Maximizing Design Efficiency with Low-Fidelity Prototypes
Low-fidelity prototyping is a powerful tool in the field of design development. It allows designers to quickly and efficiently gather feedback, collaborate with stakeholders, and make necessary revisions. In this article, we will explore the many advantages of using this, compare them to their high-fidelity counterparts, and discuss how to implement them in your design process. We will also take a glimpse into the future of low-fidelity prototyping and its potential impact on the industry.
🔩 The Nuts and Bolts:
- Low-Fidelity Prototypes Offer Quick, Cost-Effective Solutions. They allow designers to test and validate ideas early without significant investment in time or resources, facilitating rapid iteration.
- Simplicity Drives Effective Collaboration. The straightforward nature of low-fidelity prototypes encourages feedback and communication among stakeholders, leading to more informed design decisions.
- Early Feedback Uncovers Usability Issues. By testing low-fidelity prototypes, designers can identify and address potential problems before progressing to more complex, high-fidelity models.
- Flexibility and Ease of Modification Enhance Design Iteration. Changes can be made swiftly in low-fidelity prototypes, enabling designers to refine concepts based on user feedback efficiently.
- Low-Fidelity Prototypes Encourage Creativity. The lack of technical constraints allows designers to explore innovative solutions that might not emerge in more detailed, high-fidelity prototypes.
- Emerging Technologies Are Shaping the Future of Prototyping. Integrating AR and VR with low-fidelity prototypes could revolutionize how designers evaluate and test concepts in realistic environments.
Understanding Low-Fidelity Prototyping
Before we delve into the benefits, let’s define what they are and explore their key features. Low-fidelity prototypes, also known as lo-fi or paper prototypes, are simplified representations of a design concept. They are often created using basic materials such as paper, sticky notes, or wireframe software.
So, why use low-fidelity prototypes? Well, their main purpose is to quickly test and validate design ideas without investing extensive time and resources. Let’s take a closer look at why they play such a crucial role in design development.
Definition and Key Features of Low-Fidelity Prototyping
This is a rough, simplified version of a design concept. It captures the basic layout, structure, and interactions of a product or interface. Unlike high-fidelity prototypes, which aim to mimic the final product with precise details, low-fidelity prototypes focus more on the overall user experience.
Key features of low-fidelity prototyping include:
Simplicity: Low-fidelity prototypes keep things simple, allowing designers to focus on the core functionality of the design.
Quick Iteration: Due to their low complexity, these prototypes can be created, tested, and revised rapidly, facilitating an iterative design process.
Ease of Modification: Being low-tech in nature, low-fidelity prototypes are effortless to modify and adapt in response to user feedback.
The Role of Low-Fidelity Prototypes in Design Development
Low-fidelity prototypes play a pivotal role in the design development process. They help designers:
Evaluate Design Concepts: By creating low-fidelity prototypes, designers can explore multiple design concepts and identify the most effective ones.
Solicit Feedback: These prototypes enable designers to gather early feedback from users, stakeholders, and team members, leading to valuable insights and improvements.
Facilitate Collaboration: Low-fidelity prototypes serve as a communication tool, fostering collaboration between designers, developers, and other stakeholders in the design process.
Moreover, low-fidelity prototypes also have the advantage of being cost-effective. Since they can be created using simple materials, the financial investment required is minimal. This allows designers to experiment and iterate freely, without the fear of wasting resources.
Another benefit of low-fidelity prototypes is their ability to uncover usability issues early in the design process. By testing these prototypes with users, designers can identify potential problems and make necessary adjustments before moving forward with high-fidelity prototypes or development. This saves time, effort, and resources in the long run.
Furthermore, this encourage creativity and exploration. With their simplified nature, designers are not limited by technical constraints or aesthetic details. This freedom allows them to think outside the box and come up with innovative solutions that may not have been considered otherwise.
In conclusion, these are an invaluable tool in the design development process. They provide a quick, cost-effective way to test and validate design ideas, gather feedback, and foster collaboration. By embracing the simplicity and flexibility of low-fidelity prototyping, designers can create better user experiences and ultimately deliver more successful products and interfaces.
Make your design decisions count.
Subscribe to Design Under Pressure. Get insights, UX metrics, and tools for bold, informed design.
We respect your inbox. Just insights. No fluff. Privacy Policy.
