Quantitative vs Qualitative Research: A Comprehensive Comparison
Research plays a crucial role in understanding various phenomena and gathering insightful information. Regarding research methodologies, two approaches stand out – quantitative and qualitative research. Both have their unique characteristics, strengths, and limitations. If you are wondering which method to choose for your research project, this article will comprehensively compare quantitative and qualitative research.
🔩 The Nuts and Bolts:
- Optimized for Different Objectives: Quantitative research is ideal for hypothesis testing and generalizing results to larger populations, while qualitative research excels in exploring deep insights and understanding complex behaviors.
- Structured vs. Flexible Approaches: Quantitative research relies on structured methodologies and statistical analysis, providing reliable and replicable data, whereas qualitative research offers the flexibility to adapt and delve into participants’ subjective experiences.
- Statistical vs. Textual Analysis: Quantitative analysis uses statistical tools to reveal patterns and relationships, while qualitative research employs textual analysis to uncover themes and narratives within data.
- Objective vs. Subjective Perspectives: Quantitative research seeks objective measurements free from researcher bias, whereas qualitative research embraces the subjective influence of the researcher, adding depth to the data.
- Scalability of Results: Quantitative research methods are scalable, and suitable for large samples that can validate findings across populations, while qualitative methods often focus on smaller, targeted groups for in-depth analysis.
- Resource and Time Allocation: Quantitative research may require more resources and time for data processing and analysis, while qualitative research demands extensive time in data collection and interpretation and often requires less statistical expertise.
- Complementary Use in Mixed Methods: Both methodologies can be integrated in mixed-methods research, providing a comprehensive approach that leverages the strengths of each to explore complex research questions thoroughly.
Understanding Research Methodologies
Before diving into the specifics of quantitative and qualitative research, it’s essential to understand what these methodologies entail. Research methodologies refer to the systematic approaches used to gather data, analyze it, and draw conclusions.
Research methodologies play a crucial role in the field of research, as they provide a framework for conducting studies and obtaining reliable and valid results. By following a specific methodology, researchers can ensure that their findings are rigorous and can be replicated by others.
Quantitative and qualitative research are two commonly used methodologies in various disciplines, including social sciences, psychology, and market research. While they differ in their approaches and techniques, both methodologies contribute to the advancement of knowledge and understanding.
Defining Quantitative Research
Quantitative research involves collecting and analyzing numerical data to explain or predict phenomena. This approach focuses on generating statistical results that can be generalized to a larger population. It usually involves large sample sizes and structured data collection methods, such as surveys, experiments, or observations with pre-defined variables.
Quantitative research allows researchers to measure and quantify relationships between variables. Using statistical analysis, researchers can identify patterns, trends, and correlations within the data. This methodology is particularly useful when studying large populations or establishing cause-and-effect relationships.
One of quantitative research’s key strengths is its ability to provide objective and reliable data. Researchers can minimize bias and obtain accurate results using standardized measurement tools and statistical techniques. However, it is essential to note that quantitative research may only capture part of the complexity and richness of human experiences and behaviors.
Defining Qualitative Research
In contrast, qualitative research focuses on understanding the subjective experiences and meanings individuals attribute to phenomena. Rather than relying on statistical analysis, this approach emphasizes detailed observations, interviews, focus groups, and textual analysis to uncover themes, patterns, and insights.
Qualitative research allows researchers to explore in depth individuals’ thoughts, feelings, and motivations. It seeks to understand the context and complexity of human experiences, providing a more holistic and nuanced understanding of a particular phenomenon. This methodology is particularly useful when studying topics that are difficult to quantify or when exploring new areas of research.
One of the critical strengths of qualitative research is its ability to capture the richness and depth of human experiences. By using open-ended questions and allowing participants to share their perspectives, researchers can gain valuable insights that may not be captured through quantitative methods alone. However, qualitative research is often criticized for its potential subjectivity and lack of generalizability.
In conclusion, understanding research methodologies is crucial for conducting rigorous and valid studies. Quantitative research focuses on numerical data and statistical analysis, while qualitative research emphasizes subjective experiences and in-depth understanding. Both methodologies have strengths and limitations, and researchers often combine them to understand a research topic comprehensively.
