Understanding Gap Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide
In today’s fast-paced business environment, organizations must assess their current performance and identify areas for improvement. This is where gap analysis comes into play. This comprehensive guide will provide you with an in-depth understanding of gap analysis, its purpose, key components, processes, different types, and the benefits it offers.
🔩 The Nuts and Bolts:
- Gap analysis is a systematic approach used to compare a business’s current state with its desired state to gain insights and develop strategies.
- It provides a structured framework for evaluating performance, setting SMART goals, developing action plans, and monitoring progress.
- The process involves data collection, analysis, goal-setting, action plan development, implementation, and evaluation.
- Additionally, different types of gap analysis, such as market, product, and skill gap analyses, can be conducted.
- The benefits of performing a gap analysis include strategic planning advantages, efficiency improvements, and risk management.
Defining Gap Analysis
Gap analysis is a systematic approach businesses use to compare their current state with a desired state. It involves identifying the gaps or differences between the two and developing strategies to bridge them. Organizations can gain valuable insights into their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats by conducting a gap analysis.
Gap analysis is a powerful tool that allows businesses to assess their current situation and make informed decisions about their future. It provides a structured framework for evaluating performance and identifying areas for improvement. By understanding the gaps between the current state and the desired state, organizations can develop targeted action plans to achieve their goals.
The Purpose of Gap Analysis
The primary purpose of conducting a gap analysis is to determine the steps necessary to achieve a desired future state. It helps organizations set realistic goals and develop effective action plans. By understanding the gaps, businesses can make informed decisions, allocate resources wisely, and improve overall performance.
Gap analysis serves as a roadmap for organizations, guiding them toward their desired outcomes. It helps businesses identify the specific areas that need improvement and provides a clear direction for achieving success. By conducting a thorough analysis, organizations can better understand their current capabilities and identify growth opportunities.
Key Components of Gap Analysis
Several key components make up a gap analysis. To start,
- Data Collection: Gathering relevant information about the current state and desired state. Data collection is a crucial step in the gap analysis process. It involves gathering comprehensive and accurate information about the current state of the organization and the desired state. This information can be collected through various methods, such as survey intercepts, interviews, and data analysis. Organizations can ensure that their analysis is based on reliable information by collecting relevant data.
- Data Analysis: Analyzing the collected data to identify discrepancies and gaps. Data analysis examines the collected data to identify discrepancies and gaps between the current state and the desired state. This involves comparing the data points, identifying patterns, and drawing meaningful insights. Organizations can gain a deeper understanding of the gaps by analyzing the data and developing strategies to bridge them.
- Goal Setting: Setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals. Goal setting is a critical component of the gap analysis process. It involves setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals that align with the desired state. Organizations can set SMART goals to ensure that their objectives are clear, actionable, and attainable. This step helps organizations focus their efforts and resources on the most critical areas for improvement.
- Developing Action Plans: Creating detailed plans to bridge the identified gaps and achieve the desired state. Developing action plans is the next step in the gap analysis process. It involves creating detailed plans to bridge the identified gaps and achieve the desired state. These action plans outline the steps, resources, and timelines to close the gaps. Organizations can develop detailed action plans to ensure that their efforts are focused and coordinated.
Execution looks like:
- Implementation: Executing the action plans and monitoring progress. Implementation is a crucial phase in the gap analysis process. It involves executing the action plans and monitoring progress towards closing the gaps. This requires effective coordination, communication, and resource allocation. By implementing the action plans, organizations can start making tangible progress toward their desired state.
- Evaluation: Continuously assessing the effectiveness of the implemented strategies and making necessary adjustments. Evaluation is an ongoing process in the gap analysis journey. It involves continuously assessing the effectiveness of the implemented strategies and making necessary adjustments. This requires monitoring key performance indicators, gathering feedback, and analyzing the results. By evaluating the progress, organizations can identify areas for improvement and make informed decisions to ensure the success of their gap analysis efforts.
Build something your buyers *truly* want
Subscribe to Closing the Gap—a newsletter to help makers and doers get closer to customers. Learn more.
We believe in protecting your data. Here’s our Privacy Policy.
The Process of Conducting a Gap Analysis
Now that we understand the key components of a gap analysis, let’s delve into the process. Gap analysis typically involves the following steps:
Identifying Current State
The first step is to assess and document the organization’s current state thoroughly. This involves collecting data on various aspects such as performance metrics, processes, resources, and skills. It’s crucial to involve relevant stakeholders and obtain their input to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the current state.
While identifying the current state, it is important to gather data from multiple sources. This can include conducting interviews with employees at different levels of the organization, reviewing existing documentation and reports, and analyzing relevant data sets. By gathering data from various sources, a more accurate and comprehensive picture of the current state can be obtained.
Furthermore, it is essential to consider both quantitative and qualitative data during the assessment. Quantitative data provides measurable metrics that can be analyzed objectively, while qualitative data offers insights into the subjective experiences and perceptions of individuals within the organization. By combining both types of data, a more holistic understanding of the current state can be achieved.
Defining Desired State
Once the current state is established, the next step is to define the desired future state. This involves setting clear goals and objectives that align with the organization’s strategic vision and addressing any identified gaps. The desired state should be realistic, achievable, and aligned with the organization’s overall strategy.
When defining the desired state, it is important to involve key stakeholders and decision-makers. Their input and perspectives can help ensure that the goals and objectives are aligned with the organization’s vision and values. Additionally, considering the input of stakeholders can help generate buy-in and support for the desired state, increasing the likelihood of successful implementation.