The Advantages of Low-Fidelity Prototypes
Now that we have a better understanding of low-fidelity prototyping, let’s explore the numerous advantages it offers over other prototyping methods.
This serve as a foundational step in the design process, allowing designers to quickly visualize and test multiple concepts. These prototypes are intentionally kept basic and rough, focusing on core functionalities rather than intricate details. This approach helps in identifying potential design flaws early on, saving time and resources in the long run.
Cost and Time Efficiency
Creating these can be expensive and time-consuming. In contrast, low-fidelity prototypes can be produced quickly and at minimal cost. By using simple materials, designers can explore multiple design variations without breaking the bank.
Furthermore, low-fidelity prototypes are ideal for rapid ideation and iteration. Designers can swiftly sketch out ideas, gather feedback, and make necessary adjustments without getting bogged down by intricate design elements. This agile approach fosters creativity and innovation within the design team.
Encouraging Feedback and Collaboration
The simplicity of low-fidelity prototypes encourages users and stakeholders to provide honest feedback. Users feel less intimidated to share their thoughts about a rough prototype, leading to valuable insights that can enhance the design. Additionally, low-fidelity prototypes promote collaboration by facilitating effective communication between designers, stakeholders, and users.
Moreover, the tactile nature of low-fidelity prototypes enhances user engagement during usability testing sessions. Participants are more willing to interact with physical mock-ups, providing designers with real-time feedback on usability and functionality. This hands-on approach creates a more immersive testing environment, resulting in more actionable insights.
Flexibility and Ease of Revision
One of the significant advantages of low-fidelity prototypes is their flexibility. Changes and revisions can be made effortlessly during the design iteration process. Modifying a paper prototype or rearranging sticky notes is far easier than reworking a complex digital prototype.
Additionally, the iterative nature of low-fidelity prototyping allows for quick validation of design assumptions. Designers can rapidly test and refine concepts based on user feedback, ensuring that the final product meets user needs effectively. This iterative cycle of prototyping and testing is crucial in creating user-centered designs that resonate with the target audience.
UX Deliverables
Comparing Low-Fidelity and High-Fidelity Prototypes
While low-fidelity prototypes offer numerous benefits, high-fidelity prototypes have their place in the design process as well. Let’s compare the two and understand when to use each.
Low-fidelity prototypes are like rough sketches of a design idea, focusing more on functionality and structure rather than visual aesthetics. They are quick to create and easy to modify, making them perfect for brainstorming and exploring different concepts without getting bogged down by details. High-fidelity prototypes, on the other hand, are polished and detailed representations of the final product, often created using design tools that closely mimic the actual user interface.
When to Use Low-Fidelity vs. High-Fidelity Prototyping
Low-fi prototyping is ideal during the early stages of design development. It helps designers quickly iterate and gather feedback before investing time and resources in high-fi prototypes. High-fidelity is suitable for testing specific details, refining interactions, and simulating the final product experience.
Deciding between low-fi and high-fi prototypes depends on the goals of the design phase. If the focus is on concept validation and usability testing, low-fidelity prototypes are more appropriate. However, when the design is more refined and requires user testing on intricate interactions and visual elements, high-fidelity prototypes shine.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While low-fi prototypes offer advantages like speed and cost-efficiency, they do come with trade-offs. The lack of visual details and fidelity may lead to difficulties in conveying certain design aspects to stakeholders. It is crucial for designers to find the right balance between low-fidelity and high-fidelity prototyping in their design process.
On the other hand, high-fi’s provide a more realistic representation of the final product, allowing stakeholders to better visualize the end result. However, creating high-fi’s can be time-consuming and costly, especially if major design changes are needed later in the process. Designers must weigh these trade-offs carefully to ensure that the chosen prototyping approach aligns with the project’s objectives and constraints.
Implementing Low-Fidelity Prototyping in Your Design Process
Now that we understand the benefits, let’s explore some practical tips on how to implement it effectively in your design process. Low-fi prototyping is a valuable technique that allows designers to quickly and cost-effectively test ideas and gather feedback early in the design process. By creating rough, simplified versions of a design, designers can focus on the core interactions and functionality without getting bogged down in details.
