Let’s be real. Most teams are working under pressure.
We’ve run thousands of tests across product teams who work this way. The patterns are clear: teams that validate early and often don’t just move faster, they build things that work better. They avoid the long tail of rework. They sidestep the internal politics of “who’s right” and focus instead on what’s true for the user. That data fuels every part of this approach.
Most teams aren’t operating under perfect conditions. They’re working with tight deadlines, shifting goals, half-written briefs, and someone asking if this can “go live by Friday.” In that kind of chaos, agile design isn’t a luxury, it’s a way to keep momentum without losing your mind or your users.
Agile and Design
It’s the unlikely marriage of two things: agile’s obsession with momentum and design thinking’s loyalty to real people. One keeps you shipping. The other keeps you from shipping garbage.
Together, they create a process that works in the mess of real product life. You move faster. You collaborate better. And maybe most importantly, you build things that still make sense once they leave the whiteboard.
Agile Design Isn’t a Hack. It’s a Survival Skill.
Jiri Mocicka has lived this. He’s combined agile with design thinking across complex teams and walked away with something that doesn’t feel like a buzzword. It feels usable.
Here’s how he sees it:
→ Design Thinking is a stress test for ideas. You don’t just ask, “Can we build this?” You ask, “Will anyone care?” “Is it even viable?” It’s ruthless in the best way. If your idea can’t pass the test of desirability, feasibility, and viability, it doesn’t move forward.
→ Dual-Track Agile separates the dreaming from the doing. Discovery is where you explore freely, run tests, and follow the weird ideas to see where they go. Delivery is where you get focused and build what’s already been validated. No more writing code for something that should have stayed a napkin sketch.
This isn’t about being perfect. You’ll still run into friction. Some experiments will flop. Standups will still go off track. But at least you’re moving with purpose. You’re not just delivering features. You’re solving problems people actually have.
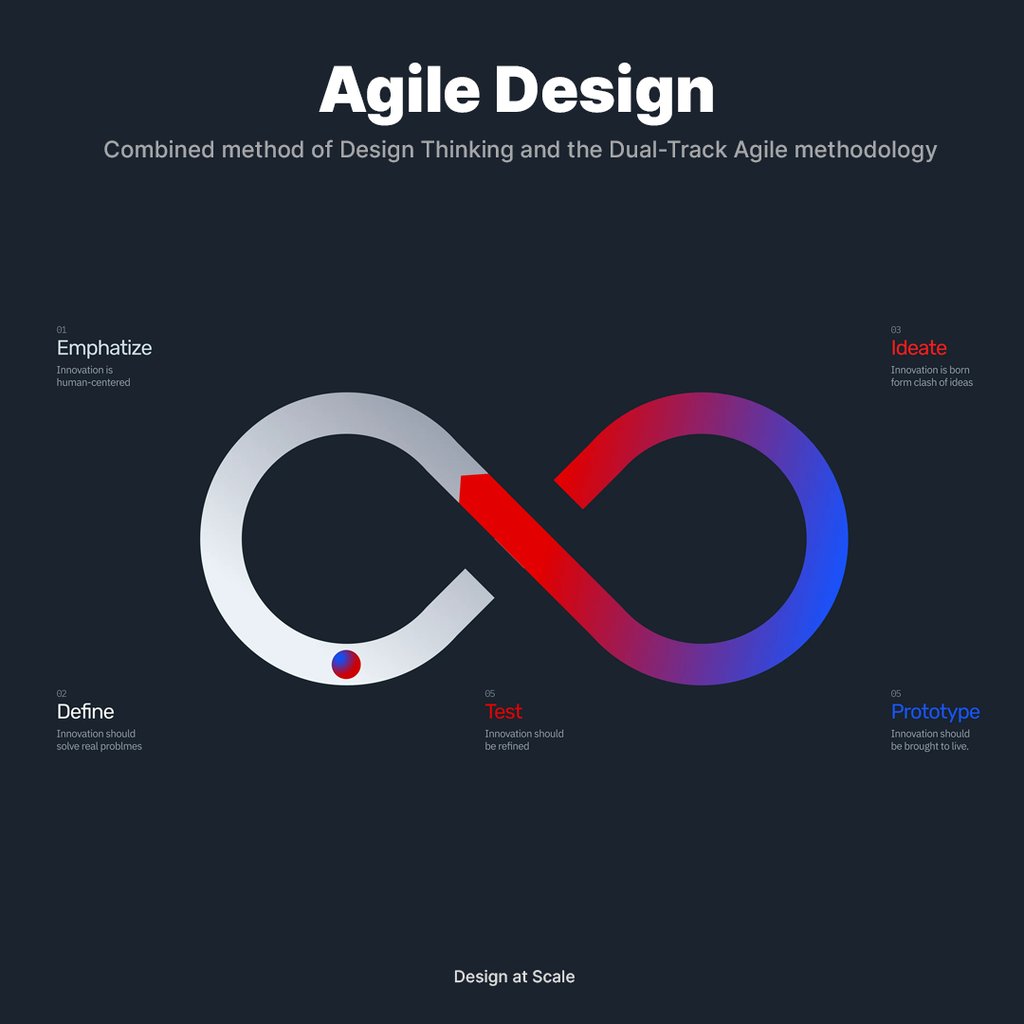
Understanding Agile Design
Agile design isn’t just a lighter version of product development. It’s a response to the pressure teams face when building something valuable within a shrinking window of opportunity.
