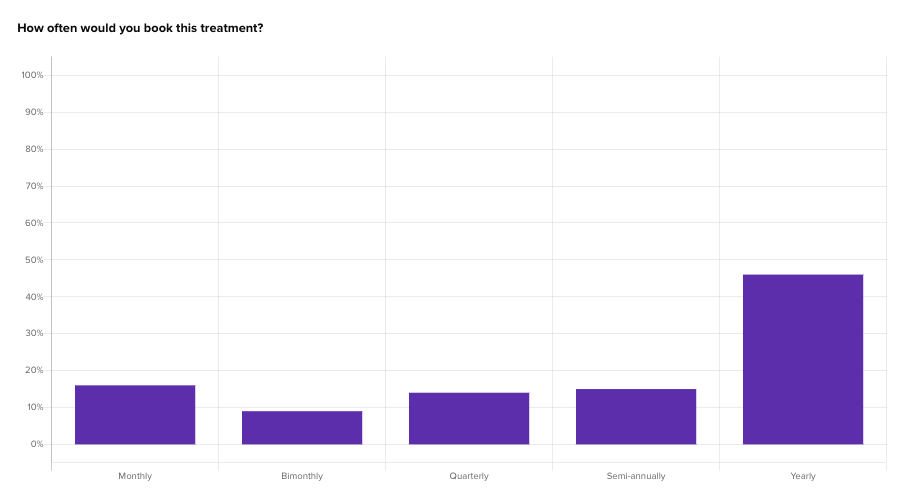
Four question types were asked in each test to gauge the reaction to that pricing package:
- Satisfaction with the price package
- Occurrence of purchasing the package
- Likelihood to purchase an extra option
- Occurrence of purchasing the extra option
Six different combinations of pricing and treatment options were tested, and then the data from each was entered into a comparison framework to determine where on the spectrum consumers are most likely to purchase.
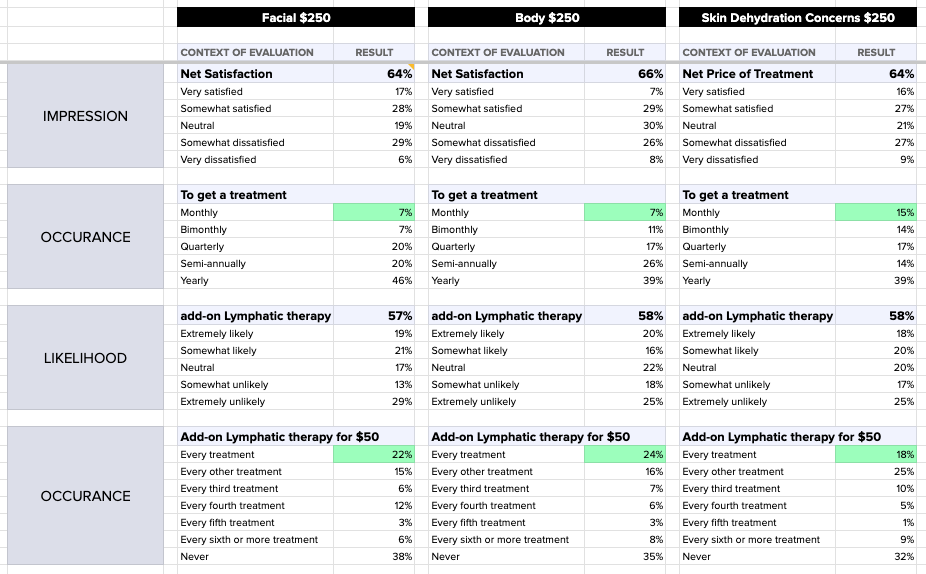
Not surprisingly, the lowest price points produced the highest satisfaction with the offer, and the highest likelihood of adding an extra treatment option to their package. However, something interesting occurred where the highest priced treatment, despite producing the lowest overall satisfaction, showed a very high likelihood for including the extra purchase.
“It doesn’t happen often so I would make the most of it.”
– Beauty Product Consumer (US)
Despite the high prices, some consumers showed a greater likelihood to include an extra purchase with each treatment, due to the importance of the routine.
This purchase decision testing was key in SkinSavvy building a better understanding of how consumers react to their current price points, and how they can better position their treatment packages to encourage conversions.
5. Post-Purchase Evaluation
The journey continues once the purchase is made. The final step in the consumer decision-making process is post-purchase evaluation. This is where you reflect on your purchase and decide whether it met your expectations. It’s a crucial stage that influences future buying decisions and brand loyalty.