One key advantage of low-fidelity prototyping is the ability to fail fast and iterate quickly. By testing multiple iterations of a design early on, designers can identify potential issues and make improvements before investing time and resources in high-fidelity prototypes. This iterative approach helps ensure that the final product meets user needs and business goals.
Tools and Techniques for Low-Fidelity Prototyping
There are various tools and techniques available for creating low-fidelity prototypes. From pen and paper to specialized wireframing software, designers can choose the approach that best suits their needs and budget. The key is to keep things simple and focus on the core interactions of the design. Some designers prefer using sticky notes or index cards to quickly sketch out different design ideas, while others opt for digital tools that allow for more detailed wireframes.
When selecting a tool or technique, consider factors such as ease of use, collaboration features, and the ability to quickly iterate on designs. It’s important to choose a method that aligns with your team’s workflow and allows for seamless communication and feedback.
🚀 If you’re using Helio
Test your prototype quickly.
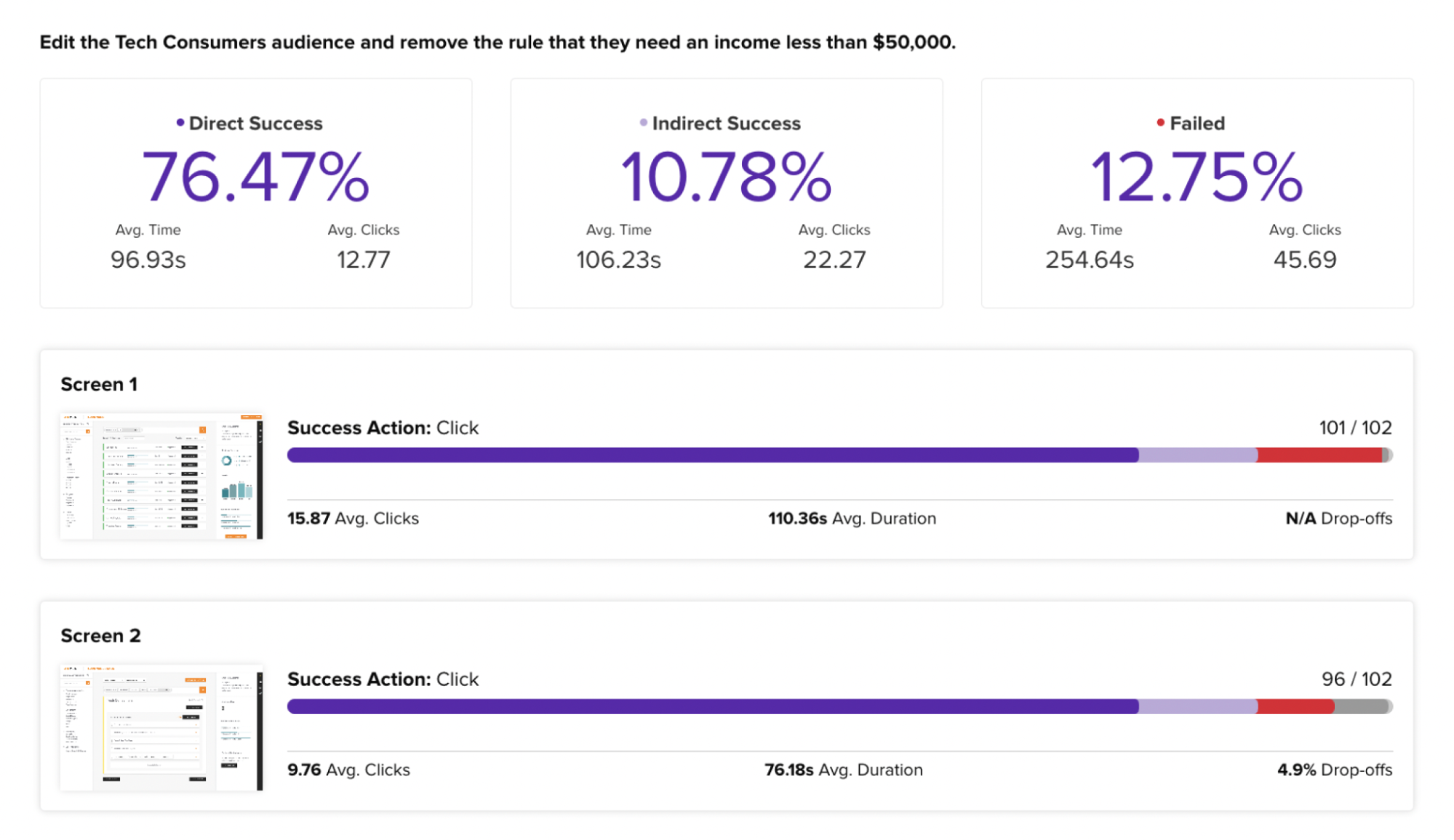
Create multiple iterations to explore different design directions.