Too often, teams overcommit to the perfect solution and end up delivering too late. Agile design counters this by focusing on momentum. It favors small, tested improvements over big, unvalidated bets—allowing teams to learn faster, adjust earlier, and stay aligned with real user needs.
Agile Design Principles
At its core, agile design is a rhythm: research, prototype, test, build, learn, adjust. Not as a side project. As the heartbeat of the team.
It connects the designer’s intuition with real user behavior. It forces prioritization, not based on what sounds good in a meeting, but on what moves the needle for people using the product. The beauty of this approach isn’t in the rituals or the velocity metrics. It’s in the focus: solving the right problems, quickly and repeatedly.
And it doesn’t mean rushing.
Agile design done well is fast because it’s clear. When the team shares the same understanding of user needs, decisions get easier. You cut the noise, align around impact, and iterate with intent.
It’s not always clean. There are tradeoffs. You’ll ship imperfect work. But over time, if you stay close to the problem and honest about what’s working, the product sharpens, and so does the team.
Dual-Track Agile helps teams balance the need for discovery with the need for delivery, ensuring that products are both innovative and viable.

Agile Design Thinking
At the heart of agile design thinking is a practical alignment of three forces: human desirability, technical feasibility, and economic viability. When these are in sync, products aren’t just well-built, they’re needed, usable, and sustainable.
- Human Desirability
Design starts with people. Not personas or assumptions—actual insight into what users care about. This means listening closely, watching behavior, and translating that into something useful. It’s not just about empathy. It’s about precision: building something that clearly answers a real need. - Technical Feasibility
A great idea that can’t be built isn’t a great idea. Agile design thinking brings engineering in early to shape solutions that work within real constraints. Prototypes are pressure-tested fast, reducing the risk of wasted effort or late-stage surprises. - Economic Viability
No product survives on desirability alone. There’s always a business case behind it—costs, pricing, margins, market dynamics. Agile design doesn’t ignore this. It helps teams stay honest about tradeoffs and build with long-term sustainability in mind.
When these three elements guide decision-making, design becomes a team sport with shared priorities. It’s not about chasing perfection. It’s about building the right thing, the right way, at the right time.
This is how agile design thinking becomes more than a process. It becomes a filter for smarter, faster, more aligned decisions across the board.
The Dual-Track Agile Methodology
Dual-track agile separates the work into two essential tracks: discovery and delivery. They run in parallel as ongoing efforts that keep the team learning while building. This structure creates space to explore what matters before committing resources to execution.
- Discovery is where questions get asked, assumptions get tested, and weak ideas are weeded out early. Research, prototypes, and fast feedback loops live here.
- Delivery is where clarity turns into code. It’s about execution—taking the ideas that passed through discovery and building them with focus and precision.
This model solves problems that slow teams down: unclear priorities, rushed builds, missed signals from users. Done right, it sharpens direction while keeping the engine running.
Benefits of Dual-Track Agile:
- Transparency- Everyone sees what’s being explored, what’s being built, and why. Fewer surprises. Better conversations.
- Scalability- As teams grow, this separation of tracks helps them avoid bottlenecks. Design and research aren’t waiting for the next sprint—they’re always ahead, feeding the pipeline.
- Faster Time to Market- With ideas validated before they hit the backlog, development isn’t dragging half-baked concepts across the finish line.
- Lower Costs- Time isn’t wasted building the wrong thing. Discovery filters out misaligned features before they consume resources.
- Better Products- Teams work with more clarity and confidence. They know what they’re building, who it’s for, and why it matters.
Resources
Agile Design Resources
Check out these links on Dual-Track Agile, as Dylan Ward, Kevin Albrecht, and Jeff Patton emphasize the importance of integrating customer feedback in product development. Paulo Caroli’s Lean Inception and Adriana Katrandzhieva’s video further highlight the approach’s focus on discovery and delivering customer value.
-
Dual-Track Agile and Customer Feedback Loop with VP of Product at Pop Pays
, by
Dalyn Ward
-
Dual Track Agile: Focusing on Customer Value
, by
Kevin Albrecht
-
[Video] Dual-Track Agile for Discovery & Development
, by
Adriana Katrandzhieva
-
Lean Inception
, by
Paulo Caroli
-
Dual Track Development is not Duel Track
, by
Jeff Patton
Key Stages in the Agile Design Process
The agile design process is structured to ensure continuous improvement and adaptability. It encompasses several key stages that help teams empathize with users, define problems clearly, generate innovative ideas, prototype solutions, and test them with real users. Each stage is crucial in creating products that meet user needs and adapt to changes efficiently.
1. Empathize
Understanding user needs is the foundation of the agile design process. During this stage, teams employ various techniques to gather insights directly from users. These techniques include user interviews, surveys, and observational studies, which help understand user behaviors, pain points, and desires.
- User-Centered Design: This approach ensures the design process revolves around the user’s needs and experiences. By keeping the user at the center, teams can create more relevant and effective solutions.
