Tree testing ensures users find what they need
Use Helio’s tree testing tools to evaluate and optimize the hierarchy and findability of topics in your website or application. Ensure your users can easily navigate and find the information they need.

Enhance User Navigation
Identify the most intuitive structure for your website or application, ensuring users can easily find the information they want.
Improve User Satisfaction
Streamlining navigation enhances overall user satisfaction and reduces frustration, leading to better engagement and retention.
Optimize Content Organization
Organize your content in a way that makes sense to your users, improving usability and accessibility.
Map to UX Metrics
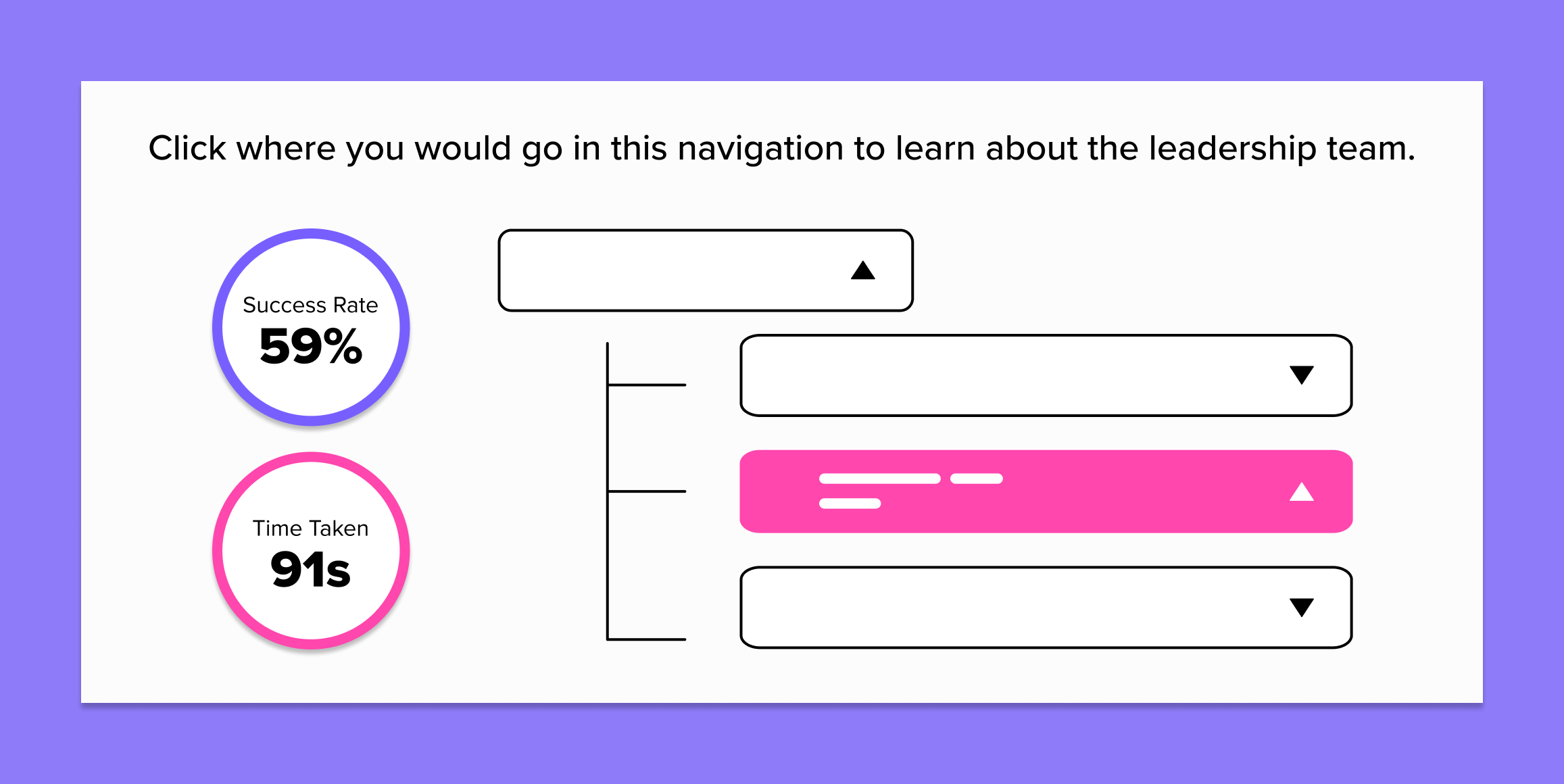
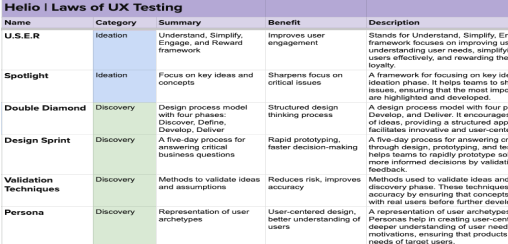
Tree Testing
