The Power of Qualitative Feedback: Unlocking Valuable Insights
In today’s fast-paced business world, gathering and analyzing feedback is more crucial than ever. While quantitative data provides valuable insights, qualitative feedback offers a deeper understanding of customers, employees, and overall business performance. This article will explore the power of qualitative input and how it can unlock valuable insights that drive growth and success.
🔩 The Nuts and Bolts:
- Enriches Quantitative Data: Qualitative feedback provides context and depth to quantitative data, offering a comprehensive understanding of the “why” behind the numbers, which is crucial for making informed decisions.
- Drives Customer-Centric Innovations: Qualitative feedback uncovers specific needs and preferences by delving into customer thoughts and emotions, guiding businesses in tailoring products and services to meet customer demands better.
- Improves Product Development: Gathering detailed insights from qualitative feedback during product testing phases can significantly improve design, functionality, and user satisfaction.
- Enhances Employee Engagement: Qualitative employee feedback helps identify areas of satisfaction and concern, allowing organizations to make necessary adjustments that improve morale and productivity.
- Facilitates Deeper Market Understanding: Through qualitative feedback, businesses gain a nuanced understanding of market dynamics and consumer behavior, enhancing their competitive edge.
- Supports Effective Change Management: Qualitative feedback captures detailed reactions to organizational changes, assisting leaders in managing transitions more effectively and aligning strategies with employee and customer expectations.
- Strengthens Stakeholder Relationships: Regular collection and consideration of qualitative feedback demonstrate a commitment to stakeholder involvement, fostering stronger relationships and building trust.
Understanding Qualitative Feedback
Qualitative feedback is about capturing individuals’ rich and nuanced experiences, opinions, and emotions. It goes beyond numbers and statistics, delving into the why and how behind people’s thoughts and behaviors. Qualitative feedback is important because of its ability to provide context and meaning to quantitative data, giving organizations a holistic view of their business.
Quantitative data can only help us understand customers’ needs and preferences. While numbers can tell us how many customers are satisfied or dissatisfied, they don’t reveal the underlying reasons behind their feelings. This is where qualitative feedback comes in. Businesses can gather rich and detailed information about their customers’ experiences by asking open-ended questions, conducting interviews, and making observations.
Imagine a scenario where a customer rates a product with a low score. With qualitative feedback, we would be able to understand why the customer was dissatisfied. Was it the product’s quality, functionality, or something else entirely? By collecting qualitative feedback, we can uncover the specific pain points and frustrations that customers are experiencing, allowing us to make targeted improvements.
Definition and Importance of Qualitative Feedback
Qualitative feedback is the subjective information collected through open-ended questions, interviews, and observations. It helps businesses understand the underlying motivations and drivers influencing customer satisfaction, employee engagement, and overall business performance. Qualitative feedback offers valuable insights into the human side of decision-making by providing detailed descriptions and anecdotes.
One of the critical advantages of qualitative feedback is its ability to capture the “why” behind people’s thoughts and behaviors. It allows us to dig deeper and understand the emotions, beliefs, and values that drive individuals’ actions. This deeper understanding can help businesses tailor their products, services, and strategies better to meet the needs and expectations of their target audience.
Moreover, qualitative feedback provides a more nuanced perspective on customer experiences. While quantitative data can tell us that most customers are satisfied, qualitative feedback can reveal the specific aspects of a product or service that delight customers. This information can be invaluable in identifying and leveraging unique selling points and strengthening customer loyalty.
Differentiating Qualitative from Quantitative Feedback
While quantitative feedback provides numerical data, such as ratings and scores, qualitative feedback is more descriptive and narrative. It aims to uncover the reasons behind customers’ likes and dislikes, employees’ challenges and aspirations, and the impact of organizational decisions. By combining quantitative and qualitative feedback, businesses gain a comprehensive understanding of their strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities for improvement.
Quantitative feedback is essential for tracking trends and measuring performance over time. It allows businesses to quantify customer satisfaction levels, identify areas of improvement, and track progress toward goals. However, it only provides a surface-level understanding of the customer experience. Qualitative feedback, on the other hand, adds depth and context to the numbers, helping businesses understand the underlying factors that drive customer satisfaction or dissatisfaction.
For example, a high customer satisfaction score may indicate that a product meets customers’ expectations. However, by analyzing qualitative feedback, we may discover that customers are primarily satisfied with the product’s functionality but have concerns about its durability. This insight can guide product development efforts and help businesses address potential issues before they become widespread.