- User Stories are short descriptions of a feature from the end user’s perspective. They help capture users’ requirements and expectations, clearly focusing on the design process.
Helio: Helio significantly enhances the empathize stage by offering robust user research tools that streamline the process of gathering user insights. With Helio, teams can quickly deploy user surveys and observational studies, making collecting and analyzing data easier. We ran one of these surveys to learn about Usage & Attitudes (U&A) patterns in an audience of male formal wear consumers in the US who prefer to shop online.
The goal was to understand what consumers currently have the most difficulty with when shopping for formal wear, to identify opportunities for a theoretical clothing brand:
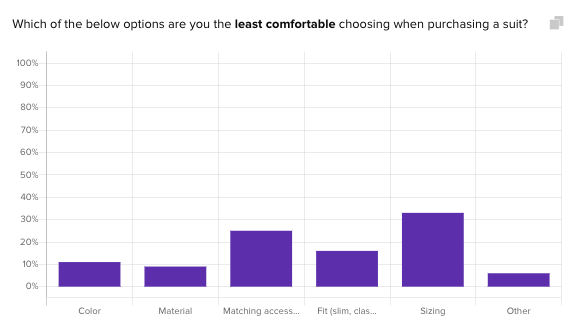
Consumers indicated that they are least comfortable with sizing and matching accessories. Their follow-up responses then provided clarity for what consumers are feeling when thinking of making a purchase:
“I am not good with choosing the size that is best for me. The ones I choose are normally to big or make me look bigger.”
- Male Formal Wear Online Shopper (US)
This type of U&A survey is the bread and butter of Helio. The platform’s intuitive interface allows teams to design and distribute surveys, track responses, and visualize data, ensuring that user feedback is at the forefront of the design process.
2. Define
After empathizing with users, the next stage is to define the problem that needs to be solved clearly. This stage involves synthesizing the information gathered during the empathize stage to create a clear problem statement. Defining the problem accurately ensures that the team is addressing the right issues.
- Design Collaboration: Collaboration among team members is essential to accurately defining problems. By working together, team members can share different perspectives and insights, leading to a more comprehensive understanding of the problem.
- Agile Workflow: An agile workflow helps break down the problem into manageable tasks. It allows teams to prioritize and tackle the most critical aspects first, ensuring steady progress towards solving the problem.
Helio supports the define stage by facilitating seamless design collaboration across teams. Using the data collected in the Empathize stage, you can provide validation (or invalidation) for different opportunities the team brings.
Opportunity Index Method
Using an Opportunity Index method, you can combine these data signals with input from business and tech stakeholders on your team to produce a clearly defined and prioritized list of opportunities to pursue. We used this research method on the same data collected above on online formal wear consumers to provide a ranked index of ideas for a theoretical brand to execute on.
We started by gathering a list of feature ideas for a mobile clothing app, such as personal online style experts, push-to-store options to try on clothes in person, and outfit suggestions for events.
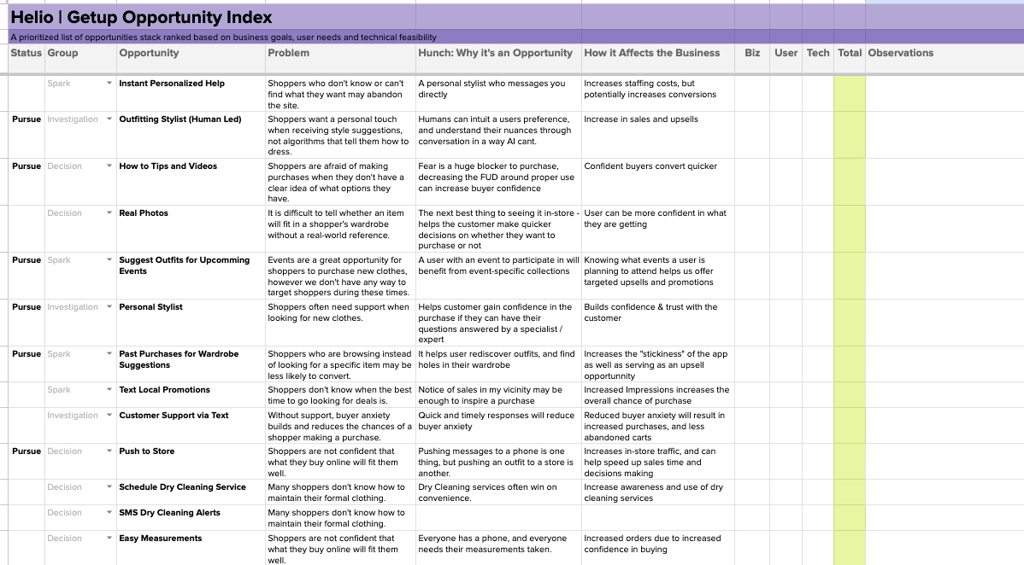
These ideas were listed in the Opportunity Index framework, with areas for the team to expand on what problem each concept is solving, why it’s important, and how it can benefit the business.