Comprehension
Time to Completion
Success Rate
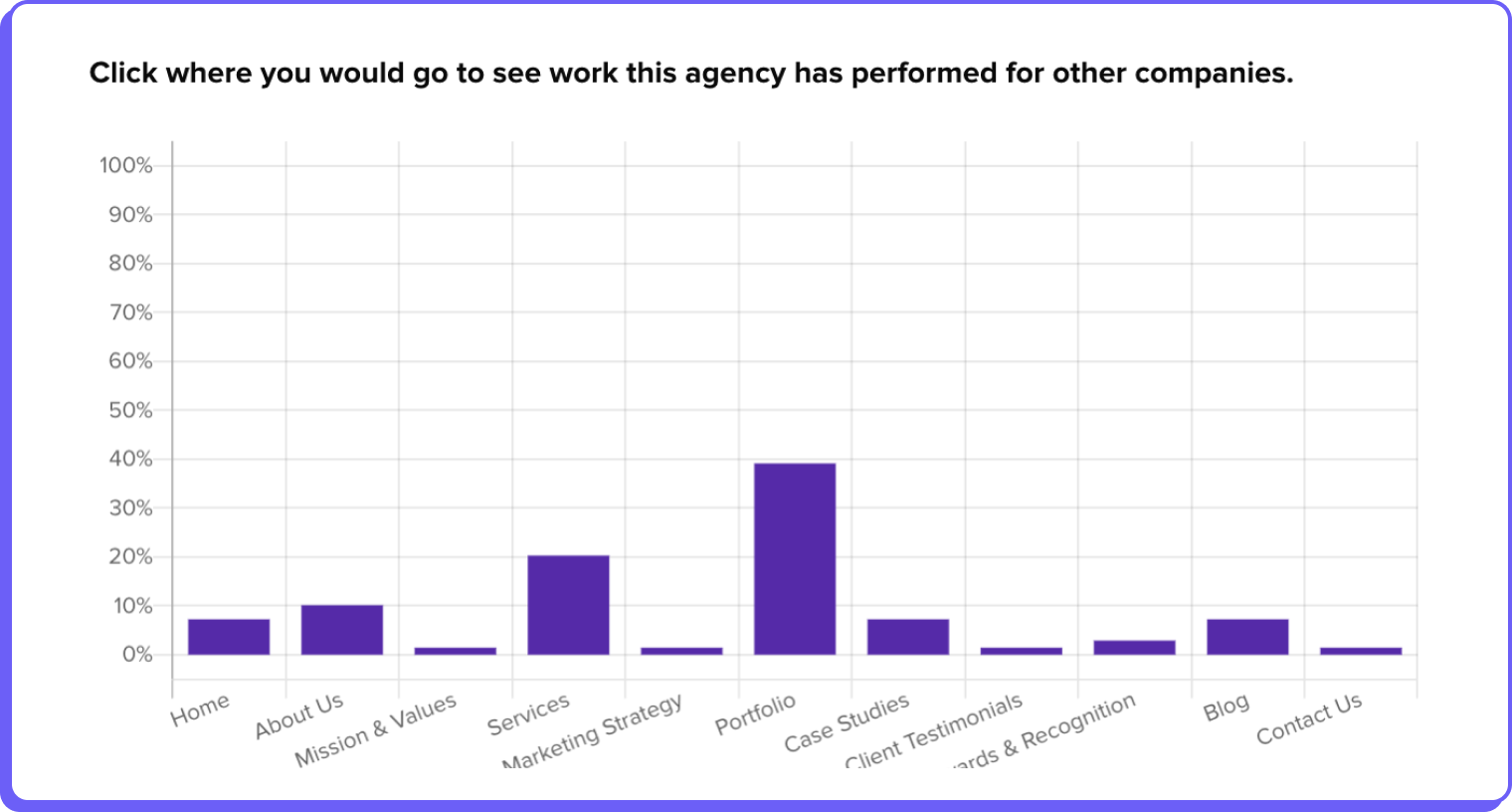
Explore a Relevant Case Study
Business questions that can be addressed with tree testing
Here are some common business questions product and marketing leaders ask that can be addressed with tree testing
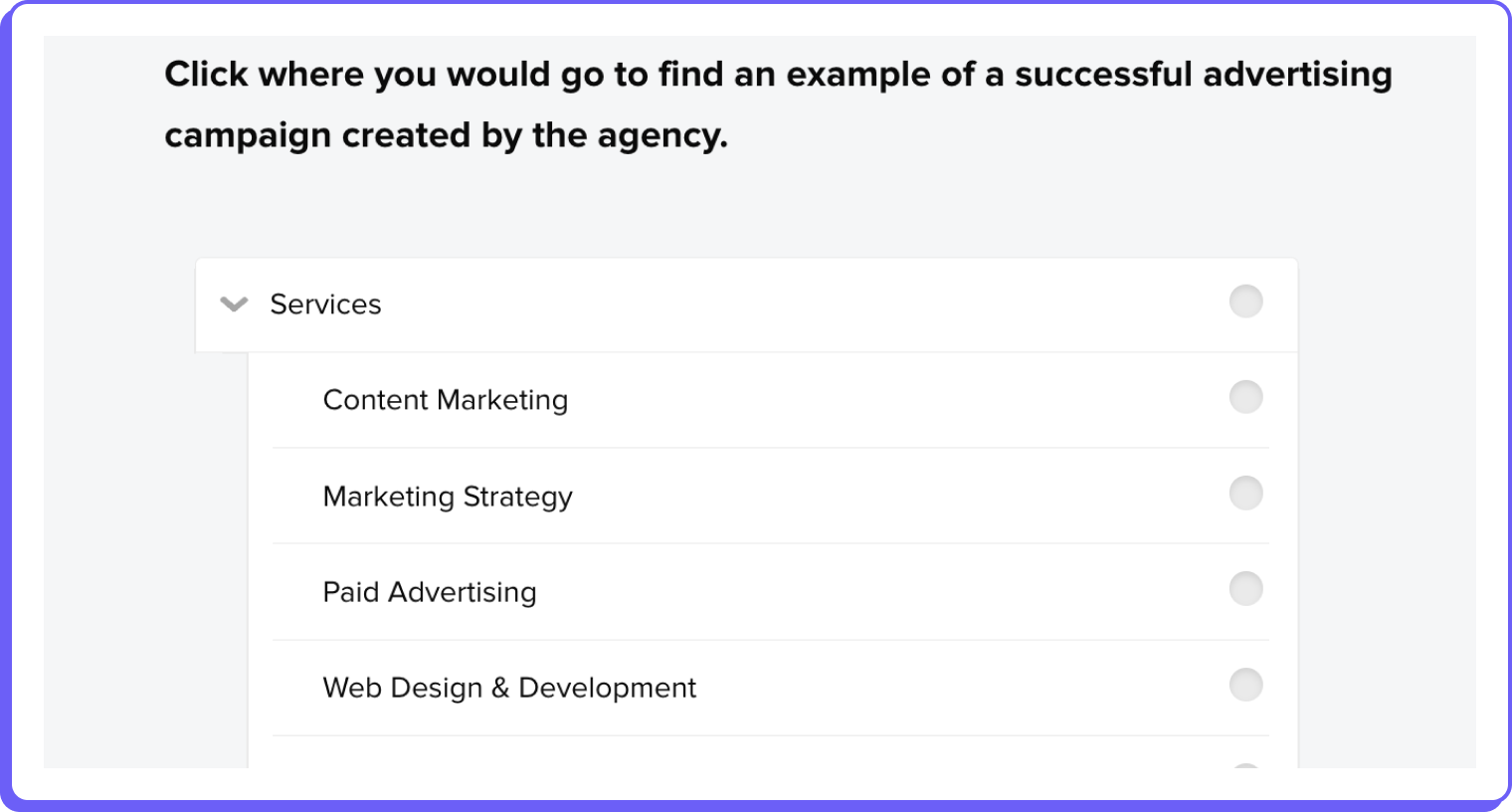
The tree is represented only by its labels and relationships, forcing