In summary, qualitative feedback is a powerful tool for businesses seeking to understand the why and how behind customer experiences. By collecting rich and detailed information, organizations can gain valuable insights into the emotions, motivations, and preferences that drive customer satisfaction and loyalty. When combined with quantitative data, qualitative feedback provides a comprehensive business view, enabling informed decision-making and targeted improvements.
Make your design decisions count.
Subscribe to Design Under Pressure. Get insights, UX metrics, and tools for bold, informed design.
We respect your inbox. Just insights. No fluff. Privacy Policy.
The Role of Qualitative Feedback in Business Growth
Qualitative feedback is pivotal in driving business growth by enabling organizations to make informed decisions and implement meaningful changes. Let’s explore two key areas where qualitative feedback can significantly impact.
Enhancing Employee Performance through Qualitative Feedback
Employees are among the most critical aspects of any organization’s success. By providing qualitative feedback, managers can gain valuable insights into employee satisfaction, engagement, and performance. Regular feedback sessions that encourage open and honest conversations create a culture of continuous improvement, motivating employees to excel and grow.
During these feedback sessions, managers can delve into specific areas of improvement and acknowledge areas where employees excel. Qualitative feedback empowers employees to take ownership of their professional development by highlighting strengths and areas for growth. This feedback loop fosters a sense of trust and collaboration between managers and employees, leading to increased job satisfaction and a more engaged workforce.
Moreover, qualitative feedback can help identify areas where additional training and support are needed. Organizations can provide targeted resources to enhance skills and knowledge by understanding the specific challenges employees face. This investment in employee development improves individual performance and contributes to the business’s overall growth and success.
Customer Satisfaction and Qualitative Feedback
Understanding customer needs and preferences is vital for any business thriving in a competitive market. Quantitative data alone may provide insights into customer behavior. Still, qualitative feedback allows organizations to go beyond surface-level data and gain a deeper understanding of customer emotions, perceptions, and experiences.
By analyzing qualitative feedback, businesses can uncover pain points that may not be apparent through quantitative analysis alone. Customers often express their frustrations, desires, and expectations in qualitative feedback, providing valuable insights into their experiences with a product or service. This feedback can help businesses identify areas for improvement and develop tailored solutions that meet customer expectations.
Furthermore, qualitative feedback allows organizations to understand the “why” behind customer behavior. Businesses can develop strategies to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty by exploring the emotions and motivations driving customer decisions. This customer-centric approach helps retain existing customers and attracts new ones through positive word-of-mouth and referrals.
In conclusion, qualitative feedback is a powerful tool that drives business growth by enhancing employee performance and customer satisfaction. By leveraging qualitative feedback, organizations can make informed decisions, implement meaningful changes, and create experiences that delight their employees and customers.
Techniques for Gathering Qualitative Feedback
Now that we recognize the importance of qualitative feedback let’s explore some effective techniques for gathering it.
Qualitative feedback is a valuable tool that provides rich insights into individuals’ thoughts, feelings, and experiences. It helps organizations understand the why behind the data, uncovering their target audience’s underlying motivations and perceptions. By utilizing various techniques, businesses can comprehensively understand their customers and make informed decisions to drive growth and improvement.
Surveys and Interviews
Online surveys and one-on-one interviews are popular methods for collecting qualitative feedback. Surveys allow organizations to reach a large audience and gather a wide range of perspectives, while interviews allow in-depth conversations and follow-up questions. These techniques enable businesses to delve deeper into their customers’ minds, uncovering valuable insights that may not be apparent through quantitative data alone.
When designing surveys, it is essential to craft open-ended questions and encourage respondents to provide detailed responses. This allows participants to freely express their thoughts and opinions, providing a wealth of qualitative data. Interviews, on the other hand, offer a more personal approach, allowing researchers to establish rapport with participants and delve into their experiences, motivations, and preferences.
By combining surveys and interviews, organizations can gather a comprehensive range of qualitative feedback, ensuring that the insights collected are relevant and actionable. This data can then be analyzed to identify patterns, themes, and trends, giving organizations a deeper understanding of their customers’ needs and expectations.
Focus Groups and Observations
Focus groups bring together a small group to discuss a particular topic or experience. This method encourages participants to share their thoughts openly and allows researchers to observe interactions and reactions. The dynamic nature of focus groups fosters a collaborative environment where participants can build on each other’s ideas and provide valuable insights.