Importance of Post-Purchase Evaluation
This stage is all about assessing your satisfaction with the product or service. If the experience is positive, you will likely become a repeat customer and even recommend the product to others. Conversely, a negative experience can lead to returns, complaints, and negative reviews.
- Satisfaction Assessment: You evaluate whether the product met your needs and expectations. Did it solve the problem you had? Is it as good as advertised?
- Feedback and Reviews: Sharing your experience with others through reviews and ratings. This helps other consumers and provides valuable feedback to the business.
- Customer Support Interaction: Contact customer support if you have any issues. How a company handles post-purchase problems can significantly impact your overall satisfaction.
Building Customer Loyalty
For businesses, the post-purchase stage is an opportunity to build loyalty and encourage repeat purchases. Here’s how they can do it:
- Follow-Up Communication: Sending thank-you emails, asking for feedback, and providing tips on using the product can enhance the customer experience.
- Loyalty Programs: Offering rewards for future purchases encourages customers to return. Effective strategies include points systems, discounts on next purchases, and exclusive offers.
- Responsive Customer Service: Quick and helpful responses to post-purchase queries or issues can turn a potentially negative experience into a positive one.
Handling Dissatisfaction
Only some purchases will meet expectations. Here’s how businesses can handle dissatisfaction effectively:
- Return Policies: Clear and hassle-free return policies make it easier for customers to return products they’re unhappy with.
- Problem Resolution: Addressing issues promptly and professionally can salvage a customer relationship. Offering solutions like replacements, refunds, or compensations shows that the business values customer satisfaction.
- Listening to Feedback: Taking customer feedback seriously and improving can prevent future dissatisfaction and show customers that their opinions matter.
Imagine you bought a new pair of headphones. After using them for a week, you evaluate whether they live up to the hype. Are they comfortable? Is the sound quality as good as promised? You might leave a review online, sharing your experience. If satisfied, you might consider buying from the same brand again. If not, you might contact customer service to address any issues.
Helio Example:
We helped the skincare company SkinSavvy conduct a post-purchase evaluation on their full client experience, from booking an appointment, to receiving an in-person treatment, and using the new mobile app to earn loyalty rewards
SkinSavvy organized a limited launch of their new app to skincare providers who already carry their products. Upon release of the app, the Helio team sent 5 of their advocates to engage in secret shopping and uncover early pain points in the usage of their MVP.
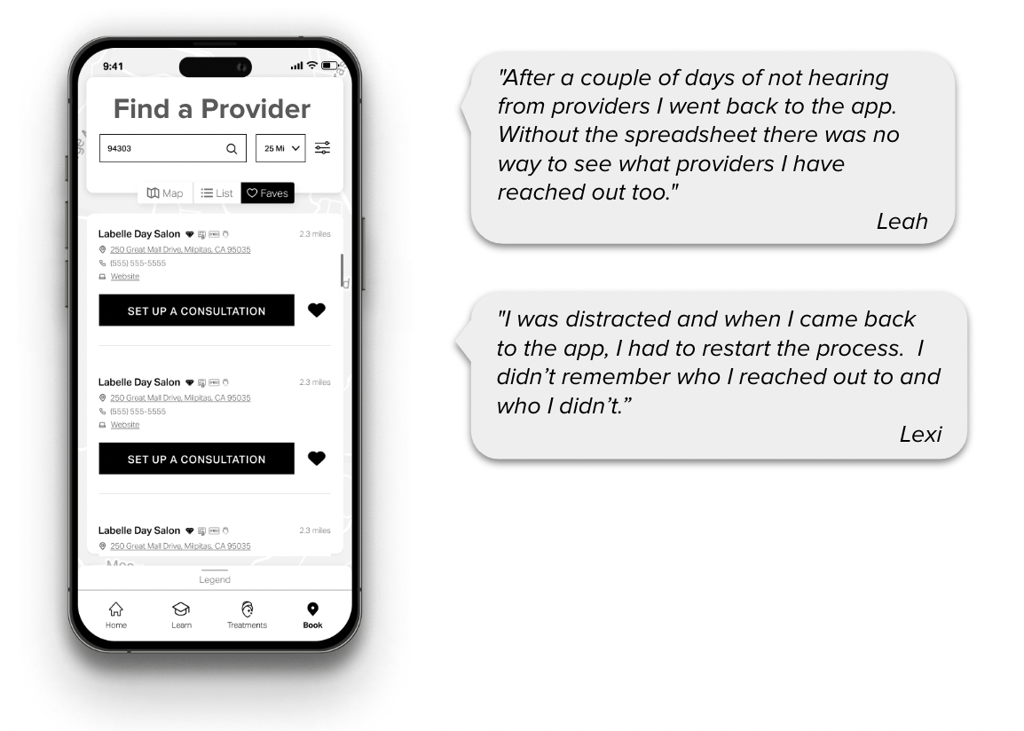
