The Importance of a High-Fidelity Prototype for Effective User Testing
Creating a High-Fidelity Prototype for Your Product. Creating a high-fidelity prototype for your product is an essential step in the product development process. It allows you to test and refine your ideas before investing time and resources into building the actual product. In this article, we will explore the definition and importance of high-fidelity prototyping, the steps involved in creating one, the tools available for this purpose, and some best practices to keep in mind. So, let’s dive in!
🔩 The Nuts and Bolts:
- High-fidelity prototypes simulate real user experiences. They offer a detailed representation of the final product, including visuals, interactions, and functionality, allowing accurate feedback.
- They bridge the gap between concept and reality. High-fidelity prototypes help stakeholders and users grasp the design and functionality, providing more insightful feedback for improvement.
- Interactive elements enhance user testing. Adding clickable buttons and navigation to the prototype enables users to experience the product’s flow, helping to refine usability.
- Purpose and scope must be clearly defined. Setting specific goals and features for your prototype ensures that you focus on testing critical aspects relevant to the product’s success.
- Prototyping tools streamline the creation process. Tools like Figma, Adobe XD, and InVision allow designers to create interactive prototypes while facilitating collaboration with stakeholders.
- Iterative testing refines the user experience. Constant testing and feedback loops help identify pain points, leading to improved user experiences before full-scale development.
Understanding High-Fidelity Prototyping
High-fidelity prototyping involves creating a prototype that closely resembles the final product in terms of its look, feel, and functionality. It aims to simulate the user experience as realistically as possible. Unlike low-fidelity prototypes, which are quick and basic representations of an idea, high-fidelity prototypes provide a more detailed and interactive experience. This helps designers and developers gather more accurate feedback from stakeholders and users.
When it comes to high-fidelity prototyping, attention to detail is key. Designers meticulously craft the prototype, ensuring that every element, from the color scheme to the typography, is consistent with the intended final product. This level of fidelity allows stakeholders and users to get a true sense of what the end result will look like.
Furthermore, high-fidelity prototypes go beyond just visual representation. They incorporate interactive elements, such as clickable buttons and navigation menus, to mimic the functionality of the final product. This interactivity enables users to navigate through different screens and perform actions, providing a more immersive and realistic experience.
Definition and Importance of High-Fidelity Prototyping
High-fidelity prototyping refers to the process of creating a highly realistic and interactive prototype for your product. It allows you to visualize the final product and test its functionality before moving forward with development. By investing time and effort into creating a high-fidelity prototype, you can identify and address any design flaws or usability issues early on, saving time and resources in the long run.
One of the key benefits of high-fidelity prototyping is its ability to gather valuable feedback from stakeholders and users. With a prototype that closely resembles the final product, stakeholders can better understand the product concept and provide more insightful feedback. This feedback can then be used to refine the design and improve the user experience, ensuring that the final product meets the needs and expectations of its intended audience.
Moreover, high-fidelity prototyping allows for effective communication and collaboration among team members. By having a tangible representation of the product, designers, developers, and other stakeholders can have more meaningful discussions and make informed decisions. This collaborative approach helps streamline the development process and ensures that everyone is aligned on the vision and goals of the product.
Differences between Low-Fidelity and High-Fidelity Prototyping
While low-fidelity prototyping serves its purpose during the early stages of product ideation, high-fidelity prototyping takes it a step further. High-fidelity prototypes offer a more accurate representation of the final product’s design, functionality, and user experience. They include detailed graphics, interactive elements, and sometimes even simulated data. This level of fidelity helps stakeholders and users better understand the product concept and provide more insightful feedback.
Low-fidelity prototypes, on the other hand, are quick and basic representations of an idea. They are often created using simple tools like pen and paper or digital wireframing software. These prototypes focus more on the overall structure and flow of the product, rather than the visual details. While low-fidelity prototypes are useful for exploring different ideas and concepts, they may not provide a realistic representation of the final product, making it harder for stakeholders and users to fully grasp the intended experience.
High-fidelity prototyping, with its attention to detail and interactive elements, bridges the gap between concept and reality. It allows designers and developers to iterate on the design, test the functionality, and gather feedback early in the development process. By creating a high-fidelity prototype, you can ensure that the final product meets the desired standards of aesthetics, usability, and overall user experience.
Make your design decisions count.
Subscribe to Design Under Pressure. Get insights, UX metrics, and tools for bold, informed design.
We respect your inbox. Just insights. No fluff. Privacy Policy.
Steps to Create a High-Fidelity Prototype
Creating a high-fidelity prototype involves a series of iterative steps. Let’s explore each of these steps in detail.
Identifying the Purpose and Scope of Your Prototype
Before diving into the prototyping process, it’s crucial to identify the purpose and scope of your prototype. What specific features or interactions do you want to test? What user flows need to be simulated? Having a clear understanding of the goals you want to achieve with your prototype will guide your design decisions and ensure that you focus on the most important aspects.