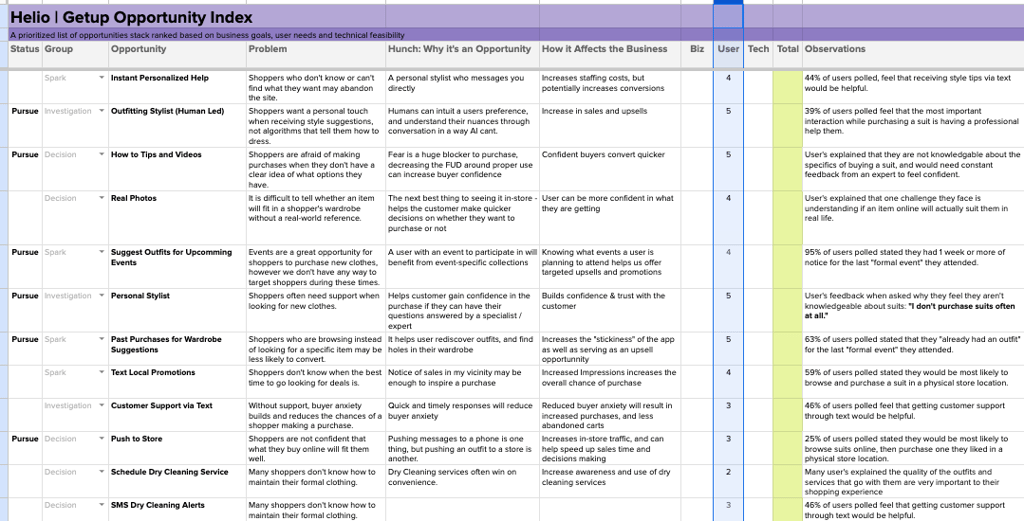
The data collected from the user surveys in the Empathize phase is entered next to each feature idea, and the value of that idea is translated into a 1 – 5 rating based on how important it would be to a Getup user. For instance, sizing was revealed as the least comfortable aspect for suit purchasers the testing above, so an opportunity that speaks to helping consumers with sizing would be rated a 5/5.
The data observation supporting each user rating is listed to the right, and a link leads to the raw data.
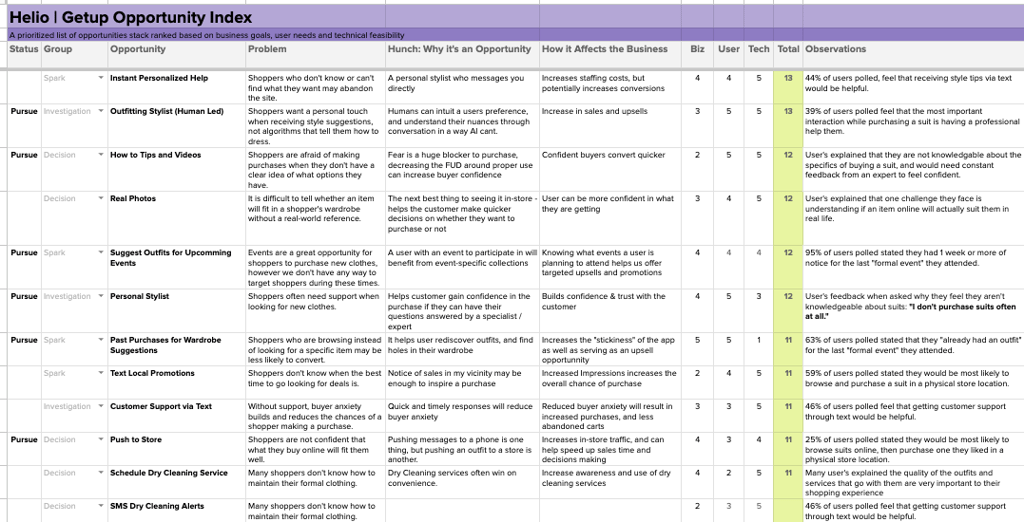
Rating each Opportunity
Now, with a user rating for each opportunity, the Biz and Tech ratings could also be applied to each idea based on input from the Getup team. Engineering stakeholders on the team rated the technical feasibility of each idea on a 1 – 5 scale (5 being easiest), and the project’s key stakeholders gave input on the Business value on a 1 – 5 scale.
The final total out of 15 is evaluated for each opportunity, with the highest-ranking opportunities representing a combination of importance to the business and users and simplicity to build from a technical standpoint.
With a fully fleshed-out and user-validated list of product opportunities ranked by priority, teams can now define exactly what ideas they should pursue that should produce the highest return on investment for their business.
View the Opportunity Index Case Study
3. Ideate
The ideate stage is where creativity flourishes. During this stage, teams brainstorm and generate various ideas to solve the defined problem. Encouraging diverse perspectives and collaborative brainstorming sessions leads to innovative and effective solutions.
- Design Thinking: This methodology encourages creative problem-solving and innovation. It involves generating multiple ideas, exploring various possibilities, and selecting the most promising ones for further development.
- Collaborative Design: Collaboration during ideation ensures that all team members contribute their unique perspectives. This collective effort results in more innovative and well-rounded solutions.
Helio helps produce a prioritized list of ideas to execute in the Define phase. Now, with ideation on the table, the team can move forward with their highest-ranked opportunities and quickly iterate on multiple versions.