participants to rely solely on the organization of these labels to navigate. This focus on the hierarchy helps identify whether the categories and labels used are logical and intuitive for users, revealing if the structure of the website aligns with how users expect information to be organized.
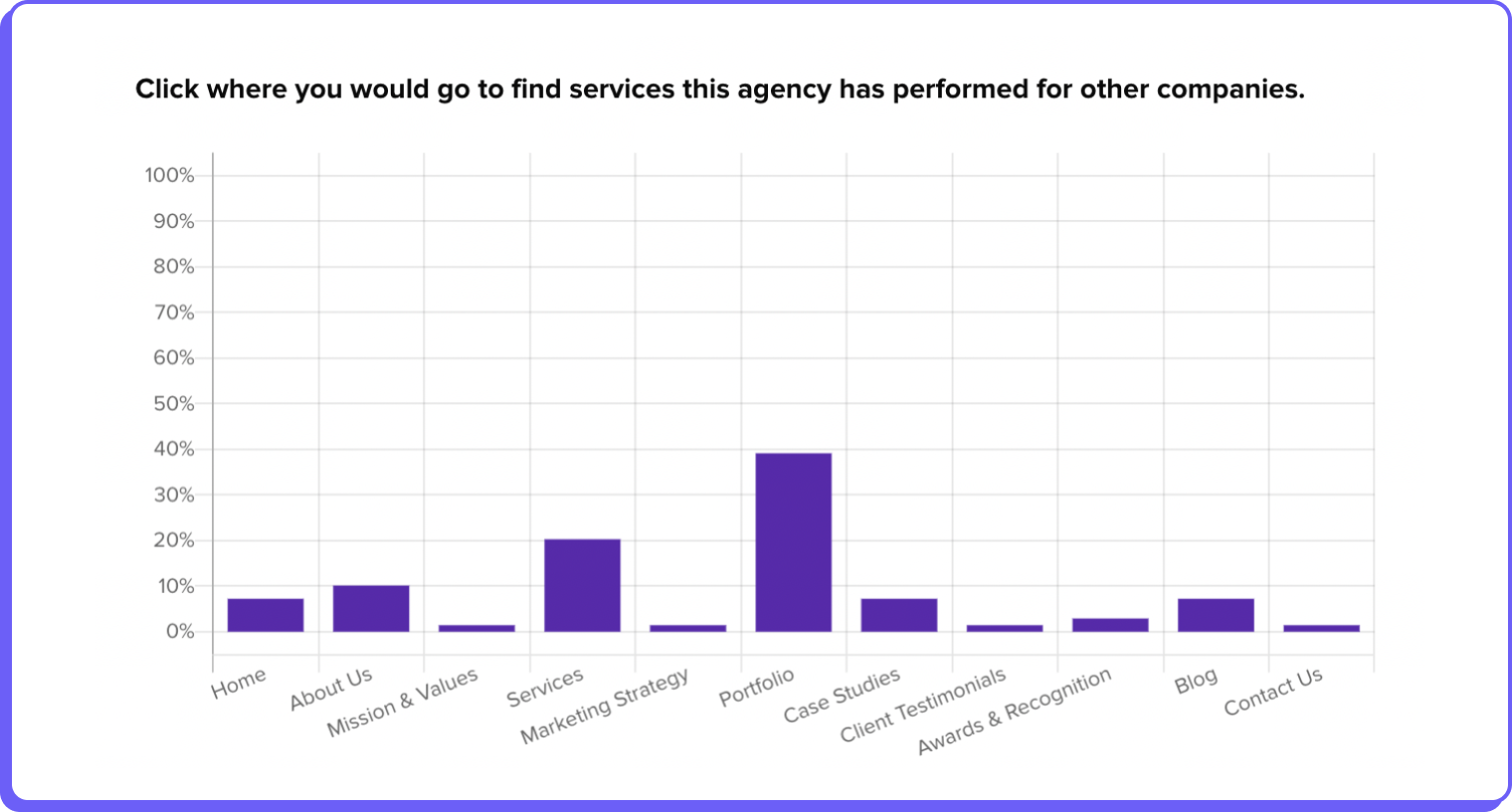
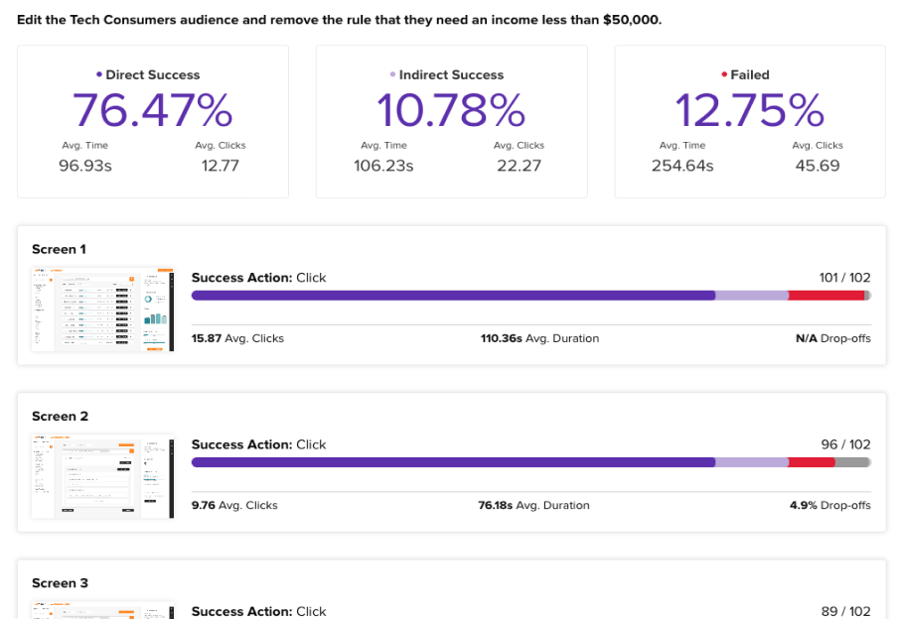
By analyzing how users navigate through the tree, companies can gain valuable insights into potential navigational issues. Metrics derived from tree testing include success rates (whether users find what they’re looking for), time taken to complete each task, and the paths taken by users. High failure rates or excessive navigation paths can indicate that certain sections of the website are hard to find or confusingly categorized.