For example, if you are creating a high-fidelity prototype for a mobile banking app, you might want to test the process of transferring funds between accounts, checking account balances, and setting up recurring payments. By identifying these specific features, you can tailor your prototype to address these functionalities and gather valuable insights from user testing.
Additionally, considering the scope of your prototype is essential. Are you creating a prototype for a single screen or multiple screens? Will it cover the entire user journey or focus on a specific section of your product? Defining the scope will help you allocate your time and resources effectively.
Sketching and Wireframing Your Ideas
Once you have a clear goal in mind, it’s time to start sketching and wireframing your ideas. This step helps you create a rough visual representation of your product’s interface and layout. You can use pen and paper or digital tools to quickly iterate on different design concepts.
During the sketching and wireframing phase, it’s important to consider the overall structure, content placement, and interactions. Think about how different elements will be organized on the screen, how users will navigate through the interface, and how they will interact with various components. By focusing on these aspects, you can create a solid foundation for your high-fidelity prototype.
For instance, if you are designing a high-fidelity prototype for an e-commerce website, you might sketch out different layouts for the product listing page, including options for grid or list views, filters, and sorting mechanisms. This process allows you to explore various design possibilities and select the most effective solution.
Adding Interactivity to Your Prototype
Now that you have a solid foundation with your wireframes, it’s time to add interactivity to your prototype. Depending on the complexity of your product, you can use prototyping tools to create interactive elements like buttons, forms, and navigation menus.
During this phase, it’s important to focus on usability and intuitiveness. Ensure that the interactions you simulate in your high-fidelity prototype accurately represent how users would interact with the final product. For example, if you are designing a mobile app, make sure that the swipe gestures, button taps, and form inputs mimic the expected behavior.
By adding interactivity, you can test the flow of your product and gather feedback on the user experience. This step allows you to identify any potential usability issues or areas for improvement before investing time and resources into development.
Testing and Refining Your Prototype
Testing is a critical step in the prototyping process. Once you have a functional high-fidelity prototype, gather feedback from users, stakeholders, and your development team.
Observe how users interact with your prototype and note any pain points or areas of improvement. Pay attention to their reactions, facial expressions, and comments to gain insights into their experience. This feedback can help you refine your design and make necessary changes to enhance the overall user experience.
For example, if users struggle to find a particular feature or feel confused about the navigation, you can iterate on your design to make it more intuitive and user-friendly. By continuously testing and refining your prototype, you can ensure that your final product meets the needs and expectations of your target audience.
Remember, the prototyping process is not a one-time event. It’s an iterative cycle that allows you to gather feedback, make improvements, and iterate on your design until you achieve the desired outcome.
UX Terms
Tools for High-Fidelity Prototyping
There are numerous prototyping tools available in the market, each offering different features and capabilities. Here’s an overview of some popular tools:
Overview of Popular Prototyping Tools
Figma: A collaborative design tool with powerful prototyping features.
Adobe XD: A comprehensive design and prototyping tool commonly used by designers and developers.