For example, a highly ranked opportunity on Indiana University’s redesigned website was improving the experience of their degree index page, where visitors search for the degree they want to pursue.
One of the team’s ideas was prioritizing how features are displayed on the degree listing page rather than maintaining the current alphabetical order.
Encouraging Exploration
The Indiana University team’s goal was to encourage the exploration of different degrees on the index page and increase engagement with 10 of their key school programs.
One hundred participants from IU’s audience of undergrad and grad students interacted with each version of the page, answering the same questions to compare their responses across variations. Once the data had been collected, the responses were copied into a data comparison framework for quick design evaluation.
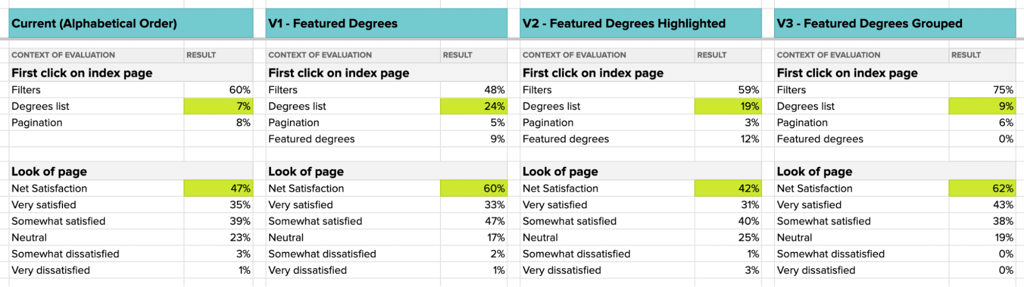
Once the data had been collected and loaded into the comparison framework, the picture of how users reacted to each different version became more clear:
In the current page version, with the degrees in alphabetical order, only 7% of participants engaged with the list, instead opting to go directly to the filters and search bar.
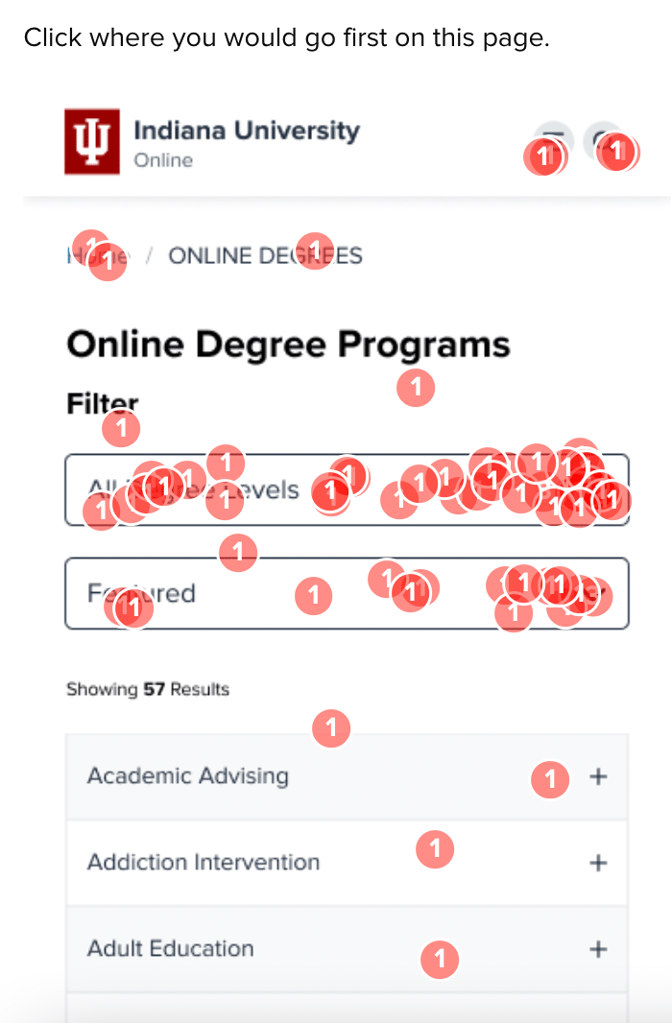
When the degrees list was reorganized to show featured degrees up top, engagement with the list jumped to 19-24%, showing a desire to interact with the page rather than resort to the search features.

The versions where we tried highlights in the degrees list both reduced satisfaction with the look of the page (V2) and reduced engagement when hidden under a dropdown (V3). The team moved forward by reordering the degree list without adding visual highlights.
Experimentation like this in the Ideate phase helps launch teams past typical collaboration woes. It addresses differing opinions and provides hard data and signals to inform the team’s decision-making.
View the Idea Validation Case Study
4. Prototype
Prototyping involves creating simple, tangible representations of the ideas generated during the ideate stage. These prototypes help teams explore potential solutions quickly and cost-effectively. Prototyping allows teams to visualize ideas and gather early feedback.
- Design Prototyping: Prototyping tools and techniques enable teams to create functional models of their ideas. These models help explore different design options and test their feasibility.
- Iterative Design: Iteration is a core principle of agile design. By continuously refining and improving prototypes based on feedback, teams can develop more effective and user-friendly solutions.