Furthermore, it is crucial to consider external factors when defining the desired state. This includes analyzing industry trends, market conditions, and competitive landscapes. By considering external factors, organizations can ensure that their desired state is not only internally focused but also responsive to external opportunities and challenges.
Analyzing the Gap
In this step, the gaps between the current state and the desired state are analyzed. This involves comparing the collected data, identifying discrepancies, and understanding the root causes of the gaps. It’s important to conduct a thorough analysis to gain a deep understanding of the factors contributing to the gaps.
During the gap analysis, it is essential to consider both internal and external factors. Internal factors may include organizational culture, leadership practices, and internal processes, while external factors may include market conditions, customer demands, and technological advancements. By considering both internal and external factors, organizations can identify the underlying causes of the gaps and develop effective strategies to bridge them.
Additionally, it is important to involve cross-functional teams and subject matter experts during the analysis. Their diverse perspectives and expertise can provide valuable insights into the root causes of the gaps and potential solutions. By fostering collaboration and knowledge-sharing, organizations can ensure a more comprehensive and accurate analysis of the gaps.
Moreover, conducting a risk assessment during the analysis phase can help identify potential obstacles and challenges that may arise while implementing strategies to bridge the gaps. By proactively addressing these risks, organizations can develop contingency plans and mitigate potential negative impacts on the overall gap analysis process.
Different Types of Gap Analysis
Gap analysis can be applied to various areas of a business. Let’s explore some of the different types:
Market Gap Analysis
Market gap analysis focuses on understanding the gaps between customer expectations and the organization’s offerings. Businesses can identify opportunities to meet unmet customer needs and gain a competitive edge by analyzing market trends, customer feedback, and competitor performance.
Product Gap Analysis
Product gap analysis involves assessing the gaps between the features and characteristics of a product or service and customer expectations. By understanding customer preferences and market demands, businesses can enhance their products or services to meet customer needs better and increase customer satisfaction.
Skills Gap Analysis
Skills gap analysis focuses on identifying the gaps between the skills and competencies of employees and the skills required to achieve organizational goals. By assessing the current skill levels, businesses can develop targeted training programs, recruit new talent, or reassign existing resources to bridge the skills gap and enhance overall productivity.
🚀 If you’re using Helio
Use A/B Testing to find concrete ways forward with your team.
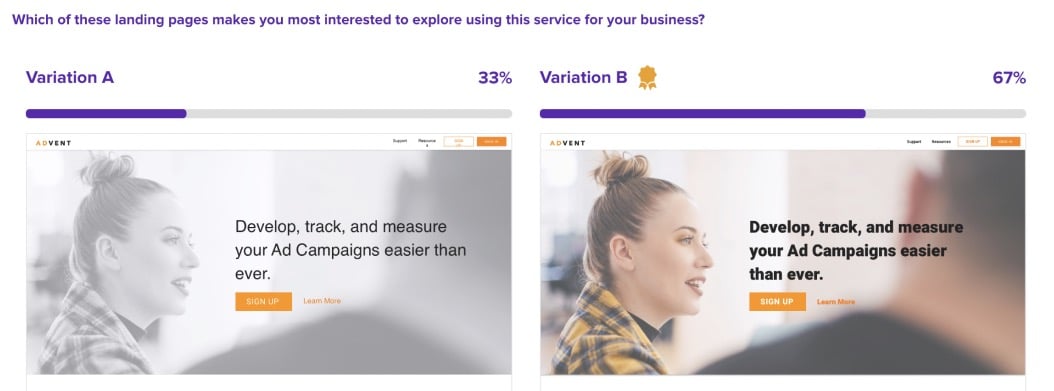
Enhance decision-making and increase the chances of success.
Benefits of Performing a Gap Analysis
Performing a gap analysis offers several benefits for organizations. Let’s explore some of them:
Strategic Planning Advantages
Organizations gain valuable insights that inform their strategic planning process by conducting a gap analysis. It helps them align their goals, resources, and actions to close the identified gaps and achieve their desired future state. This, in turn, enhances decision-making and increases the chances of success.
Efficiency Improvements
Identifying and addressing gaps can lead to significant efficiency improvements. Organizations can streamline operations, reduce waste, and increase productivity by optimizing processes, reallocating resources, or implementing new technologies. This can result in cost savings, improved customer satisfaction, and a competitive advantage.
Risk Management
Gaining a deep understanding of gaps allows organizations to manage risks proactively. By identifying potential risks and developing contingency plans, businesses can mitigate the impact of unforeseen events and maintain operational continuity. This helps build resilience and ensures the organization is prepared for any challenges.
In conclusion, gap analysis is a powerful tool for organizations to assess their current state, identify gaps, and develop strategies to bridge them. By following a systematic process, businesses can set realistic goals, improve efficiency, and achieve their desired future state. Performing a gap analysis offers valuable insights that inform strategic planning, enhance decision-making, and mitigate risks. So, take the time to conduct a gap analysis and unlock your organization’s full potential.
Gap Analysis FAQs
Gap analysis is a systematic approach businesses use to compare their current state with a desired state. It involves identifying the gaps or differences between the two and developing strategies to bridge them.
The primary purpose of conducting a gap analysis is to determine the steps necessary to achieve a desired future state. It helps organizations set realistic goals and develop effective action plans.
The key components of gap analysis are data collection, data analysis, goal setting, developing action plans, implementation, and evaluation.
A gap analysis typically involves identifying the current state, defining the desired state, analyzing the gap, and developing strategies to bridge the gap.
The different types of gap analysis are market gap analysis, product gap analysis, and skills gap analysis.
The benefits of performing a gap analysis include strategic planning advantages, efficiency improvements, and risk management.