Make your design decisions count.
Subscribe to Design Under Pressure. Get insights, UX metrics, and tools for bold, informed design.
We respect your inbox. Just insights. No fluff. Privacy Policy.
Critical Characteristics of Quantitative Research
Quantitative research is renowned for its structured nature and objectivity. Let’s explore some of its essential characteristics further.
Structure and Objectivity in Quantitative Research
One of the significant strengths of quantitative research is its structured approach. Researchers create hypotheses and develop data collection methods based on pre-determined variables. By adhering to strict procedures, researchers can minimize biases and enhance the reliability and validity of the results. This allows for replication and comparison with other studies.
Furthermore, the structured nature of quantitative research enables researchers to establish straightforward research questions and objectives. This clarity helps design research studies that can effectively address the research problem. The structured approach also facilitates the organization and presentation of data, making it easier for researchers to analyze and interpret the findings.
In addition to structure, objectivity is another crucial characteristic of quantitative research. Researchers strive to maintain objectivity by minimizing personal biases and emotions during the data collection and analysis. This objectivity ensures that the research findings are based on empirical evidence rather than subjective interpretations.
Statistical Analysis in Quantitative Research
Quantitative research heavily relies on statistical analysis to conclude. Researchers use mathematical models, statistical tests, and software to analyze data and identify patterns or relationships. This offers a quantitative understanding of the research question and allows for generalization to the larger population.
Statistical analysis in quantitative research involves various techniques such as descriptive statistics, inferential statistics, and regression analysis. Descriptive statistics summarize and describe the data, providing measures of central tendency (e.g., mean, median) and variability (e.g., standard deviation, range). Inferential statistics, on the other hand, help researchers make inferences and draw conclusions about the population based on the sample data.
Regression analysis is another commonly used statistical technique in quantitative research. It examines the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables, allowing researchers to identify the strength and direction of the relationship. This enables researchers to make predictions and test hypotheses.
Moreover, statistical analysis in quantitative research allows researchers to quantify the magnitude of the effects or relationships observed. This quantitative understanding allows for comparisons between different variables and research studies, contributing to the cumulative knowledge in the field.
Critical Characteristics of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research, on the other hand, embraces a more flexible and subjective approach. Let’s explore its distinctive characteristics further.
Qualitative research is a methodological approach that focuses on understanding and interpreting social phenomena from the perspective of the individuals involved. Unlike quantitative research, which aims to measure and quantify data, qualitative research explores the complexities and nuances of human experiences, motivations, and emotions.
One key characteristic of qualitative research is its flexibility. Researchers can adapt their approach throughout the research process, allowing for a more dynamic and responsive exploration of the research topic. This flexibility enables researchers to delve deeper into the subject matter, uncovering hidden insights and capturing the richness of human experiences.
Researchers often use open-ended questions, interviews, or observations to gather data in qualitative research. These methods allow for in-depth exploration and allow participants to share their thoughts, feelings, and perspectives in their own words. By engaging in conversations and interactions with participants, researchers can better understand the social context and the meanings individuals attach to their experiences.
Flexibility and Subjectivity in Qualitative Research
Qualitative research allows researchers to adapt their approach throughout the research process. It allows for in-depth exploration of the research topic and the opportunity to capture rich and nuanced data. Researchers often use open-ended questions, interviews, or observations to gather detailed insights into individuals’ experiences, motivations, and emotions.
Subjectivity is another critical aspect of qualitative research. Unlike quantitative research, which aims to be objective and detached, qualitative research acknowledges that the researcher’s perspective and interpretation play a crucial role in shaping the findings. Researchers know that their biases, assumptions, and preconceptions can influence the research process and outcomes. This recognition of subjectivity allows for a more holistic understanding of the research topic, as it considers the multiple perspectives and interpretations within a social context.
By embracing subjectivity, qualitative researchers can uncover the complexities and contradictions that may arise in their data. They can explore the diverse range of meanings and interpretations individuals attribute to their experiences, providing a more comprehensive understanding of the social phenomena under investigation.
