Maximizing UX Usability Through Testing
In user experience (UX) design, usability is king. A website, app, or product may have a stunning design and innovative features, but users will quickly become frustrated and look for alternatives if it’s challenging to use. This is where UX usability testing comes into play. By testing the usability of a design, we can identify pain points, gather valuable feedback, and make informed improvements to enhance the overall user experience.
🔩 The Nuts and Bolts:
- UX usability testing is crucial for user satisfaction. Designers can identify and resolve pain points through testing, significantly improving the user experience and fostering loyalty.
- User-centered design hinges on practical UX usability. Designing with the user in mind involves creating interfaces that are not only visually appealing but also intuitive and functional, enhancing overall interaction.
- Different testing methods offer unique insights. From exploratory to A/B testing, each approach helps understand user behavior and preferences, guiding better design decisions.
- Continuous iteration improves product success. Gathering feedback and making informed improvements based on UX testing results can lead to products that exceed user expectations.
- The process involves precise objective setting and user research. Successful UX testing starts with defining goals, choosing the right participants, and creating realistic scenarios to test.
- Analyzing testing results leads to actionable insights. By examining data from usability tests, designers can pinpoint areas for improvement and optimize the user journey.
- Best practices enhance testing effectiveness. Engaging real users who represent the target demographic naturally can yield more accurate and valuable feedback.
Understanding the Importance of UX Usability
Before delving into the details of UX usability testing, it’s crucial to grasp the significance of this aspect of design. UX usability refers to how easily and efficiently users can interact with a product to achieve their desired goals. It encompasses factors like intuitiveness, simplicity, and overall user satisfaction. By prioritizing UX usability, designers can ensure that users have a positive and enjoyable experience, leading to increased engagement and loyalty.
When designing a product, whether it’s a website, a mobile app, or a physical device, the user experience is paramount. Users expect products to be intuitive and effortless, allowing them to accomplish their tasks with minimal effort. A product with poor UX usability can lead to frustration, confusion, and user abandonment. On the other hand, a product with exceptional UX usability can create a seamless and enjoyable experience, fostering user satisfaction and loyalty.
Defining UX Usability
UX usability is more than just a buzzword; it’s a critical component of user-centered design. It involves designing interfaces that are visually appealing but also functional and user-friendly. Simply put, a usable design allows users to navigate effortlessly, find what they need quickly, and accomplish their tasks without jumping through hoops.
When designing for UX usability, it’s essential to consider the target audience and their specific needs and preferences. A design that may be intuitive for one group of users may not be for another. Conducting user research, such as interviews and usability testing, can provide valuable insights into users’ behaviors, expectations, and pain points. This information can then be used to inform the design process and create a user experience that is tailored to the target audience.
The Role of UX Usability in User Satisfaction
UX usability directly impacts user satisfaction. When a product is easy to use and meets users’ needs, it fulfills its purpose and leaves a lasting positive impression. On the flip side, if users need help understanding how to accomplish tasks or encounter frequent roadblocks, they will likely become frustrated and abandon the product altogether. By prioritizing UX usability, designers can cultivate a sense of trust and satisfaction among users, encouraging them to continue using and advocating for the product.
User satisfaction is closely tied to the overall success of a product. Satisfied users are likelier to engage with the product, recommend it to others, and become loyal customers. They are also more forgiving of minor flaws or issues that may arise as long as the overall user experience remains positive. In contrast, dissatisfied users are quick to voice their frustrations and may actively discourage others from using the product.
To ensure high levels of user satisfaction, designers must continuously iterate and improve the UX usability of their products. This involves gathering user feedback, analyzing their behaviors and preferences, and making informed design decisions based on these insights. By actively seeking user input and incorporating it into the design process, designers can create products that meet users’ needs and exceed their expectations.
Build something your buyers *truly* want
Subscribe to Closing the Gap—a newsletter to help makers and doers get closer to customers. Learn more.
We believe in protecting your data. Here’s our Privacy Policy.
The Concept of Testing in UX Design
In the world of UX design, testing plays a pivotal role in validating design decisions and avoiding potential pitfalls. Testing allows designers to gather empirical data, identify areas for improvement, and validate or refute assumptions. When it comes to UX usability, testing is an essential step in the design process that helps ensure the final product meets users’ expectations and goals.
Testing in UX design goes beyond simply asking users for their opinions. It involves conducting systematic experiments to measure user behavior, preferences, and performance. By collecting data through testing, designers can make informed decisions and create user-centered designs.
Different Types of UX Testing
UX testing comes in various forms, each serving a unique purpose. One common type is exploratory testing, where users are given tasks to complete while an observer watches and gathers feedback. This type of testing allows designers to observe how users interact with the product and identify any usability issues or pain points.