Best Practices for Effective Low-Fidelity Prototyping
For successful low-fi prototyping, consider the following best practices:
Start with a clear plan and defined objectives. Outline what you hope to learn from the prototyping process and how it will inform the final design.
Involve stakeholders and users early in the process. By including key stakeholders and potential users in the prototyping phase, you can gather valuable insights and ensure that the design meets their needs.
Create multiple iterations to explore different design directions. Don’t be afraid to experiment with different ideas and approaches to find the best solution.
Test and gather feedback throughout the design cycle. Conduct usability tests and gather feedback from users to identify pain points and areas for improvement.
Iterate based on feedback and insights gained from testing. Use the feedback gathered during testing to make informed design decisions and refine your prototypes.
Use annotation and storytelling techniques to convey the design intent. Clearly communicate the purpose and functionality of your prototypes to stakeholders and users to ensure a shared understanding of the design direction.
The Future of Prototyping
As technology continues to advance, the future of low-fi prototyping looks promising. Let’s discuss some emerging trends and the potential impact of technology on this design practice.
Emerging Trends in Low-Fidelity Prototyping
Emerging trends in low-fidelity prototyping include the integration of augmented reality and virtual reality technologies. These immersive experiences can enhance the evaluation and testing of design concepts, allowing users to interact with low-fidelity prototypes in a more realistic environment.
The Impact of Technology on Low-Fidelity Prototyping
Technology has already revolutionized the way designers create low-fi prototypes. From digital wireframing tools to interactive prototyping software, designers now have more options and capabilities at their disposal. However, it is essential to remember that the core principles of low-fi prototyping, such as simplicity and quick iteration, remain crucial regardless of the technology used.
In conclusion, this offers significant benefits in design development. Its simplicity, cost and time efficiency, and ability to encourage collaboration make it an indispensable tool for designers. By understanding the trade-offs and effectively implementing low-fidelity prototyping in your design process, you can unlock the full potential of this versatile approach. As technology continues to evolve, low-fidelity prototyping will undoubtedly experience exciting advancements and continue to shape the future of design.
Low Fidelity Prototypes FAQs
Low-fidelity prototypes are simplified, rough versions of a design concept, often created using basic materials like paper or wireframe software. They focus on the overall user experience, layout, and structure, allowing designers to quickly test and validate ideas without detailed visuals.
Low-fidelity prototypes are crucial because they enable rapid iteration, cost-effective testing, and early feedback collection. This approach allows designers to explore multiple concepts, uncover usability issues, and make necessary revisions before investing in more detailed, high-fidelity prototypes.
Low-fidelity prototypes focus on core functionality and structure, making them ideal for early-stage design development. In contrast, high-fidelity prototypes provide detailed, polished representations closer to the final product. Each serves a different purpose in the design process, with low-fidelity being better for initial concept validation and high-fidelity for refining and testing detailed interactions.
Low-fidelity prototypes are best used in the early stages of design development when the goal is to explore concepts, gather feedback, and make quick adjustments. They are particularly useful for brainstorming, early user testing, and facilitating collaboration among team members and stakeholders.
Common tools for creating low-fidelity prototypes include pen and paper, sticky notes, index cards, and basic wireframing software like Balsamiq or Sketch. The choice of tools depends on the designer’s preference and the specific needs of the project, with an emphasis on simplicity and ease of modification.&lt;/span></p>
The key benefits include cost and time efficiency, the ability to encourage collaboration and feedback, flexibility in making revisions, and the promotion of creativity by focusing on the essence of the design without being constrained by details.
The future of low-fidelity prototyping is evolving with the integration of technologies like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), which provide more immersive ways to test and evaluate designs. These advancements will likely enhance the effectiveness of low-fidelity prototypes, making them even more valuable in the design process.