Textual Analysis in Qualitative Research
In qualitative research, textual analysis plays a vital role. Researchers analyze transcriptions, field notes, or documents to identify themes and patterns. Through careful interpretation and coding, they extract meaningful information and gain a deeper understanding of the research topic. This approach provides a qualitative lens to explore complex phenomena.
Textual analysis involves systematically examining the text, looking for recurring themes, ideas, or patterns. Researchers immerse themselves in the data, reading and re-reading the text to identify significant statements, metaphors, or symbols that shed light on the research question. By organizing and categorizing these findings, researchers can generate insights and develop theoretical frameworks that capture the phenomenon’s essence.
Qualitative researchers often use various techniques to analyze textual data, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, or narrative analysis. These methods allow researchers to uncover the underlying meanings and interpretations embedded within the text, providing a deeper understanding of the social context and the experiences of the individuals involved.
Through textual analysis, qualitative researchers can uncover the complexities and nuances of human experiences. They can identify the social, cultural, and historical factors that shape individuals’ perspectives and actions, contributing to a more comprehensive understanding of the research topic.
🚀 If you’re using Helio
Numerical results obtained through quantitative research offer clarity and support evidence-based decision-making.
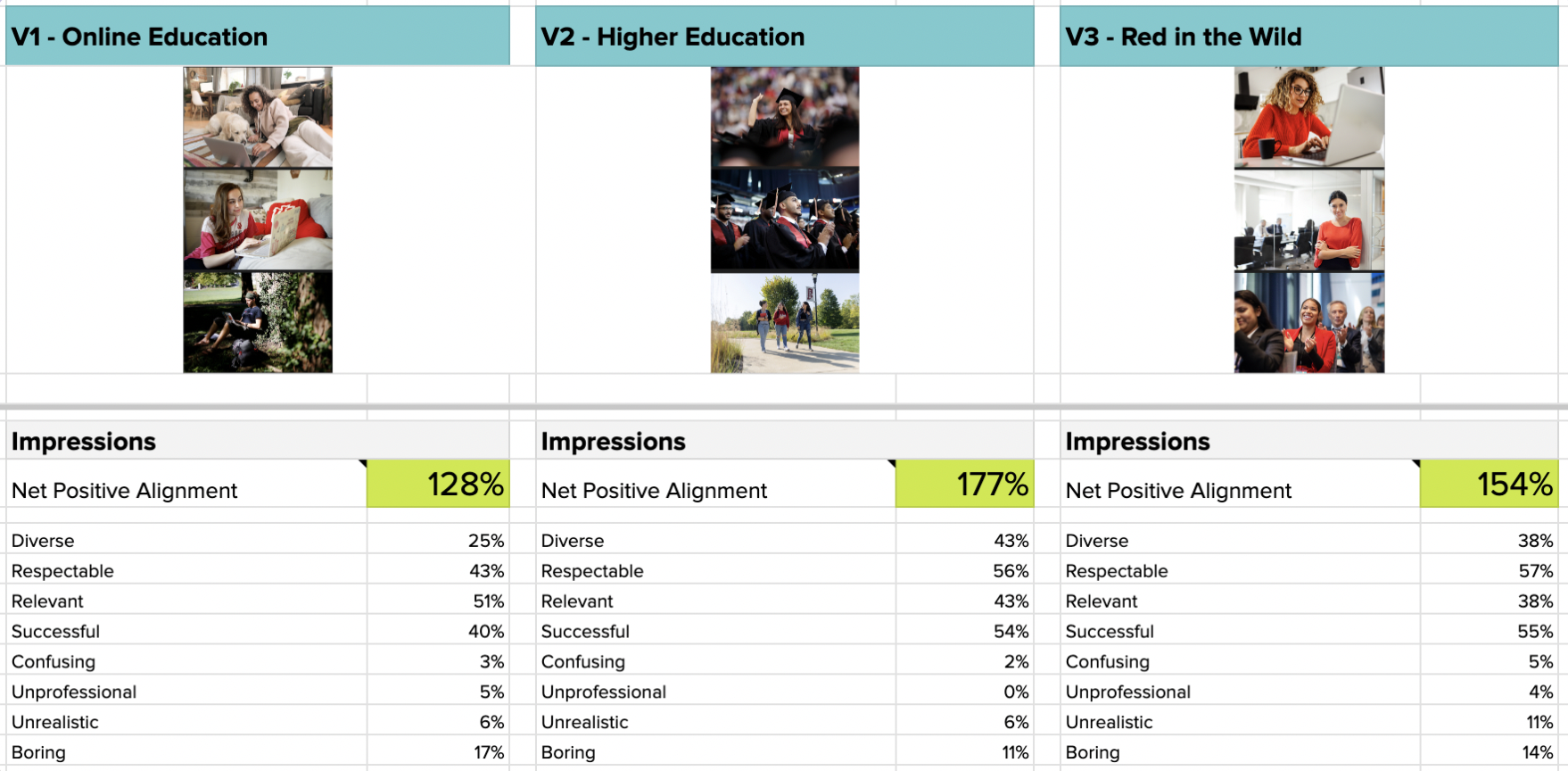
When deciding between quantitative and qualitative research, several factors should be considered.