The Helio advocates put the new SkinSavvy app to the test by scheduling appointments through the new platform, following through with in-person treatments, and observing interactions around the app between providers and customers.After reaching out to 30 beauty providers each through the app, and following through with a treatment, Helio advocates conducted interviews with each participant to understand their user experiences:
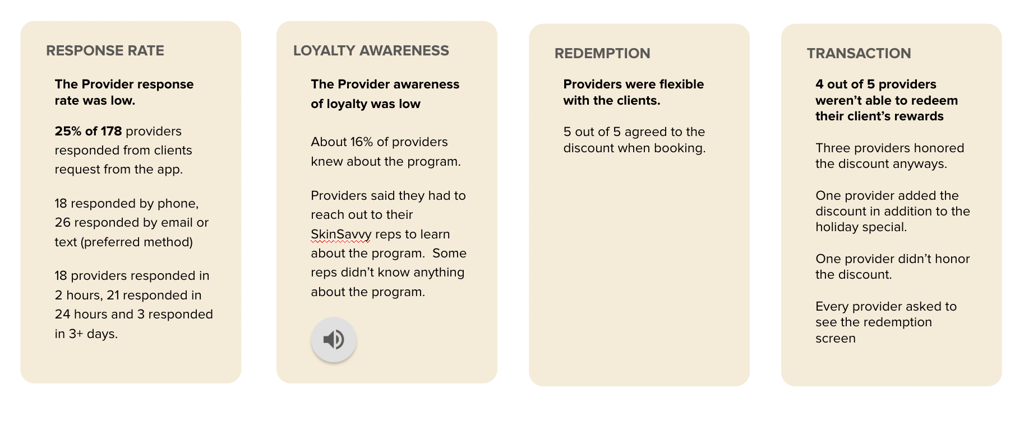
The most impactful insight in this ethnographic study came in the form of hard data, with only 25% of beauty providers contacted through the app actually providing a response.
Interviews with the participants also revealed that the process of completing customer transactions through the app was anything but smooth, with 4 out of 5 providers handling loyalty discounts outside of the platform after treatment.
Bumps in the road are to be expected with early product releases, so the difficulty with SkinSavvy’s MVP release can be alleviated through consistent communication to their customer base. With post-purchase feedback, teams building products like SkinSavvy can elevate their user experience and provide a smoother decision making process for their consumers.
The Impact of Post-Purchase Evaluation on Future Decisions
Your evaluation of a purchase influences your future decisions. A positive experience can lead to brand loyalty and repeat purchases, while a negative experience can push you to look for alternatives. Businesses that excel in this stage can turn one-time buyers into long-term customers.
In summary, post-purchase evaluation is a critical part of the consumer decision making process. It determines customer satisfaction and loyalty. Businesses that actively engage with customers after the purchase, provide excellent customer service, and listen to feedback can build strong, lasting relationships with their customers. This stage not only impacts future buying decisions but also helps businesses improve their products and services based on real customer insights.
Resources
Consumer Decision Making Process Resources
Check out what else we found as we dug deeper into the consumer decision-making process and how to test it! Depending on the stages outlined by the authors, the numbers five and six appear frequently. At the bottom, there is a video from a CEO for your viewing pleasure.
-
Six Questions to Test Your Prospect’s Decision Process
, by
Rachel Clapp Miller
-
Measuring the Consumer Decision-Making Process
, by
Survey Monkey
-
Inside the Mysterious Consumer Decision-Making Process
, by
Lusha
-
5 Stages of the Consumer Decision-Making Process and How it’s Changed
, by
Garrett Mehrguth
Buyer’s Characteristics
Understanding the buyer’s personal characteristics is key to predicting their behavior and tailoring marketing strategies accordingly. Helio is a great way to build personas based on real input from a targeted audience.
Personal Factors
- Beliefs and Values: Deeply held beliefs and values shape consumer behavior. For example, eco-conscious consumers prefer sustainable products.
- Attitudes: Positive or negative attitudes toward a brand or product affect the likelihood of purchase. Marketing efforts often aim to improve consumer attitudes.