During focus group sessions, skilled moderators guide the discussion, ensuring that all participants have an opportunity to share their perspectives. This technique allows organizations to gain a deeper understanding of their target audience‘s collective opinions and experiences. Businesses can uncover valuable insights that inform product development, marketing strategies, and overall business decisions by analyzing the discussions and interactions within focus groups.
In addition to focus groups, observations provide another powerful technique for gathering qualitative feedback. Observations involve directly observing customers or employees in their natural environments, such as retail stores, workplaces, or online platforms. By watching behavior and listening to conversations, businesses can gain valuable insights into preferences, challenges, and opportunities.
Observations allow organizations to see firsthand how customers interact with their products or services, identifying pain points and areas for improvement. This technique provides a unique perspective that complements other qualitative research methods, offering a holistic view of the customer experience.
Businesses can gather a comprehensive range of qualitative feedback by utilizing a combination of surveys, interviews, focus groups, and observations. This rich data gives organizations a deep understanding of their customers’ needs, preferences, and motivations. With these insights, businesses can make informed decisions, develop targeted strategies, and create exceptional experiences that resonate with their target audience.
🚀 If you’re using Helio
This rich data gives organizations a deep understanding of their customers’ needs, preferences, and motivations.
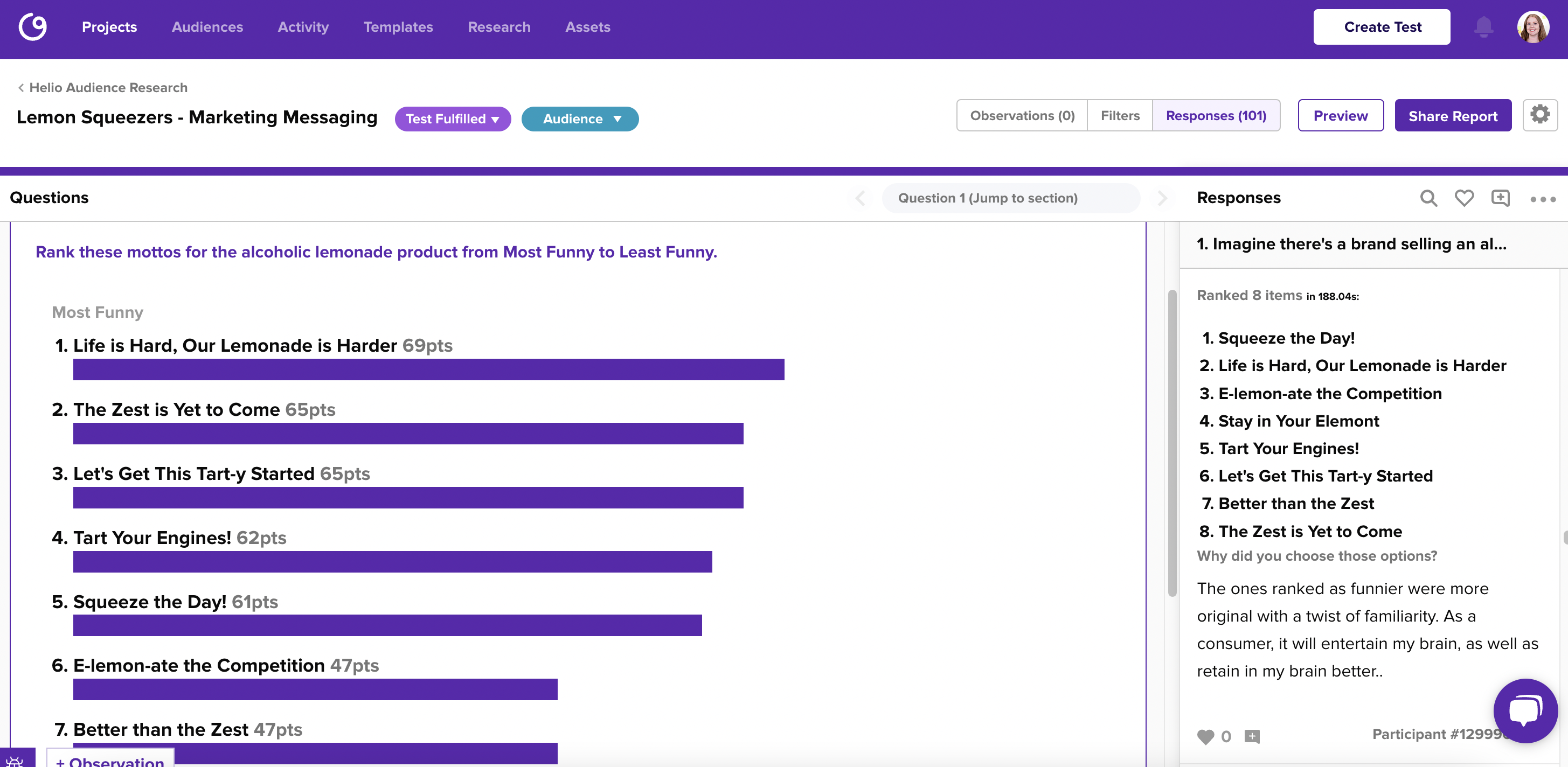
Once qualitative feedback is collected, the next crucial step is to analyze and interpret it effectively.