Helio provides powerful prototyping testing tools that allow teams to quickly test functional models of their ideas. The platform supports testing interactive Figma prototypes that can be shared with users for feedback.
For example, Indiana University aimed to enhance the user experience on its homepage by determining which visual elements most positively influenced user impressions and satisfaction. To create this effective homepage, the Indiana University team hypothesized that animating their city’s skyline on the page would better align with their desired brand impressions.
Figma Prototyping
The team placed each version of the homepage into a Figma prototype to showcase its animated aspects, allowing participants to experience the animations in an interactive environment. After interacting with the Figma prototype, we asked participants a series of evaluative questions to compare satisfaction and brand impressions across the three versions.
Our team presented three homepage variations to users:
- Simple, no skyline: Basic design without any background imagery.
- Skyline V1: Features the city skyline during the day as a background.
- Skyline V2: Incorporates a vibrant evening city skyline with prominent university branding.

We randomly assigned participants to review one of the three versions and they provided feedback on their satisfaction and overall impression of the page.
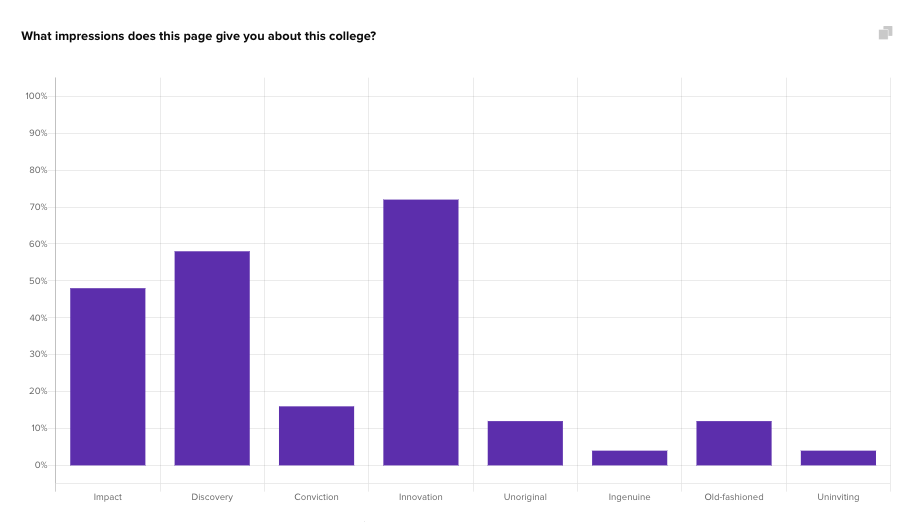
We quickly copied the data from the Indiana University skyline testing from each separate Helio test into the framework below:
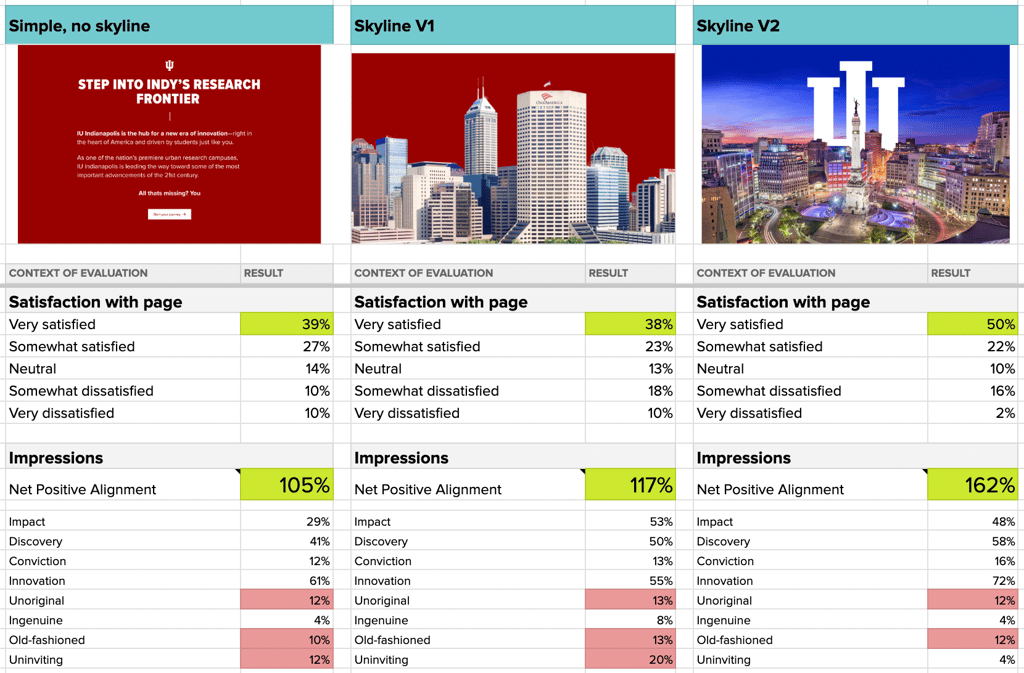
Positive Participant Feedback
This side-by-side view quickly reveals which variations received the most positive participant feedback. Brand impressions such as Impact, Discovery, and Innovation increased compared to version 1. Skyline version 2’s net positive alignment (total positive impressions minus total negative impressions) was much greater than the other versions. Combined with the higher satisfaction, the IU team confidently moved forward with their plans for an animated skyline on the homepage.