- Knowledge: The amount of information a consumer has about a product can influence their decision-making process. More informed consumers make more deliberate choices.
- Motives: Underlying motives, such as the need for security, comfort, or status, drive purchasing decisions.
- Perceptions: How consumers perceive a product based on their experiences and marketing messages impacts their choice.
- Lifestyle: A consumer’s way of living, including their interests and activities, influences their buying behavior. Products that fit seamlessly into their lifestyle are more appealing.
Behavioral Segmentation
- Complex Buying Behavior: Involves a high level of consumer involvement in the purchase and significant differences between brands. Example: Buying a car.
- Dissonance-Reducing Buying Behavior: High involvement but few differences between brands. Example: Buying a home appliance.
- Habitual Buying Behavior: Low involvement and few perceived differences between brands. Example: Purchasing everyday items like toothpaste.
- Variety-Seeking Buying Behavior: Low involvement but significant perceived differences between brands. Example: Trying out different snacks.
Helio Example
To understand the consumer banking market more clearly, we used Helio testing to develop distinct personas that represent ideal customer profiles (ICP) for the theoretical financial company called Banko.
This is where the data filtering shown earlier in Banko’s customer research was most powerful for segmenting their audience and understanding different user perspectives.
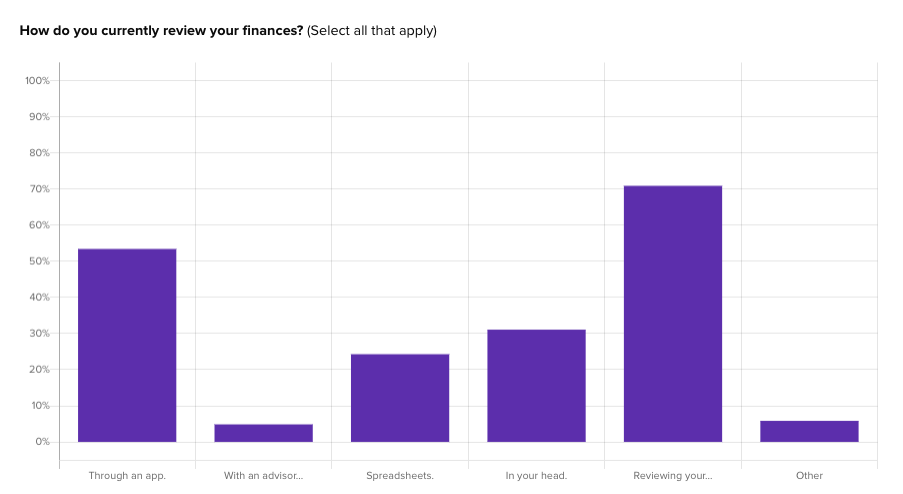
Experience questions were used to gauge what types of actions Banko’s audience currently take when it comes to their finances:
With responses about their experiences gathered, the Banko team then used Helio’s data filters to isolate specific demographic segments that they believed might yield different results:
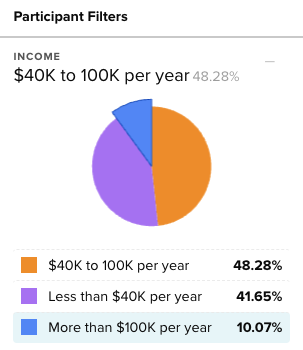
Once the responses are filtered, Helio’s data reports reveal the difference in answers between the new filtered group and the overall audience:
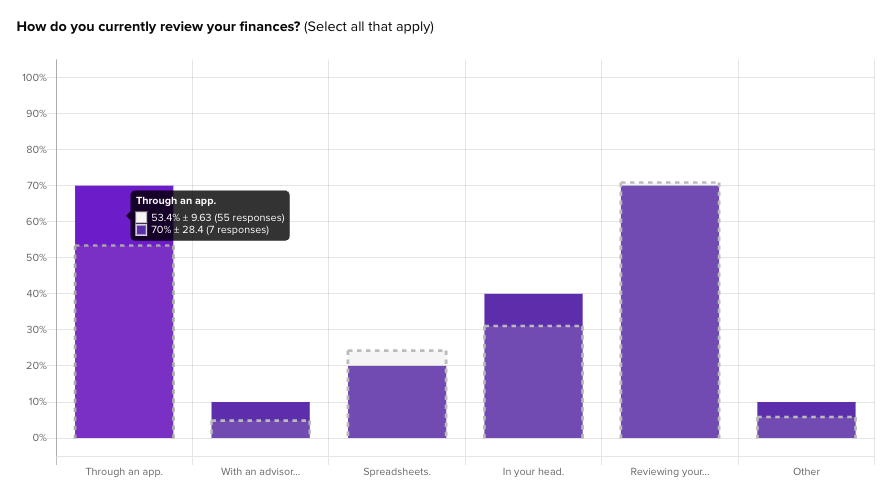
For instance, Banko found that participants with higher incomes over $100k/year are actually much more likely to use an app to track their finances right now.