As participants navigate through the tree, their ability to quickly and successfully find information provides direct feedback on how well the site’s structure matches user expectations and understanding. High completion rates and direct navigation paths suggest that parts of the website are well-organized and intuitively labeled. Conversely, frequent missteps, backtracking, or failure to complete tasks indicate areas where the content organization is confusing or misaligned with user expectations.
Qualitative feedback gathered during the testing process can provide further insights into why certain structures work better than others, offering specific suggestions for improvement. By iteratively refining the site’s structure based on this feedback, companies can develop a more user-friendly and logically organized website that enhances the user experience by making information easy and natural to find.
By having users perform specific tasks using only the text-based structure of the site’s hierarchy, without the influence of design elements like graphics or interactive menus, tree testing isolates and evaluates the clarity and logic of the site’s organizational framework. This focus helps identify if users can find information efficiently or if they encounter issues such as confusing category labels, illogical groupings of content, or an overly complex hierarchy.
Common indicators of navigational barriers include high rates of task failure, excessive time spent on tasks, frequent backtracking, and user-reported frustration or confusion. These findings can guide necessary revisions to the site’s structure to enhance overall navigability and user experience.
By examining metrics such as task completion rates, the paths users take, and the time they spend on tasks, you can pinpoint where users struggle to find information due to confusing labels, illogical content groupings, or overly complex navigation paths.
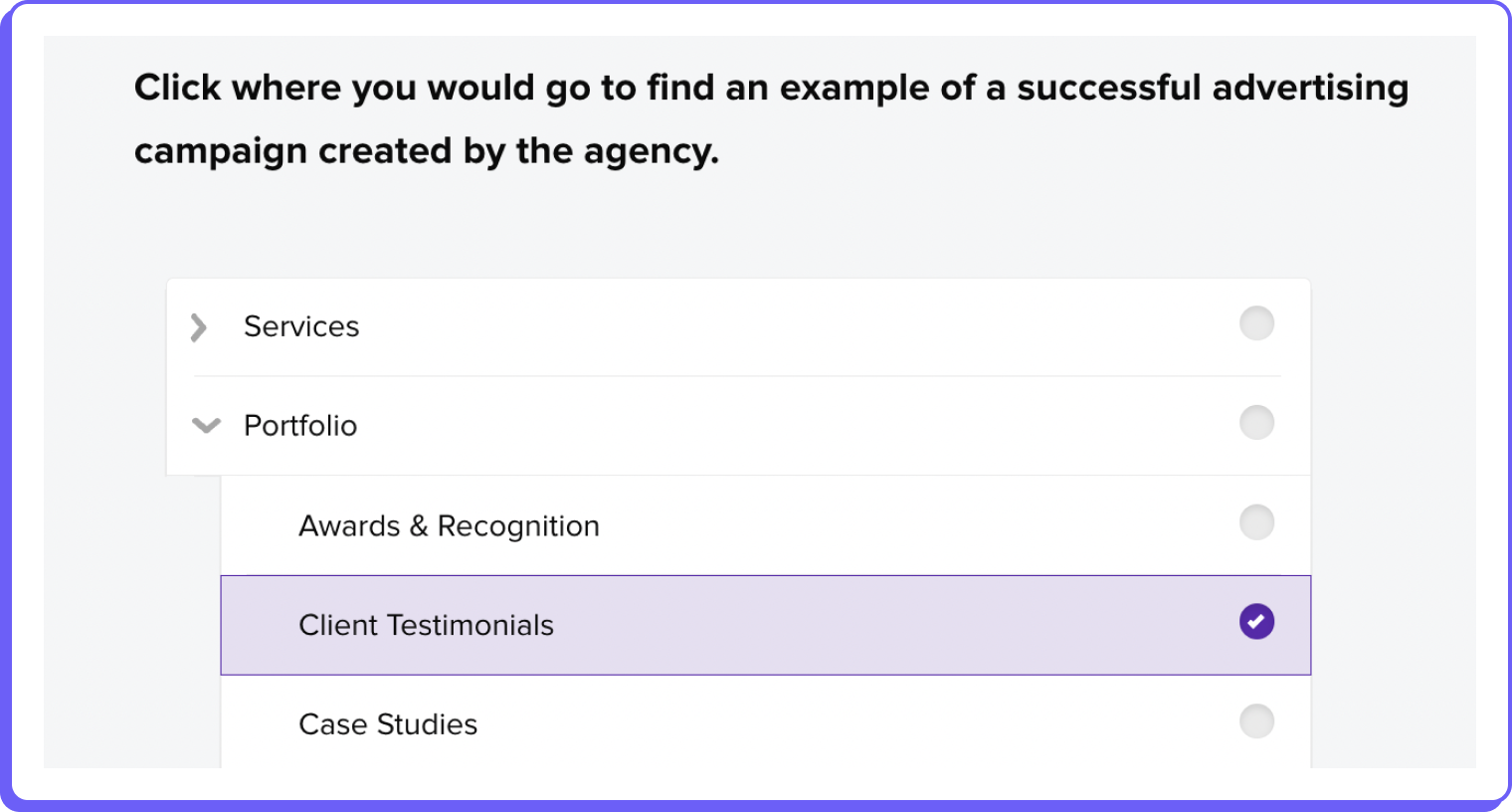
“Portfolio and case study is where I think I will see an example of a successful advertising campaign.”
– Advertising Professional (US)
Gathering qualitative feedback from participants can provide insights into why certain aspects of the structure may be problematic. Using this information, you can make informed decisions about how to reorganize content, simplify navigation paths, and adjust labels to better align with user expectations and behavior. This iterative process of testing and refining helps ensure that the site’s structure is optimized for ease of use, enhancing the overall user experience.