Helio’s user testing capabilities enable teams to gather insights on their prototypes, ensuring that they can refine and improve their designs iteratively. This accelerates the prototyping process and helps teams develop more effective solutions.
View the Prototype Testing Case Study
5. Test
The testing stage is critical for validating the effectiveness of the prototypes. By testing prototypes with real users, teams can gather valuable feedback and identify areas for improvement. Continuous testing and refinement ensure that the final product meets user needs and expectations.
- Agile Development: Agile development methodologies support the iterative testing process. By breaking down the development into small, manageable increments, teams can systematically test and refine each component.
- Continuous Improvement: This principle emphasizes the importance of ongoing refinement and enhancement. By continuously testing and improving the design, teams can ensure that the final product is of the highest quality and meets user needs.
Helio provides user feedback throughout the agile process and excels in the testing stage with its comprehensive user testing tools. The prototyping tools we discussed above also provide detailed usability metrics about how users navigate the flow.
Prototype of an ad management platform
For example, we tested a prototype of a theoretical ad management platform called Advent, which allows users to adjust the audience targeting parameters of their ad campaigns.
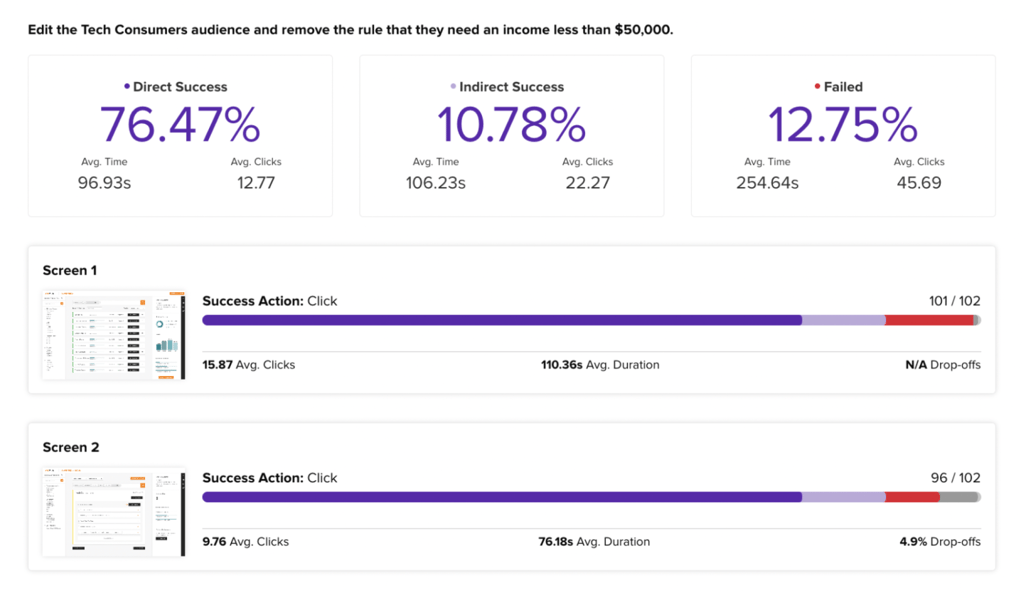
This Advent prototype data revealed that up to 13% of participants were unsuccessful at editing their target audience. Most of these failures occurred on the very first step, indicating that the initial action of finding the specific audience demographic information on the page was complex for users.
This usability data can be combined with evaluative questions that paint how a participant navigates a product and feels about that experience.
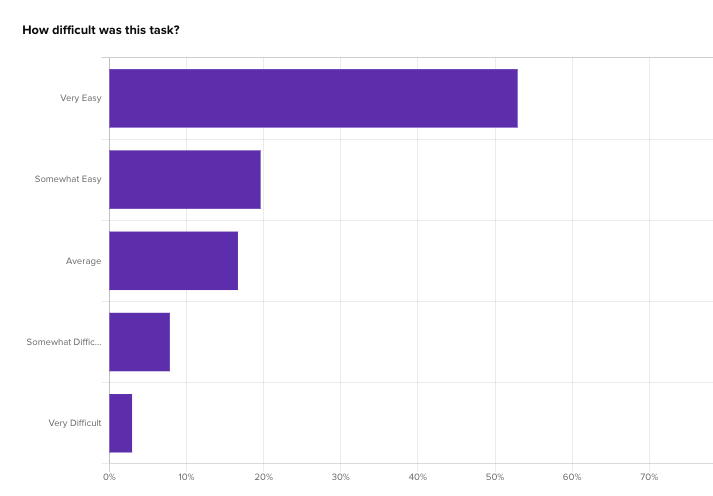
“there was a lot of information on the page. It took me a second to find the right group as they were not in an order I recognized. I then needed to find the correct line to edit with income; this did not match up with a previous line with a different income level. So it took me a few seconds to find the correct line.”
- Small Business Advertiser (US)
Our recommendation for future iterations of Advent’s audience page would be to emphasize top-level demographics on the page that users may gravitate towards more often, such as age and location, to improve the usability for those key actions.