As the differences in these segments are revealed, the Helio team helped Banko load their results into a Persona framework:
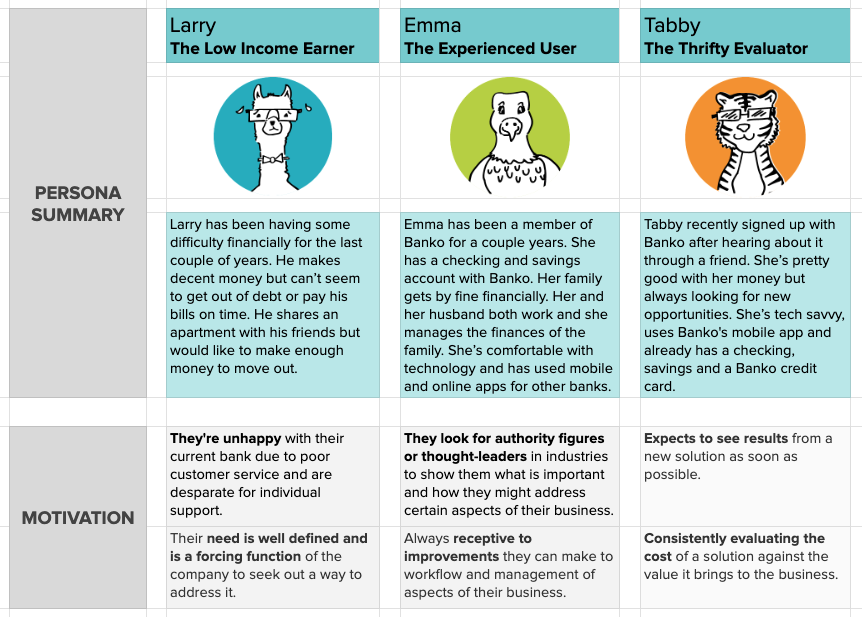
As Banko continues to refine these personas, they will be most key to their marketing efforts and understanding how they can speak to different consumer segments most effectively.
View the Banko Persona Framework
Consumer Decision Making Process FAQ
The consumer decision-making process is a series of steps that consumers go through when deciding to purchase a product or service. These steps typically include need recognition, information search, evaluation of alternatives, purchase decision, and post-purchase evaluation. Understanding this process helps businesses tailor their marketing strategies to effectively meet consumer needs.
Need recognition can be triggered by internal factors like personal desires or problems and external factors like advertisements or recommendations. Internal triggers arise from within, such as feeling hungry or realizing an old product no longer meets your needs. External triggers come from outside influences, like seeing an ad for a new smartphone or hearing a friend’s recommendation for a restaurant.
Consumers search for information through internal and external sources. Internal search relies on memory and past experiences, while external search involves gathering information from friends, family, online reviews, advertisements, and other public sources. In the digital age, search engines and social media play a significant role in the information search process.
During the evaluation of alternatives, consumers consider factors such as price, quality, brand reputation, and reviews. Psychological factors like personal preferences and biases, social factors like peer recommendations, and situational factors like urgency also play a role. Businesses can influence this stage by highlighting their unique selling points and leveraging customer testimonials.
Businesses use various techniques to influence purchase decisions, including marketing strategies like discounts and promotions, personalized marketing messages, and effective product page designs. Overcoming barriers to purchase, such as offering flexible payment options and providing clear information, can also help convert leads into customers.
Post-purchase evaluation is crucial because it determines customer satisfaction and influences future buying decisions. A positive experience can lead to repeat purchases and brand loyalty, while a negative experience can result in returns, complaints, and negative reviews. Businesses can enhance post-purchase satisfaction through follow-up communication, responsive customer service, and loyalty programs.
External factors such as economic conditions, technological advancements, political stability, cultural norms, and demographic trends significantly impact consumer decisions. Economic factors affect purchasing power and choices, while technological advancements change how consumers search for information and make purchases. Cultural and demographic factors shape preferences and needs, influencing the overall decision-making process.