How to set up a competitive review
Define Your Objectives
Clearly outline what you aim to achieve through tree testing, such as improving findability or optimizing content organization.
Select Appropriate Research Methods
Choose methods that best suit your objectives, including tree tests, card sorting, and usability testing.
Gather User Feedback
Collect feedback from your target audience using Helio’s tools to gather reliable and actionable insights.
Analyze Feedback
Synthesize the data to identify patterns and insights, focusing on the most effective content hierarchies.

Refine and Optimize Structure
Use the insights to refine your site structure and prioritize changes that will significantly impact usability.
Implement Changes
Incorporate the feedback into your development process to ensure your final structure meets user expectations.
Tree testing helps us validate the effectiveness of our site’s organization and labeling by revealing how real users navigate our structures. This method provides clear, actionable insights that guide improvements in our navigation, ensuring that our users can find what they need quickly and efficiently.

Melanie Buset, Senior UX Researcher at Shopify
Testing Template Example
FAQs
Tree testing involves evaluating the hierarchy and findability of topics in your website or application. This process helps ensure users can easily locate information, enhancing overall usability.
Tree testing is crucial because it ensures that your site’s structure aligns with user expectations. By optimizing navigation, you can improve user satisfaction, engagement, and retention.
Common methods include tree tests to evaluate the hierarchy, card sorting to understand user categorization, and usability testing to identify navigation issues.
Tree testing specifically assesses the structure and findability of content, focusing on user navigation. Other research types might address broader issues such as overall user experience or content effectiveness.
Challenges include gathering representative feedback, ensuring comprehensive coverage of all content areas, and integrating feedback effectively into the site structure.
To ensure accurate interpretation, businesses should engage experienced researchers, validate findings across multiple data sources, and be mindful of biases that could skew interpretations.
Businesses can use insights to refine the site structure, prioritize changes that improve navigation, and tailor content organization to meet user needs better.