InVision: A prototyping tool that allows you to create interactive mockups and gather feedback from stakeholders.
Proto.io: A user-friendly tool that supports both low and high-fidelity prototyping.
Selecting the Right Tool for Your Needs
When choosing a prototyping tool, consider factors such as ease of use, collaboration features, and compatibility with your existing workflow. It’s important to select a tool that aligns with your specific needs and preferences, as this will greatly influence the efficiency and effectiveness of your prototyping process.
🚀 If you’re using Helio
Test your Figma prototypes.
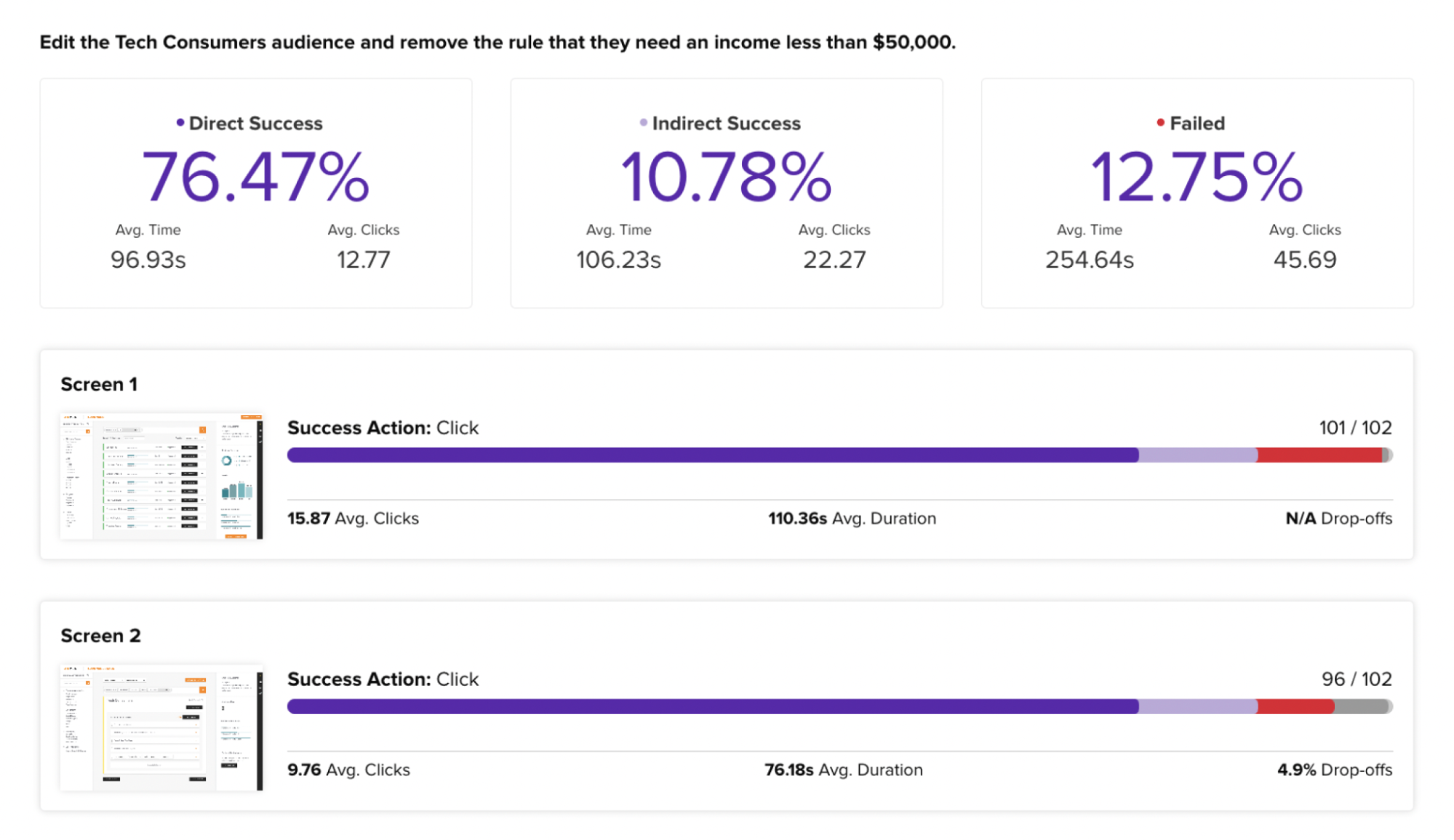
Focus on creating an intuitive and user-friendly experience.
Best Practices for High-Fidelity Prototyping
To make the most out of your high-fidelity prototyping process, keep the following best practices in mind:
Keeping User Experience in Mind
Design your prototype with the end-user in mind. Focus on creating an intuitive and user-friendly experience. Use realistic content, visuals, and interactions that replicate the final product as closely as possible. This will provide users with a more accurate representation of what to expect.
Iterating and Improving Your Prototype
Prototyping is an iterative process. Use the feedback you receive from stakeholders and users to iterate on your design and continuously improve your prototype. Don’t be afraid to make changes and experiment with different ideas. Remember, the goal is to gather insights and refine your product concept.
Collaborating with Your Team Effectively
Collaboration is key during the prototyping process. Encourage open communication and gather input from all stakeholders. Share your prototype with your team and gather their feedback. This collaborative approach will help identify any blind spots and ensure that your prototype aligns with the overall vision of the product.
Creating a high-fidelity prototype is a valuable step in product development. It allows you to save time, reduce costs, and gather vital feedback before moving forward with the actual product development. By following the steps outlined in this article and incorporating best practices, you can create a compelling and user-centered prototype for your product. So, go ahead and start bringing your product ideas to life!
High-Fidelity Prototype FAQs
A high-fidelity prototype is a detailed, interactive model of a product that closely simulates its final design and functionality. It includes visual elements, clickable interactions, and mimics the user experience, helping designers gather actionable feedback.
A high-fidelity prototype is a more advanced, detailed, and interactive version of the product compared to a low-fidelity prototype. Low-fidelity prototypes are basic sketches or wireframes used for early-stage brainstorming, while high-fidelity prototypes resemble the final product more closely.
High-fidelity prototyping allows designers to test the look, feel, and functionality of a product before development. It helps gather precise feedback, identify usability issues, and refine the design, saving time and resources in the long run.
The steps include identifying the purpose and scope of the prototype, sketching and wireframing the layout, adding interactivity to mimic user behavior, and then testing and refining based on user feedback. Iteration is key to improving the prototype.
Popular tools include Figma, Adobe XD, InVision, and Proto.io. These tools provide features for creating detailed, interactive prototypes and offer collaboration capabilities for teams and stakeholders.
You can gather feedback by conducting usability tests with real users or stakeholders, observing how they interact with the prototype, and collecting their reactions and comments. This feedback will guide improvements and refinements to the design.
Key practices include focusing on the user experience, using realistic content and interactions, continuously iterating based on feedback, and maintaining open collaboration with your team to ensure alignment on the product’s goals and vision.