Analyzing and Interpreting Qualitative Feedback
Once qualitative feedback is collected, the next crucial step is to analyze and interpret it effectively. Let’s explore two popular methods for making sense of qualitative data.
Thematic Analysis
Thematic analysis identifies recurring themes, patterns, and trends within the qualitative feedback. By categorizing information and extracting key insights, businesses can comprehensively understand the topics and issues that matter most. This method helps to uncover not only the what but also the why behind customer and employee experiences.
Content Analysis
Content analysis focuses on analyzing the content and language used in qualitative feedback. By examining word choices, tone, and sentiment, businesses can gain insights into customers’ emotions, satisfaction levels, and areas that require immediate attention. Content analysis allows organizations to dig deeper into the meaning and implications of qualitative feedback, empowering them to make informed decisions.
Implementing Changes Based on Qualitative Feedback
Collecting qualitative feedback is just the beginning; the true power lies in taking action based on the insights gained. Let’s explore essential steps for implementing changes.
Prioritizing Feedback for Action
Not all feedback can be acted upon immediately, so it’s crucial to prioritize based on impact and feasibility. By categorizing feedback into short-term and long-term goals, businesses can focus on areas that will significantly impact customer satisfaction, employee engagement, and business growth.
Monitoring and Evaluating Changes
Implementing changes based on qualitative feedback is an iterative process. It’s essential to monitor the impact of changes, gather additional feedback, and evaluate the effectiveness of the implementation. By continuously collecting and analyzing qualitative feedback, businesses ensure they are on the right track and can make further adjustments.
In conclusion, qualitative feedback is a powerful tool that unlocks valuable insights and drives business growth. By capturing the rich tapestry of human experiences and perceptions, organizations can go beyond numbers and statistics to understand the why and how behind customer and employee behavior. Through effective gathering, analysis, and implementation of qualitative feedback, businesses can stay customer-centric, enhance employee performance, and make informed decisions that propel them toward success.
Qualitative Feedback FAQs
Qualitative feedback involves detailed, narrative data that provides insights into the reasons behind behaviors and opinions, unlike quantitative feedback, which is numerical and measures trends and magnitudes. Qualitative feedback is invaluable for understanding complex issues and emotional responses.
Qualitative feedback is crucial because it allows businesses to understand the emotions, thoughts, and detailed opinions of customers and employees. This information informs better decision-making, enhances product development, and improves customer service strategies.
Businesses can gather qualitative feedback through one-on-one interviews, focus groups, open-ended survey questions, and direct observations. These approaches allow for collecting in-depth responses about user experiences and expectations.
Interpreting qualitative feedback can be challenging due to its subjective nature and the need for significant analysis to identify themes and patterns. It requires skilled interpretation to ensure that biases do not influence the conclusions drawn from the feedback.
Qualitative feedback should be systematically analyzed and integrated into business strategies by identifying key themes and insights that align with business goals. Based on this feedback, actionable strategies should be developed to address specific needs and improvements identified.
Technology, including advanced data analytics tools and feedback management systems, plays a crucial role in efficiently collecting, storing, and analyzing qualitative feedback. These technologies can help synthesize large volumes of data into actionable insights.
Organizations can use qualitative feedback effectively by regularly updating their feedback collection methods, training staff on effective analysis techniques, and creating a culture that values and uses feedback to drive decisions and improvements. Continuous monitoring and adaptation based on feedback can lead to sustained improvements and innovation.