Another approach is A/B testing, which involves presenting users with different design variations and collecting data on their preferences and performance. By comparing the results of different design variations, designers can determine which design elements are more effective in achieving the desired user outcomes.
Usability testing can also involve remote or moderated sessions, depending on the project requirements and available resources. Remote testing allows designers to reach a wider audience and gather user feedback in different locations. Moderated sessions, on the other hand, involve direct interaction between the participant and the moderator, allowing for more in-depth insights into the user’s thoughts and experiences.
The Process of UX Testing
The process of UX testing typically involves several stages. It begins with defining the objectives of the test and establishing a clear plan. This includes determining what aspects of the design will be tested, what metrics will be measured, and what specific goals the testing aims to achieve.
Next is recruiting participants who reflect the target user demographic. It is important to select participants representing the intended user base to ensure the test results are relevant and applicable. This may involve conducting user research and creating user personas to guide recruitment.
Once the participants are identified, a test script or set of tasks is created to simulate real-world scenarios. These tasks should be designed to evaluate specific design aspects and measure user performance and satisfaction. The test script should be clear and concise, providing participants with instructions that are easy to understand and follow.
During the testing phase, participants are observed, and their interactions are recorded. This can be done through various methods, such as screen recording, eye-tracking technology, or simply taking notes. The goal is to capture the user’s actions, thoughts, and emotions as they navigate the design.
After gathering the necessary data, it is analyzed and interpreted to derive actionable insights for improvement. This involves identifying patterns, trends, and key findings from the test results. The insights gained from UX testing can help designers make informed decisions, prioritize design changes, and iterate on the design to create a better user experience.
Overall, testing is an integral part of the UX design process. It allows designers to validate their decisions, uncover usability issues, and gain valuable insights into the user’s perspective. By incorporating testing into the design workflow, designers can create products that are not only visually appealing but also intuitive, efficient, and enjoyable to use.
Usability Test
Implementing UX Usability Testing
Now that we understand the significance of UX usability testing let’s explore how to implement it effectively in our design process. By following a structured approach, we can ensure that our testing efforts yield meaningful results and drive positive changes.
Preparing for UX Usability Testing
Before conducting UX usability testing, it’s crucial to define the goals and objectives of the test clearly. Determine the specific areas of focus and the target user group. Create tasks or scenarios that are realistic and relevant to the users’ goals. Remember to test not just the design itself but also the interaction flows and overall user journey. Finally, gather any necessary materials, such as prototypes or testing tools, to ensure a smooth testing process.
Conducting UX Usability Testing
During the actual testing phase, creating a comfortable environment for participants is essential. Explain the test’s purpose and reassure them that their feedback is valuable. Encourage participants to “think out loud” as they navigate through the tasks, making note of any issues or confusion they encounter along the way. As an observer, avoid leading participants or providing solutions; instead, focus on observing their natural behavior and collecting unbiased data.
Analyzing UX Usability Testing Results
Once the testing phase is complete, it’s time to analyze the gathered data and derive meaningful insights. The data collected may include metrics like success rates, completion times, and subjective ratings from participants. By examining this data, designers can identify patterns, common pain points, and areas for improvement.
Interpreting UX Testing Data
When interpreting the UX testing data, it’s important to consider both quantitative and qualitative aspects. Look for trends and recurring themes in the participants’ feedback. Identify any major hurdles or critical usability issues that may be impacting the overall user experience. Additionally, take note of positive feedback or moments where participants express satisfaction, as these can inform design decisions and help retain successful elements.
Making Improvements Based on Testing Results
The ultimate goal of UX usability testing is to improve the user experience. Based on the insights gained from the testing results, make necessary adjustments to the design. Address identified usability issues, simplify complex interactions, and optimize the user journey. Iteratively refine the design based on user feedback until the desired level of usability is achieved.
🚀 If you’re using Helio
Iteratively refine the design based on user feedback until the desired level of usability is achieved.