Using Helio
Teams can easily set up user tests, gather real-time feedback, and analyze results within the platform. Helio’s advanced reporting helps identify critical areas for improvement, enabling continuous refinement of the prototypes. This ensures the final product is optimized to meet user needs and expectations, enhancing overall product quality and user satisfaction.
View the Advent Prototype Survey!
By following these key stages in the agile design process, teams can create innovative, user-centric, adaptable, and efficient products. This structured yet flexible approach ensures that every stage of product development is focused on delivering the best possible outcomes for users.
Putting Agile Design into Practice
Agile design only works if it fits how your team actually operates. The goal isn’t to adopt a method—it’s to build a system that helps you move faster with more clarity.
Here’s what that looks like in real terms:
- Start with the problem, not the roadmap
Too many teams jump straight to solutions because deadlines demand it. Slow down just enough to understand what users are really trying to do. Then design from there. It’ll save weeks down the line. - Test early, test often, test with purpose
Don’t wait for a polished prototype. Rough ideas tested early will tell you more than polished ones tested too late. Treat testing like a pulse check, not a milestone. - Keep discovery alive—even in delivery
Discovery isn’t a phase. It’s a parallel track. Keep asking questions while building. Stay curious. If something starts to feel off mid-sprint, flag it. Fix it before it ships. - Work in slices, not layers
Build thin vertical slices that go end to end—just enough design, dev, and logic to test a real experience. Don’t layer design one week, development the next. That just delays learning. - Make research accessible to everyone
Don’t silo user insights with the research team. Share what you learn—raw clips, quotes, reactions. Let the whole team hear how users actually talk and think. - Anchor design conversations in metrics
Shift design critiques away from “I like this” to “does this improve comprehension?” or “will users trust this screen?” Metrics bring clarity. They help teams focus on what matters.
The strongest agile design teams don’t chase perfection. They aim for consistent clarity, fast learning loops, and shared responsibility across the board. That’s how design becomes a force multiplier, not a bottleneck.
Dual-Track Development emphasizes the importance of integrating customer feedback throughout the process, ensuring that the end product truly meets user needs.

Overcoming Common Challenges in Agile Design
While agile design offers many benefits, it also presents certain challenges. Common obstacles include manAgile design isn’t supposed to be smooth. It works because it brings issues to the surface early, while there’s still time to adjust.
A common challenge is the disconnect between design and engineering. Discovery happens in isolation, and delivery moves ahead without validation. Features get built that haven’t been tested, or ideas are prototyped that can’t be shipped. The fix is shared visibility. Bring both sides into the same conversation early and often.
Speed also creates risk. Under pressure to deliver, teams skip research and testing. But skipping learning doesn’t save time—it pushes risk downstream. Small tests upfront prevent bigger delays later.
Design debt builds fast. One quick fix at a time, and suddenly the system feels slow and inconsistent. Good teams clean as they go. Maintenance is part of the work, not something saved for later.
Feedback needs structure. Vague comments like “this feels off” slow teams down. Tie feedback to intent. Ask if users will understand the content, trust the interface, or know what to do next.
And if the process itself starts to feel heavy, adjust it. Agile is a tool, not a checklist. The focus should always stay on building the right thing, not just following the routine.
These moments of friction are signals. Teams that respond to them early grow stronger over time.
Agile Design FAQ
Agile design is a methodology that combines the iterative nature of agile development with the user-centered focus of design thinking. This approach prioritizes flexibility, collaboration, and user feedback, allowing teams to adapt quickly to changes, continuously improve their designs, and effectively create products that meet user needs.
Agile design differs from traditional design methodologies by emphasizing iterative development, continuous user feedback, and cross-functional collaboration. While traditional methods often follow a linear process, agile design allows for ongoing refinement and adaptation, ensuring that products evolve based on real-time user insights and changing requirements.
The core principles of agile design include flexibility, collaboration, and user-centricity. Flexibility ensures the ability to adapt to changes, collaboration fosters teamwork across different disciplines, and user-centricity focuses on creating solutions that address real user problems, enhancing the overall user experience.
The dual-track agile methodology separates the design and development processes into two parallel tracks: discovery and delivery. The discovery track focuses on user research and prototype creation, while the delivery track turns validated ideas into production-ready software. This approach enhances transparency, scalability, time to market, and product quality.
Helio.app enhances the agile design process by providing robust tools for user research, collaboration, and testing. It streamlines the gathering of user insights, facilitates real-time collaboration among team members, and supports iterative prototyping and testing. This ensures continuous improvement and alignment with user needs throughout the design process.
Best practices for implementing agile design include fostering cross-functional teams, maintaining regular check-ins, and continuously incorporating user feedback. Cross-functional teams ensure diverse perspectives and holistic solutions, regular check-ins keep the team aligned and identify issues early, and ongoing user feedback helps refine ideas to meet user needs effectively.
Teams can overcome common challenges in agile design by clearly defining roles and responsibilities to manage dependencies and regularly communicating goals and progress to ensure team alignment. Establishing clear boundaries and expectations prevents confusion, and consistent communication keeps everyone on the same page, facilitating a smooth and efficient design process.