Choosing the Right Method: Factors to Consider
When deciding between quantitative and qualitative research, several factors should be considered. Let’s explore some critical considerations.
Research Goals and Objectives
The nature of your research goals and objectives significantly influences your choice of methodology. If you aim to quantify relationships or test hypotheses, quantitative research is more suitable. On the other hand, qualitative research is the way to go if you seek to explore subjective experiences, understand motivations, or generate new theories.
Available Resources and Time
The availability of resources, such as budget, expertise, and time, can affect the choice of research methodology. Quantitative research often requires larger sample sizes, specialized software, and statistical knowledge. Conversely, qualitative research may require extensive fieldwork, transcription services, and qualitative analysis software.
Strengths and Limitations of Quantitative Research
While quantitative research offers valuable insights, it is essential to recognize its strengths and limitations.
Advantages of Quantitative Research
The strengths of quantitative research lie in its ability to produce statistically valid and reliable data. Its structured nature allows for comparisons with other studies, enabling researchers to identify trends and make generalizations. The numerical results obtained through quantitative research offer clarity and support evidence-based decision-making.
Disadvantages of Quantitative Research
However, quantitative research has its limitations. The strict structures and predefined variables may overlook subtle nuances or unique experiences. Due to its focus on numbers, it may fail to capture the complexities and deeper meanings associated with particular phenomena. Additionally, the reliance on large sample sizes and statistical analysis can be time-consuming, expensive, or limited by external factors.
In conclusion, quantitative and qualitative research methodologies have their place in the research landscape. The choice between them depends on your research goals, available resources, and the nature of the phenomena you aim to study. By understanding each approach’s key characteristics, strengths, and limitations, you can make an informed decision and conduct research that aligns with your objectives.
Quantitative vs Qualitative Research FAQs
Quantitative research quantifies data and generalizes results across populations using statistical analysis. Qualitative research aims to understand individual experiences and perspectives, relying on textual and thematic analysis of non-numerical data.
Researchers should use quantitative methods when their goal is to test hypotheses or theories, they need to quantify variables, and they are using a large sample size to generalize findings across a wider population.
Qualitative research provides deeper insights into complex issues by allowing researchers to explore thoughts, emotions, and motivations that are not easily quantifiable. It’s beneficial for understanding contexts, social realities, and the richness of human experiences.
The choice depends on whether the research aims to quantify data and apply findings broadly (quantitative) or to gain a deep, contextual understanding of a phenomenon (qualitative).
Yes, combining both methods in a mixed-methods approach allows researchers to exploit both strengths by quantifying data while gaining deeper insights into the research context.
Researchers should consider their specific research questions, the nature of the data, the resources available, and the desired outcomes. The chosen method should align with the study’s overall objectives and practical constraints.
Quantitative research often requires more initial setup for creating surveys and gathering large datasets, which can be time-consuming but may lead to faster analysis with the right tools. Qualitative research typically requires less initial setup but more time for data collection, detailed analysis, and interpretation of results.