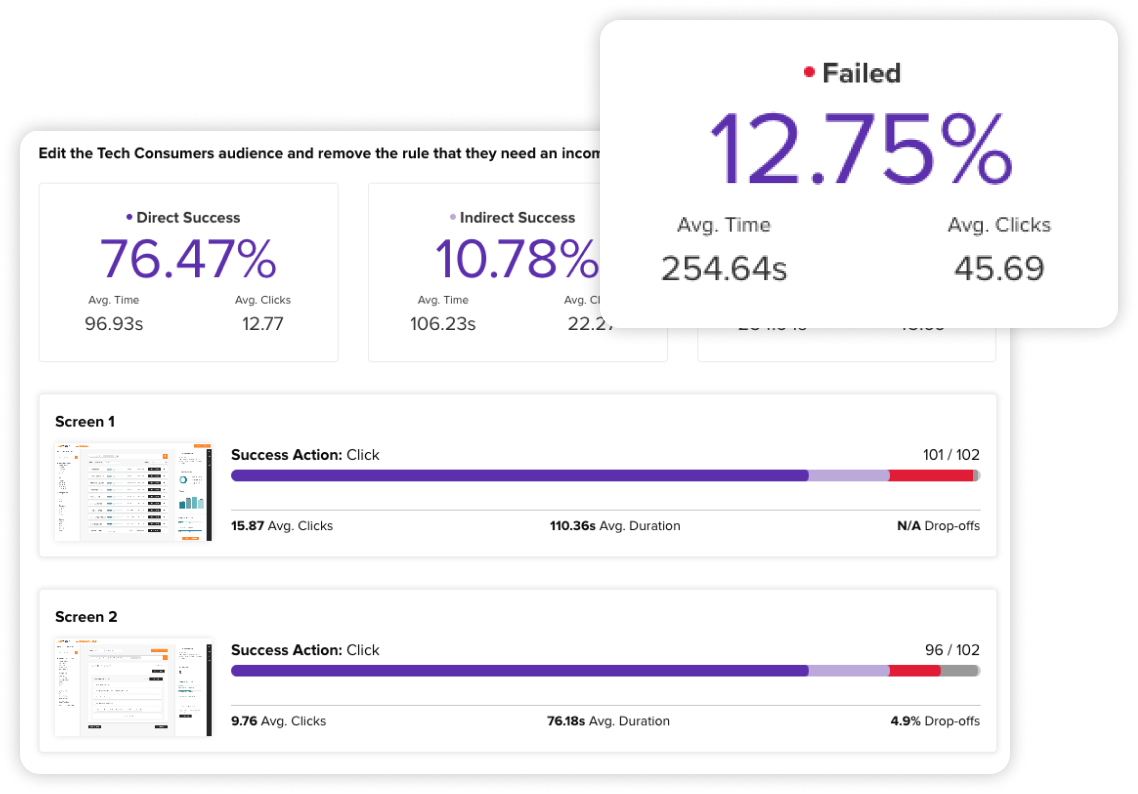
Maximize the impact of the results and drive significant improvements
Best Practices for UX Usability Testing
To ensure effective UX usability testing, it’s important to follow a few best practices. By incorporating these into the testing process, designers can maximize the impact of the results and drive significant improvements in the product’s overall user experience.
Ensuring Effective UX Testing
First and foremost, testing should be conducted with real users who represent the target demographic. The more representative the participants, the more accurate the insights gathered. Creating an environment that mimics real-world usage scenarios as closely as possible is also essential. By observing participants in a natural setting, designers can better understand their needs and pain points.
Avoiding Common UX Testing Mistakes
When conducting UX usability testing, there are a few common mistakes that designers should be aware of and avoid. Creating unbiased tasks that don’t lead participants toward specific solutions is crucial. Similarly, avoid asking leading questions that may influence participants’ responses. Additionally, be mindful of not oversimplifying or overcomplicating the testing process, as both approaches can skew the test results.
By embracing UX usability testing as an integral part of the design process, designers can create products that look visually stunning and provide a seamless and enjoyable user experience. The insights gained through testing empower designers to make informed decisions, refine their designs, and ultimately deliver products that maximize UX usability and user satisfaction.
UX Usability Testing FAQs
UX usability testing involves evaluating a product’s interface to ensure it’s easy for users to navigate and use, aiming to enhance the overall user experience.
It helps identify usability issues before a product goes to market, ensuring that users find it intuitive and satisfying.
Ideally, a mix of UX researchers, designers, and product managers should be involved to cover all aspects of the user experience.
It should be conducted at multiple stages of the design process, from initial concepts to final products, to improve usability continuously.
Define clear objectives, select tasks representing real user scenarios, and choose participants that reflect your target audience.
Methods include exploratory testing, A/B testing, and remote and moderated sessions, each providing different insights into user behavior.
Look for patterns and trends in user behavior, success rates, and feedback to identify areas for improvement.
Based on insights, redesign elements to enhance usability, simplify user flows, and address any identified pain points.
Test with real users, create realistic scenarios and avoid leading questions or tasks to get genuine feedback.
Yes, remote testing allows for a broader participant pool and can be as effective as in-person testing when adequately managed.